Question: head 2 5 8 Consider the linked list diagram above. Assume it uses the general node we have been using in class, namely: struct Node
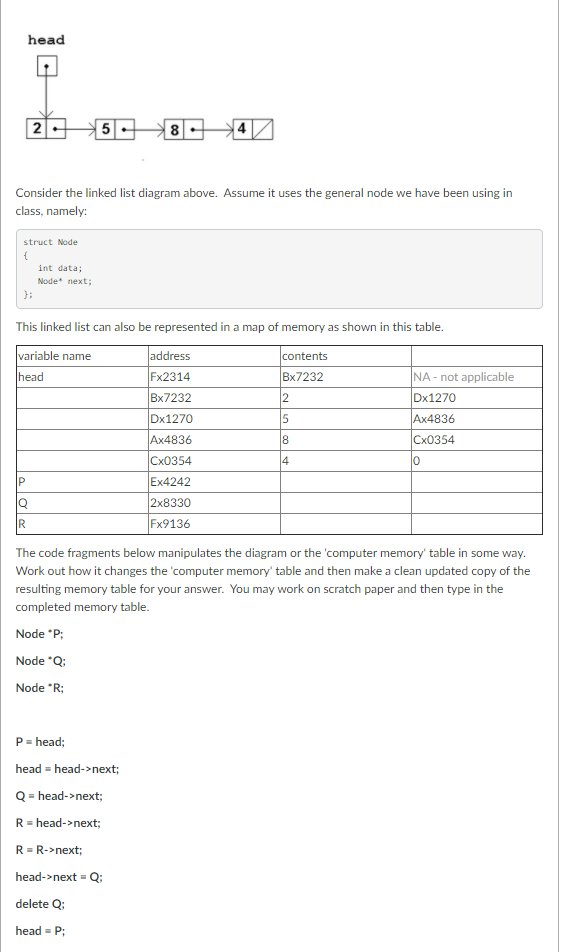
head 2 5 8 Consider the linked list diagram above. Assume it uses the general node we have been using in class, namely: struct Node { int data; Nodenext; }; This linked list can also be represented in a map of memory as shown in this table. address contents variable name head Fx2314 Bx7232 NA - not applicable Dx1270 Bx7232 2 Dx1270 5 Ax4836 8 Ax4836 Cx0354 Cx0354 o 4 P Ex4242 Q 2x8330 R Fx9136 The code fragments below manipulates the diagram or the computer memory' table in some way. Work out how it changes the computer memory' table and then make a clean updated copy of the resulting memory table for your answer. You may work on scratch paper and then type in the completed memory table. Node "P; Node *Q; Node eR; P = head; head = head->next; Q=head->next; R =head->next; R=R->next; head->next = Q: delete Q: head P
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


