Question: HELP FOR PART C. Is it possible that a sample result could fall outside the control limits due to pure chance? It is statistically that
HELP FOR PART C.
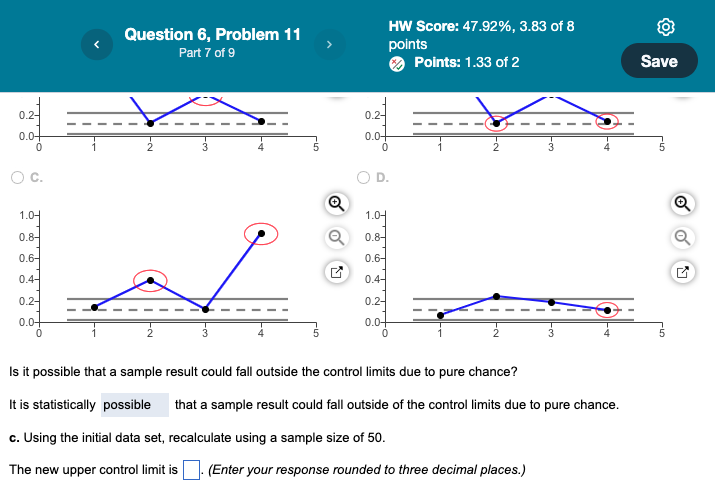
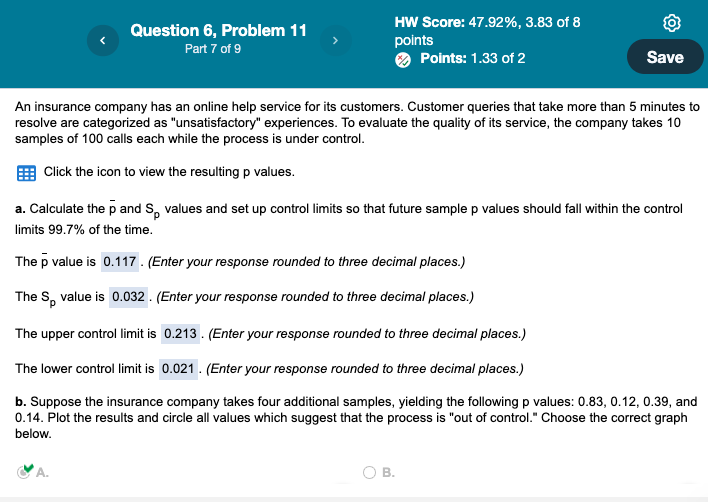
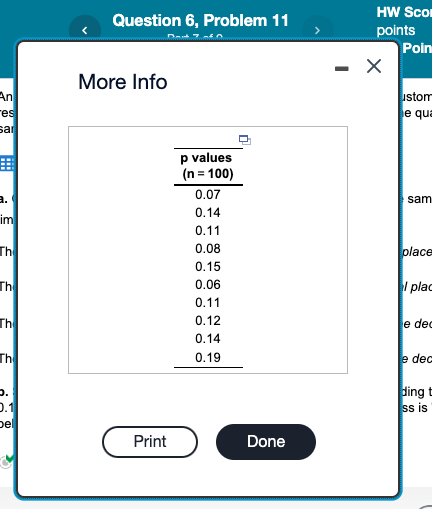
Is it possible that a sample result could fall outside the control limits due to pure chance? It is statistically that a sample result could fall outside of the control limits due to pure chance. c. Using the initial data set, recalculate using a sample size of 50. The new upper control limit is (Enter your response rounded to three decimal places.) An insurance company has an online help service for its customers. Customer queries that take more than 5 minutes to resolve are categorized as "unsatisfactory" experiences. To evaluate the quality of its service, the company takes 10 samples of 100 calls each while the process is under control. Click the icon to view the resulting p values. a. Calculate the p and Sp values and set up control limits so that future sample p values should fall within the control limits 99.7% of the time. The p value is . (Enter your response rounded to three decimal places.) The Sp value is . (Enter your response rounded to three decimal places.) The upper control limit is . (Enter your response rounded to three decimal places.) The lower control limit is . (Enter your response rounded to three decimal places.) b. Suppose the insurance company takes four additional samples, yielding the following p values: 0.83,0.12,0.39, and 0.14. Plot the results and circle all values which suggest that the process is "out of control." Choose the correct graph below. A. B. More Info
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


