Question: Given two nodes v and u in a connected, undirected graph G = , their distance is the length of the shortest path between v
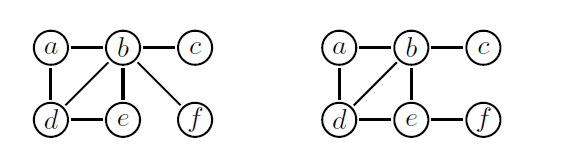
Given two nodes v and u in a connected, undirected graph G = , their distance is the length of the shortest path between v and u (here each edge is of length 1). The remoteness of a node is its distance to the node furthest away, that is, rem(v) = max{dist (v, u) | u V }. A hub in G is a node which has minimal remoteness, compared to all other nodes. That is, v is a hub iff rem(v) = min{rem(u) | u V }. For example, b is a hub in the graph on the left (below), whereas b, d and e all are hubs in the graph on the right. Note that a connected graph always has at least one hub.
(a) Using pseudo-code, design a function that, given a connected undirected graph and a node v V , determines all distances from v, that is, for each u V , gives dist(v, u). Assume that nodes are labelled 1 to n, so that your function can return an array dist with dist [i] giving is distance to v. The algorithm should run in time that is linear in the size of the graph.
(b) Design an algorithm that, given a connected undirected graph , identifies a hub (any hub) in the graph. More precisely, use pseudo-code to define a function Hub that takes as input and returns a node which is a hub. Aim for an O(n2) algorithm, where n is the size of the graph.




