Question: Given a singly linked list as below write a recursive function to re-orient the next pointers of all the nodes in a list to each
Given a singly linked list as below
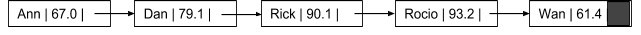
write a recursive function to re-orient the next pointers of all the nodes in a list to each point to the previous element.
Use code available below, with modifications to illustrate approach.
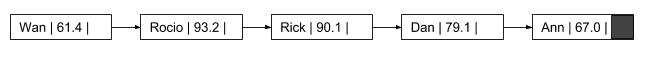
Example of end result:
| #pragma once | |
| #include | |
| template | |
| struct Node { | |
| T data; | |
| Node | |
| Node() = delete; // Intentionally no default constructor | |
| Node( const T & element ) : data( element ), next( nullptr ) {} | |
| }; | |
| template | |
| class SinglyLinkedList { | |
| private: | |
| Node | |
| Node | |
| public: | |
| // Constructors | |
| SinglyLinkedList(); | |
| SinglyLinkedList(const SinglyLinkedList&); | |
| SinglyLinkedList& operator=(const SinglyLinkedList&); // assignment operator | |
| ~SinglyLinkedList(); // destructor | |
| // Getters / Setters | |
| bool empty(); | |
| int size() = delete; // INTENTIONALLY NOT IMPLEMENTED !! | |
| void append( const T& ); | |
| void prepend( const T& ); | |
| void insertAfter( Node | |
| void removeAfter( Node | |
| void pop_front(); // remove element at front of list | |
| T& front(); // return list's front element | |
| T& back(); // return list's back element | |
| void clear(); | |
| }; | |
| template | |
| SinglyLinkedList | |
| template | |
| bool SinglyLinkedList | |
| return head == nullptr; | |
| } | |
| template | |
| void SinglyLinkedList | |
| Node | |
| if (head == nullptr) { // List empty | |
| head = newNode; | |
| tail = newNode; | |
| } | |
| else{ | |
| tail->next = newNode; | |
| tail = newNode; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| template | |
| void SinglyLinkedList | |
| Node | |
| if (head == nullptr) { // list empty | |
| head = newNode; | |
| tail = newNode; | |
| } | |
| else { | |
| newNode->next = head; | |
| head = newNode; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| template | |
| void SinglyLinkedList | |
| // Construct new node | |
| Node | |
| if (head == nullptr) { // List empty | |
| head = newNode; | |
| tail = newNode; | |
| } else if (curNode == tail) { // Insert after tail | |
| tail->next = newNode; | |
| tail = newNode; | |
| } else { | |
| newNode->next = curNode->next; | |
| curNode->next = newNode; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| template | |
| void SinglyLinkedList | |
| if( empty() ) throw std::length_error( "empty list" ); | |
| // Special case, remove head | |
| if (curNode == nullptr && head != nullptr) { | |
| Node | |
| head = sucNode; | |
| if (sucNode == nullptr) { // Removed last item | |
| tail = nullptr; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| else if (curNode->next != nullptr) { | |
| Node | |
| curNode->next = sucNode; | |
| if (sucNode == nullptr) { // Removed tail | |
| tail = curNode; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| template | |
| void SinglyLinkedList | |
| removeAfter(nullptr); | |
| } | |
| template | |
| T& SinglyLinkedList | |
| if( empty() ) throw std::length_error( "empty list" ); | |
| return head->data; | |
| } | |
| template | |
| T& SinglyLinkedList | |
| if( empty() ) throw std::length_error( "empty list" ); | |
| return tail->data; | |
| } | |
| template | |
| void SinglyLinkedList | |
| while( !empty() ) | |
| pop_front(); | |
| } | |
| template | |
| SinglyLinkedList | |
| clear(); | |
| } | |
| template | |
| SinglyLinkedList | |
| // Walk the original list adding copies of the elements to this list maintaining order | |
| for( Node | |
| append( position->data ); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| template | |
| SinglyLinkedList | |
| if( this != &rhs ) // avoid self assignment | |
| { | |
| // Release the contents of this list first | |
| clear(); // An optimization might be possible by reusing already allocated nodes | |
| // Walk the right hand side list adding copies of the elements to this list maintaining order | |
| for( Node | |
| append( position->data ); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| return *this; | |
| } |
Ann l 67.0 Dan l 79.1 I- Rick I 90.1 1 Roco l 93.2 1 Wan I 61.4 . Wan | 61.4 R ocio 93.2 | Rick | 90.1I Dan | 79.1 Ann | 67.0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


