Question: Help is required solving the tasks that are possible to solve given this information. Note! Calculations are also needed, not just answers. Beta 0.005 2.
Help is required solving the tasks that are possible to solve given this information.
Note! Calculations are also needed, not just answers.
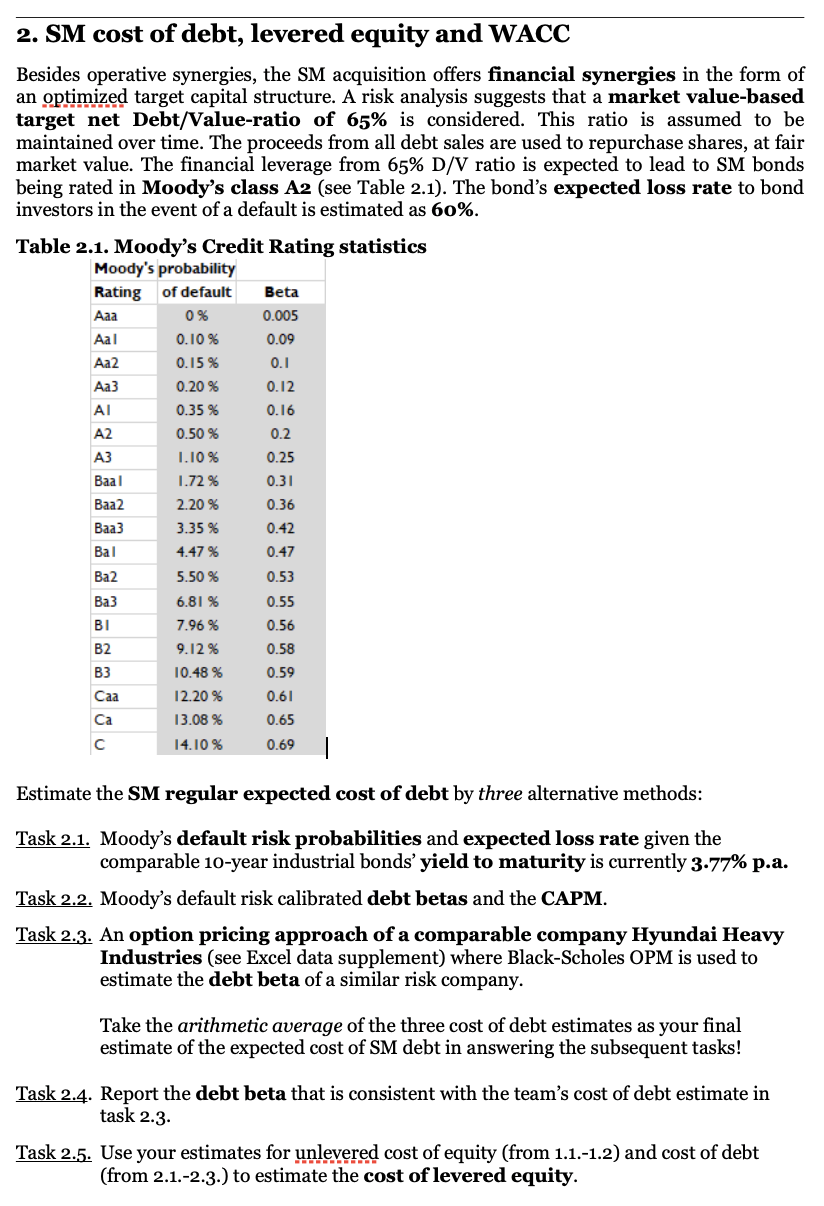

Beta 0.005 2. SM cost of debt, levered equity and WACC Besides operative synergies, the SM acquisition offers financial synergies in the form of an optimized target capital structure. A risk analysis suggests that a market value-based target net Debt/Value-ratio of 65% is considered. This ratio is assumed to be maintained over time. The proceeds from all debt sales are used to repurchase shares, at fair market value. The financial leverage from 65% D/V ratio is expected to lead to SM bonds being rated in Moody's class A2 (see Table 2.1). The bond's expected loss rate to bond investors in the event of a default is estimated as 60%. Table 2.1. Moody's Credit Rating statistics Moody's probability Rating of default 0% Aal 0.10 % 0.15% 0.20 % 0.35 % A2 1.10 % 1.72 % Baa2 2.20 % Baa3 3.35 % 4.47% 5.50 % 6.81 % 7.96 % 9.12% 10.48 % 0.09 0.1 Aa2 Aa3 0.12 0.16 0.50 % 0.2 A3 Baal 0.25 0.31 0.36 0.42 0.47 Bal Ba2 0.53 Ba3 0.55 BI 0.56 0.58 B2 B3 0.59 Caa 12.20 % 0.61 Ca 0.65 13.08 % 14.10 % 0.69 Estimate the SM regular expected cost of debt by three alternative methods: Task 2.1. Moody's default risk probabilities and expected loss rate given the comparable 10-year industrial bonds' yield to maturity is currently 3.77% p.a. Task 2.2. Moody's default risk calibrated debt betas and the CAPM. Task 2.3. An option pricing approach of a comparable company Hyundai Heavy Industries (see Excel data supplement) where Black-Scholes OPM is used to estimate the debt beta of a similar risk company. Take the arithmetic average of the three cost of debt estimates as your final estimate of the expected cost of SM debt in answering the subsequent tasks! Task 2.4. Report the debt beta that is consistent with the team's cost of debt estimate in task 2.3 Task 2.5. Use your estimates for unlevered cost of equity (from 1.1.-1.2) and cost of debt (from 2.1.-2.3.) to estimate the cost of levered equity. Task 2.6. Use your estimates for unlevered cost of equity (from 1.1.-1.2) and cost of debt (from 2.1.-2.3.) to estimate the pre- and after-tax WACC. Verify that your pre- tax WACC and your cost of unlevered equity are equal. Summarize all you cost of capital estimates, rounding off into three decimals (e.g. x.xxx%) in the following table 2. in your case report (8 items): Table 2.2. SM cost of capital and beta Cost of capital % p.a. Beta Assets (unlevered equity) Debt Levered Equity After-tax WACC Pre-tax WACC 3. SM deal operative and financial synergies Re-evaluate the SM M&A deal value with and without the operative synergies using the target capital structure with 65% D/V-ratio (raising regular bond market financing) using three valuation methods: Task 3.1. WACC-method Task 3.2. Adjusted Present Value-method Task 3-3. Free Cash Flow to Equity-method. Demonstrate that the same enterprise and (total) equity values are obtained by each of the three methods. Apply the cost of capital estimates from your summary table 2. Task 3.4. Given FCG makes the offer with the price 13 per share for the purchase of 100% of the shares of SM, calculate the NPV of the deal for FCG's owners without and with operative and financial (leverage) synergies. Fill in the following tables in your team's case report (2x10 items, MEUR or per share) Table 3.1. SM M&A analysis summary without any operative synergies () All Equity financed 65% Target D/V-ratio No operative synergies Enterprise value Market value of Equity Market value of debt Price per share NPV for FCG owners at bid price 13 per share Table 3.2. SM M&A analysis summary with operative synergies () All Equity financed 65% Target D/V-ratio