Question: Hello, I'm stuck at this question. Can you help me to solve this with code using Python. Thank you so much. We will now leam
Hello, I'm stuck at this question. Can you help me to solve this with code using Python. Thank you so much.

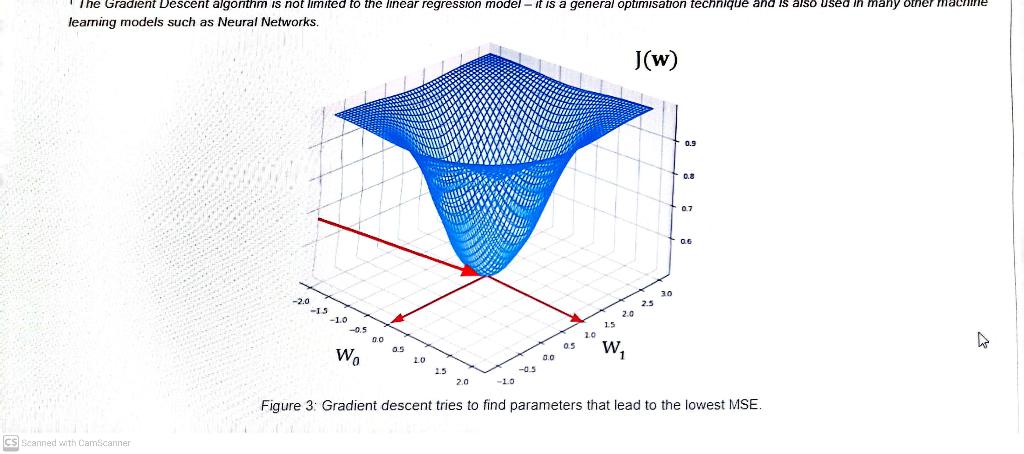
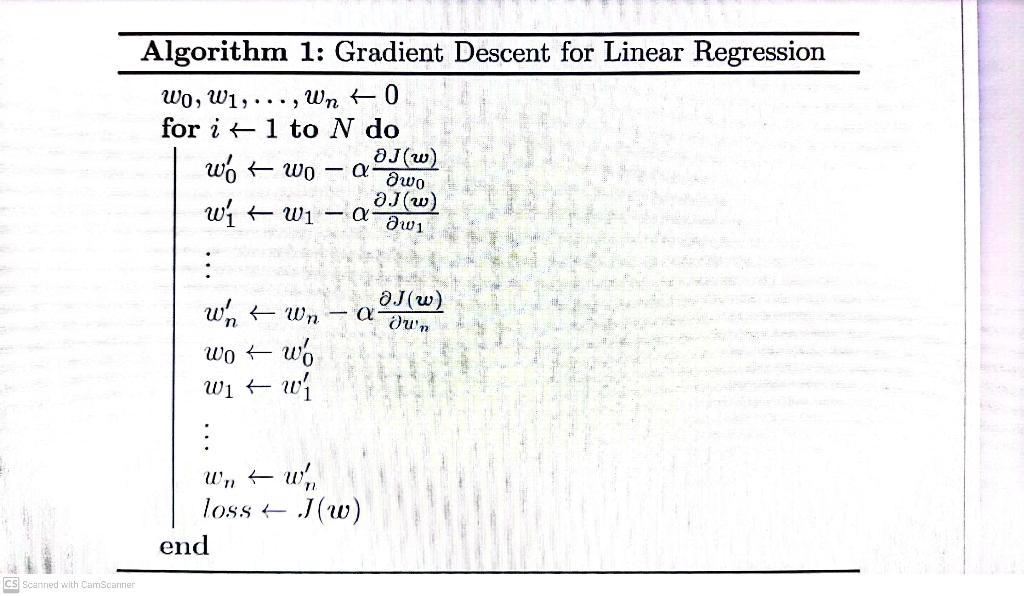


We will now leam to use gradient descent to approximate w=(w0,w1,,wn). Gradient descent is an algorithm that minimizes the cost function by iteratively trying to find the best parameters. In linear regression, we will try to minimize the Mean Squared Error. The outline of the algorithm is as follows: - Start with some w=(w0,,wn) - Keep changing w0,,wn to minimize J(w), where J is our cost function In this problem set, we will initially set w0,w1,,wn to all be 0 s. Then, we will set a learning rate that will affect the rate of change of w0,,wn. Lastly, we will set N to specify the number of epochs of gradient descent we want to run. The pseudo-code of Gradient Descent for linear regression is defined in Algorithm 1. Note: In the following gradient descent-related tasks, calculate the value of the loss function after updating the bias and weights. t The Gradient Descent algorithm is not limited to the linear regression model - it is a general optimisation technique and is also used in many other machine leaming models such as Neural Networks. leaming models such as Neural Networks. Figure 3: Gradient descent tries to find parameters that lead to the lowest MSE. \begin{tabular}{l} Algorithm 1: Gradient Descent for Linear Regression \\ \hlinew0,w1,,wn0 \\ for i1 to N do \\ w0w0w0J(w)w1w1w1J(w)wnwnwnJ(w)w0w0w1w1wnwnlossJ(w)end \end{tabular} For MSE, The partial derivative utJ(w) with m training samples can bo derived as: wiJ(w)=m1j=1m(hw(x(i))y(j))xi(j) where hw is our heuristic function. Task 2.4: Gradient Descent on a single feature Write the function gradient_descent_one_variable (x,y,1r, number_of_epochs) that returns: - w0 - a number representing the bias constant - w1 - a number representing the weight constant - loss - a list that contains the MSE scores calculated during the gradient descent process. The default value is 105 for 1r and 250 for number_of_epochs Note: You can use the mean_squared_error function for this task (You do not need to re-define the function in Coursemology. However, you are free to do so if you explicitly want to use your own implementation of the function for this task.) ]:f gradient_descent_one_variable (x,y,1r=1e5, number_of_epochs =250): Approximate bias and weight that give the best fitting line. Parameters x (np.ndarray) :(m,1) numpy matrix representing a feature column (np.ndarray): (m,1) numpy matrix representing target values lr (float) : Learning rate number_of_epochs (int) : Number of gradient descent epochs Returns bias (float): The bias constant weight (float): The weight constant loss (list): A list where the i-th element denotes the MSE score at i-th epoch. \# not change bias = weight = loss =[] for in range(number_of_epochs): \# TODo: add your sotution here and remove raise NotImplementedError raise NotImplementedError return bias, weight, loss CS Scanned with Carnscantier
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


