Question: Graphing demand for labor and computing the optimal quantity 1. COMPLETE THE TABLE: A company operates in a perfectly competitive market, selling each unit of
Graphing demand for labor and computing the optimal quantity
1. COMPLETE THE TABLE:
A company operates in a perfectly competitive market, selling each unit of output for a price of $20 and paying the market wage of $270 per day for each worker it hires.
In the following table, complete the column for the marginal revenue product of labor (MRPL) at each quantity of workers.
| Labor | Output | Marginal Product of Labor | Marginal Revenue Product of Labor | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Number of workers) | (Units of output) | (Units of output) | (Dollars) | -------- |
| 0 | 0 | 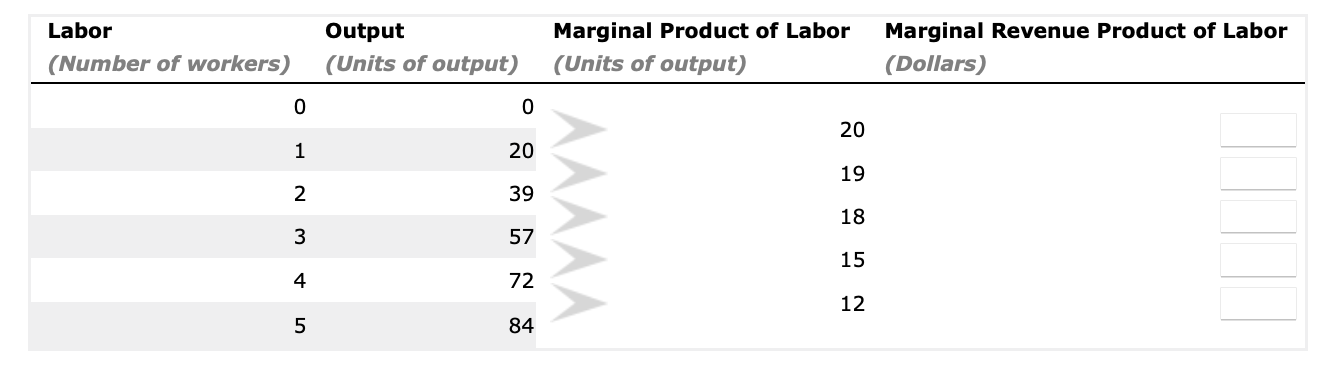 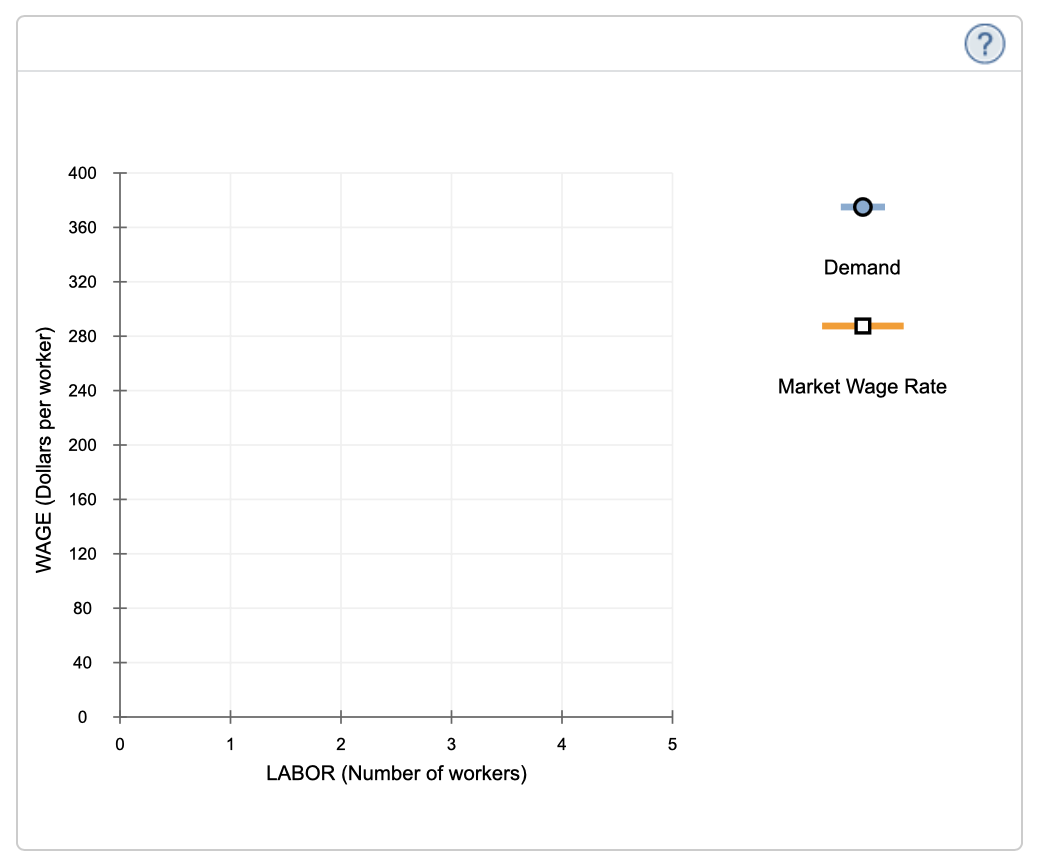         |
Labor (Number of workers) o um A W N Output (Units of output) 0 20 39 57 72 84 Marginal Product of Labor (Units of output) 20 19 18 15 12 Marginal Revenue Product of Labor (Dollars) WAGE (Dollars per worker) 400 360 320 280 240 200 160 120 80 40 2 3 LABOR (Number of workers) Demand 0 Market Wage Rate The profit-maximizing quantity of labor at the market wage is one worker two workers three workers four workers five workers \f\f\f\f\f\fTo answer this question, we can first calculate the marginal revenue product (MRP) of labor for each level of employment. The marginal revenue product of labor is the additional revenue generated by hiring one more unit of labor. To find the MRP, we multiply the marginal product of labor (MPL) by the price of the output (which is the marginal revenue, MR, in this case). Given that the marginal revenue is provided in dollars, we can directly use it to calculate the MRP. Here's the calculation: MRP = MPL x MR Given: . For 1 worker, MPL = 20 and MR = 20 . For 2 workers, MPL = 19 and MR = 57 . For 3 workers, MPL = 15 and MR = 72 . For 4 workers, MPL = 12 and MR = 84 . For 5 workers, MPL = 18 and MR = 18 We can calculate the MRP for each level of employment: For 1 worker: MRP = 20 x 20 = 400 For 2 workers: MRP = 19 x 57 = 1,083 For 3 workers: MRP = 15 x 72 = 1,080 For 4 workers: MRP = 12 x 84 = 1,008 For 5 workers: MRP = 18 x 18 = 324 Now, let's fill in the table with these values: Marginal Revenue Labor (Number Output (Units Marginal Product of Product of Labor of workers) of output) Labor (Units of output) (Dollars) 20 20 400 2 39 19 1,083 3 15 1,080 4 12 1,008 5 18 324 Now, let's fill in the missing values for labor 3, 4, and 5 in the table. We can do this by referencing the given data for output and MPL
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