Operative synergies Enterprise value Market value of Equity Market value of debt Price per share NPV for FCG owners at bid price 13 per share Beta 0.005 2. SM cost of debt, levered equity and WACC Besides operative synergies, the SM acquisition offers financial synergies in the form of an optimized target capital structure. A risk analysis suggests that a market value-based target net Debt/Value-ratio of 65% is considered. This ratio is assumed to be maintained over time. The proceeds from all debt sales are used to repurchase shares, at fair market value. The financial leverage from 65% D/V ratio is expected to lead to SM bonds being rated in Moody's class A2 (see Table 2.1). The bond's expected loss rate to bond investors in the event of a default is estimated as 60%. Table 2.1. Moody's Credit Rating statistics Moody's probability Rating of default 0% Aal 0.10 % 0.15% 0.20 % 0.35 % A2 1.10 % 1.72 % Baa2 2.20 % Baa3 3.35 % 4.47% 5.50 % 6.81 % 7.96 % 9.12% 10.48 % 0.09 0.1 Aa2 Aa3 0.12 0.16 0.50 % 0.2 A3 Baal 0.25 0.31 0.36 0.42 0.47 Bal Ba2 0.53 Ba3 0.55 BI 0.56 0.58 B2 B3 0.59 Caa 12.20 % 0.61 Ca 0.65 13.08 % 14.10 % 0.69 Estimate the SM regular expected cost of debt by three alternative methods: Task 2.1. Moody's default risk probabilities and expected loss rate given the comparable 10-year industrial bonds' yield to maturity is currently 3.77% p.a. Task 2.2. Moody's default risk calibrated debt betas and the CAPM. Task 2.3. An option pricing approach of a comparable company Hyundai Heavy Industries (see Excel data supplement) where Black-Scholes OPM is used to estimate the debt beta of a similar risk company. Take the arithmetic average of the three cost of debt estimates as your final estimate of the expected cost of SM debt in answering the subsequent tasks! Task 2.4. Report the debt beta that is consistent with the team's cost of debt estimate in task 2.3 Task 2.5. Use your estimates for unlevered cost of equity (from 1.1.-1.2) and cost of debt (from 2.1.-2.3.) to estimate the cost of levered equity. Task 2.6. Use your estimates for unlevered cost of equity (from 1.1.-1.2) and cost of debt (from 2.1.-2.3.) to estimate the pre- and after-tax WACC. Verify that your pre- tax WACC and your cost of unlevered equity are equal. Summarize all you cost of capital estimates, rounding off into three decimals (e.g. x.xxx%) in the following table 2. in your case report (8 items): Table 2.2. SM cost of capital and beta Cost of capital % p.a. Beta Assets (unlevered equity) Debt Levered Equity After-tax WACC Pre-tax WACC 3. SM deal operative and financial synergies Re-evaluate the SM M&A deal value with and without the operative synergies using the target capital structure with 65% D/V-ratio (raising regular bond market financing) using three valuation methods: Task 3.1. WACC-method Task 3.2. Adjusted Present Value-method Task 3-3. Free Cash Flow to Equity-method. Demonstrate that the same enterprise and (total) equity values are obtained by each of the three methods. Apply the cost of capital estimates from your summary table 2. Task 3.4. Given FCG makes the offer with the price 13 per share for the purchase of 100% of the shares of SM, calculate the NPV of the deal for FCG's owners without and with operative and financial (leverage) synergies. Fill in the following tables in your team's case report (2x10 items, MEUR or per share) Table 3.1. SM M&A analysis summary without any operative synergies () All Equity financed 65% Target D/V-ratio No operative synergies Enterprise value Market value of Equity Market value of debt Price per share NPV for FCG owners at bid price 13 per share Table 3.2. SM M&A analysis summary with operative synergies () All Equity financed 65% Target D/V-ratio Operative synergies Enterprise value Market value of Equity Market value of debt Price per share NPV for FCG owners at bid price 13 per share
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


