Question: Given n securities with random return r e R, Expected Return u and Covariance , denote by rplw) the return of an investor's portfolio who
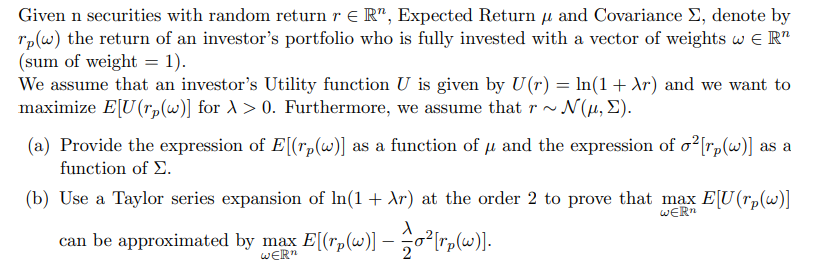
Given n securities with random return r e R, Expected Return u and Covariance , denote by rplw) the return of an investor's portfolio who is fully invested with a vector of weights wern (sum of weight = 1). We assume that an investor's Utility function U is given by U(r) = ln(1 + Ar) and we want to maximize E[U (rp(W)] for 1> 0. Furthermore, we assume that r~ N(1, 2). (a) Provide the expression of E[(Tp(w)] as a function of u and the expression of o[rp(w)] function of . (b) Use a Taylor series expansion of In(1 + Ar) at the order 2 to prove that max E[U (rp(W)] WER as a can be approximated by max E[[Fr(w) 02 [rr(w). Given n securities with random return r e R, Expected Return u and Covariance , denote by rplw) the return of an investor's portfolio who is fully invested with a vector of weights wern (sum of weight = 1). We assume that an investor's Utility function U is given by U(r) = ln(1 + Ar) and we want to maximize E[U (rp(W)] for 1> 0. Furthermore, we assume that r~ N(1, 2). (a) Provide the expression of E[(Tp(w)] as a function of u and the expression of o[rp(w)] function of . (b) Use a Taylor series expansion of In(1 + Ar) at the order 2 to prove that max E[U (rp(W)] WER as a can be approximated by max E[[Fr(w) 02 [rr(w)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


