Question: help 0=0.3 Me EN os os 6. In a normal-phase separation, a solute was found to have a retention time of 32.5 min, and an
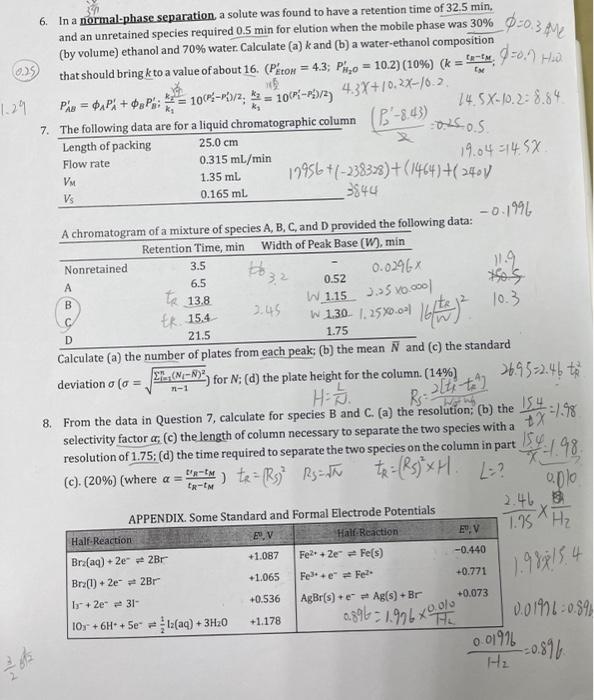
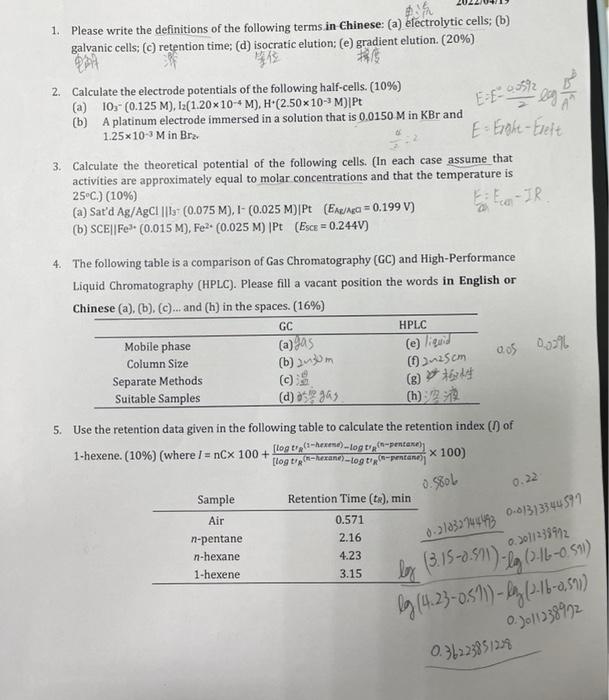
0=0.3 Me EN os os 6. In a normal-phase separation, a solute was found to have a retention time of 32.5 min, and an unretained species required 0.5 min for elution when the mobile phase was 30% (by volume) ethanol and 70% water. Calculate (a) k and (b) a water-ethanol composition 0.) that should bring kto a value of about 16. (Piton = 4.3; PO = 10.2) (10%) (k = 9-M, 7701) Hua 1.29 Pns = oxPx+ P : * = 100;-P)/2, * = 106-29/3 4.3X+10,2%-16.2. 14.5X-10.228.84 7. The following data are for a liquid chromatographic column (-8.43) Length of packing 25.0 cm Flow rate 0.315 ml/min 19.04 =145X 1.35 ml 19956 +1-238328)+(1464)+(2401) 0.165 ml 3844 A chromatogram of a mixture of species A, B, C, and provided the following data: -0.1996 Retention Time, min Width of Peak Base (W), min Nonretained 0.0296 11.9 0.52 VM Vs 3.5 6.5 Do 32 te 13.8 W 1.15 3.5 x .000 B tk. 15.4 W 1.390 1.3590.00 bytes hot say? 10.3 te 2.45 D 21.5 1.75 Calculate (a) the number of plates from each peak: (b) the mean N and (c) the standard deviation o (o EE.CN-8) for N; (d) the plate height for the column. (14%) 26.95=2.46 to H-5. 8. From the data in Question 7, calculate for species B and C. (a) the resolution; (b) the 154 -198 selectivity factor a, (c) the length of column necessary to separate the two species with a resolution of 1.75; (d) the time required to separate the two species on the column in part 154 (C). (20%) (where a = tet 1) te= (Rs) Rs=uth 0.010 Re: altit #2 t2 = (RS) X H. L? x 1.98 ER-EM EXH2 1.988154 APPENDIX. Some Standard and Formal Electrode Potentials 1.95 Half-Reaction Half Reaction E, V EU. V Bra(aq) + 2e + 2Br +1.087 Fe22e = Fe(s) -0.440 Brz(1) +2e 2Br +1.065 Fel: +e Fel +0.771 1 +2e" 31 +0.536 AgBr(s) Ag(s) + Br +0.073 10,- + 6H+ + Se = 1+ (aq) + 3H20 0.01-0.35 +1.178 THE 0.01916 -=0.896 H 0.396 1.976 0.0% M h 1. Please write the definitions of the following terms in Chinese: (a) electrolytic cells: (b) galvanic cells: (C) retention time; (d) isocratic elution; (e) gradient elution. (20%) EF-off cha 2. Calculate the electrode potentials of the following half-cells. (10%) (a) 10:- (0.125 M), 12(1.20*10-4 M). H (2.50X10-M)]Pt (b) A platinum electrode immersed in a solution that is 0.0150 M in KBr and 1.25x10-M in Bra: E- Erohe-Eleft 3. Calculate the theoretical potential of the following cells. (In each case assume that activities are approximately equal to molar concentrations and that the temperature is 25C.) (10%) (a) Sat'd Ag/AgC1 || 1 (0.075 M), 1-(0.025 M)|Pt (Ex = 0.199 V) E: Eco-IR (b) SCE||Fe (0.015 M), Fe2+ (0.025 M) Pt (Esce = 0.2440) 4. The following table is a comparison of Gas Chromatography (GC) and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Please fill a vacant position the words in English or Chinese (a), (b), (c)...and (h) in the spaces. (16%) GC HPLC Mobile phase (a) a5 Column Size (b) om Separate Methods Suitable Samples (d):18903 (h) 2 (e) liquid 25 cm (8) tarde aos 0.2% 5. Use the retention data given in the following table to calculate the retention index (1) of 1-hexene. (10%) (where I = nCx 100+ [logt (hexene)...og trg-pentane) x 100) [log tip-herane) --Log tipontaner 0.580L 0.22 Sample Air n-pentane n-hexane 1-hexene Retention Time (tr), min 0.571 2.16 4.23 0.2 1033944493 0-81313344599 0301238912 3.15 box (3.15-0.59m) -29 60-6-0.59 by(4.23-0,5 %) - By (16-0,59) 0.2011 238972 0.36223851229 0=0.3 Me EN os os 6. In a normal-phase separation, a solute was found to have a retention time of 32.5 min, and an unretained species required 0.5 min for elution when the mobile phase was 30% (by volume) ethanol and 70% water. Calculate (a) k and (b) a water-ethanol composition 0.) that should bring kto a value of about 16. (Piton = 4.3; PO = 10.2) (10%) (k = 9-M, 7701) Hua 1.29 Pns = oxPx+ P : * = 100;-P)/2, * = 106-29/3 4.3X+10,2%-16.2. 