Question: Given any set S and any symmetric relation ~ on S we saw that we can form a simple graph G = G(S ) with

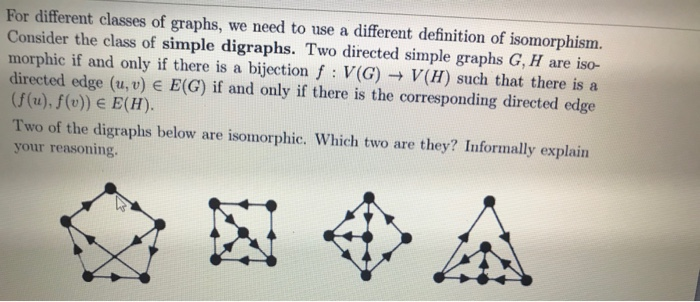
Given any set S and any symmetric relation ~ on S we saw that we can form a simple graph G = G(S ) with V(G) = S and E(G) = {{u, v} Slu~ v}. We further say that is transitive if the following holds (u~ v and v~ w) => u~w, or, graphically, "in G(S ), if there is an edge between u and v and an edge between v and w, then there is an edge between u and w." ) when is transitive and give a proof of your (a) Describe the structure of G(S claim. For different classes of graphs, we need to use a different definition of isomorphism. Consider the class of simple digraphs. Two directed simple graphs G, H are iso- morphic if and only if there is a bijection f : V(G) + V(H) such that there is a directed edge (u, v) E(G) if and only if there is the corresponding directed edge (f(u), f()) E E(H). Two of the digraphs below are isomorphic. Which two are they? Informally explain your reasoning
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