14.5X-10.228.84 7. The following data are for a liquid chromatographic column (-8.43) Length of packing 25.0 cm Flow rate 0.315 ml/min 19.04 =145X 1.35 ml 19956 +1-238328)+(1464)+(2401) 0.165 ml 3844 A chromatogram of a mixture of species A, B, C, and provided the following data: -0.1996 Retention Time, min Width of Peak Base (W), min Nonretained 0.0296 11.9 0.52 VM Vs 3.5 6.5 Do 32 te 13.8 W 1.15 3.5 x .000 B tk. 15.4 W 1.390 1.3590.00 bytes hot say? 10.3 te 2.45 D 21.5 1.75 Calculate (a) the number of plates from each peak: (b) the mean N and (c) the standard deviation o (o EE.CN-8) for N; (d) the plate height for the column. (14%) 26.95=2.46 to H-5. 8. From the data in Question 7, calculate for species B and C. (a) the resolution; (b) the 154 -198 selectivity factor a, (c) the length of column necessary to separate the two species with a resolution of 1.75; (d) the time required to separate the two species on the column in part 154 (C). (20%) (where a = tet 1) te= (Rs) Rs=uth 0.010 Re: altit #2 t2 = (RS) X H. L? x 1.98 ER-EM EXH2 1.988154 APPENDIX. Some Standard and Formal Electrode Potentials 1.95 Half-Reaction Half Reaction E, V EU. V Bra(aq) + 2e + 2Br +1.087 Fe22e = Fe(s) -0.440 Brz(1) +2e 2Br +1.065 Fel: +e Fel +0.771 1 +2e" 31 +0.536 AgBr(s) Ag(s) + Br +0.073 10,- + 6H+ + Se = 1+ (aq) + 3H20 0.01-0.35 +1.178 THE 0.01916 -=0.896 H 0.396 1.976 0.0% M h 1. Please write the definitions of the following terms in Chinese: (a) electrolytic cells: (b) galvanic cells: (C) retention time; (d) isocratic elution; (e) gradient elution. (20%) EF-off cha 2. Calculate the electrode potentials of the following half-cells. (10%) (a) 10:- (0.125 M), 12(1.20*10-4 M). H (2.50X10-M)]Pt (b) A platinum electrode immersed in a solution that is 0.0150 M in KBr and 1.25x10-M in Bra: E- Erohe-Eleft 3. Calculate the theoretical potential of the following cells. (In each case assume that activities are approximately equal to molar concentrations and that the temperature is 25C.) (10%) (a) Sat'd Ag/AgC1 || 1 (0.075 M), 1-(0.025 M)|Pt (Ex = 0.199 V) E: Eco-IR (b) SCE||Fe (0.015 M), Fe2+ (0.025 M) Pt (Esce = 0.2440) 4. The following table is a comparison of Gas Chromatography (GC) and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Please fill a vacant position the words in English or Chinese (a), (b), (c)...and (h) in the spaces. (16%) GC HPLC Mobile phase (a) a5 Column Size (b) om Separate Methods Suitable Samples (d):18903 (h) 2 (e) liquid 25 cm (8) tarde aos 0.2% 5. Use the retention data given in the following table to calculate the retention index (1) of 1-hexene. (10%) (where I = nCx 100+ [logt (hexene)...og trg-pentane) x 100) [log tip-herane) --Log tipontaner 0.580L 0.22 Sample Air n-pentane n-hexane 1-hexene Retention Time (tr), min 0.571 2.16 4.23 0.2 1033944493 0-81313344599 0301238912 3.15 box (3.15-0.59m) -29 60-6-0.59 by(4.23-0,5 %) - By (16-0,59) 0.2011 238972 0.36223851229
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


