Question: help plz dip type cell, 150 cm narrow tall beakers, 100 cm volumetric flasks or 50 cm volumetric flasks, 10 cm pipette, bulb pipette filler,
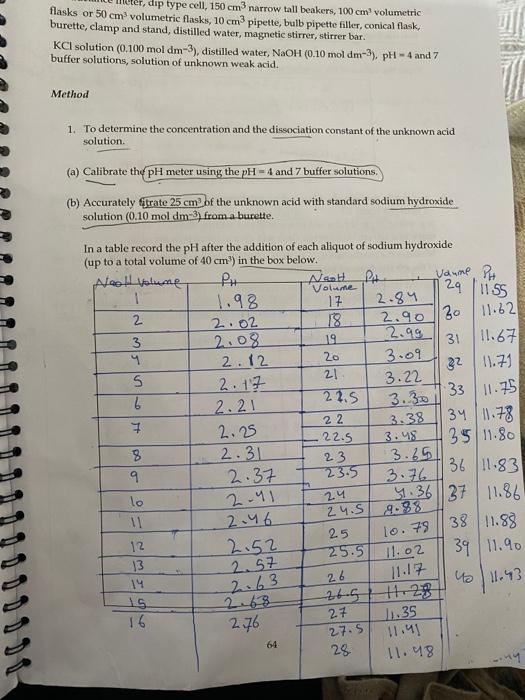

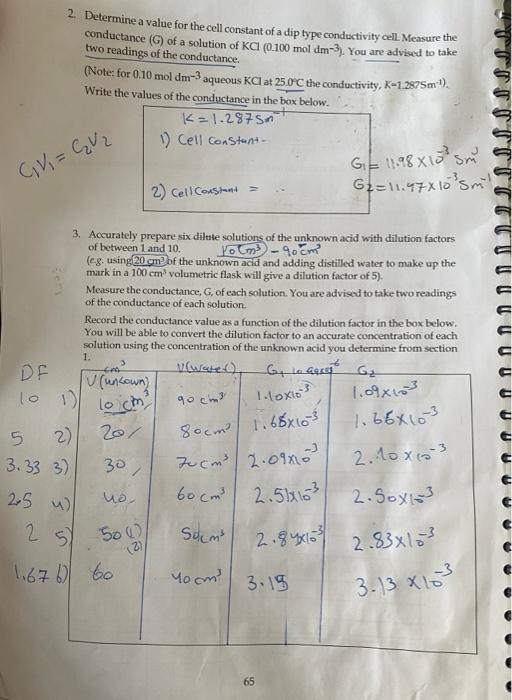

dip type cell, 150 cm narrow tall beakers, 100 cm volumetric flasks or 50 cm volumetric flasks, 10 cm pipette, bulb pipette filler, conical flask. burette, clamp and stand, distilled water, magnetic stirrer, stirrer bar. KCl solution (0.100 mol dm-3), distilled water, NaOH (0.10 mol dm-), pH-4 and 7 buffer solutions, solution of unknown weak acid. Method 1. To determine the concentration and the dissociation constant of the unknown acid solution (a) Calibrate the pH meter using the pH = 4 and 7 buffer solutions. (b) Accurately rate 25 cm of the unknown acid with standard sodium hydroxide solution (0.10 mol dm-3) from a burette. 2.90 30 0 11.75 sw 34 In a table record the pH after the addition of each aliquot of sodium hydroxide (up to a total volume of 40 cm) in the box below. Nool volume PH Naalt.PL Vaune Volume 1 24 1.98 17 2.84 1155 2 2.02 18 11.82 3 2.08 19 2.99 31 11.67 2.12 20 3.09 22 21 11.71 S 2.17 3.22 22.5 33 2.21 3.30 1 22 2.25 3.38 11.78 3.48 35 11.80 8 2.31 23 3.65 9 2.37 23.5 3.76 36 11.83 lo 4.36 37 11.86 11 24.5 2.46 38 11.88 25 12 2.52 25.5 11.02 39 11.90 13 14 411.43 15 16 27 2.76 J1.35 11.41 28 11.48 2-41 2.4 8.38 lo. 79 2.57 2.63 26 11.17 27.5 64 You are required to perform the following tasks before you leave the test: 1. Plot a suitable pH titration graph. Hence determine (a) The concentration of the unknown acid (b) The acid dissociation constant 2. Determine a value for the cell constant of a dip type conductivity cell Measure the conductance (G) of a solution of KC (0.100 mol dm-3). You are advised to take two readings of the conductance. (Note: for 0.10 mol dm-3 aqueous KC at 25.0C the conductivity, K-1.2875m?). Write the values of the conductance in the box below. K=1.28750 1) Cell constant GVI = GV2 GE 11.988158 sm 2) Cell Constant G2 = 11.97X10 sml > 3. Accurately prepare six diliste solutions of the unknown acid with dilution factors of between 1 and 10. Poems 90cm (eg. using 20cm of the unknown acid and adding distilled water to make up the mark in a 100 cm volumetric flask will give a dilution factor of 5). Measure the conductance, G, of each solution. You are advised to take two readings of the conductance of each solution Record the conductance value as a function of the dilution factor in the box below. You will be able to convert the dilution factor to an accurate concentration of each solution using the concentration of the unknown acid you determine from section 1. DF CA G lo Gary G (uncown) 10 1 loch 90 cm 1.098103 1.66x103 5 2) 20/ 3.33 3) 30 2.5 ) no 60cm 2.5163 2. Soxl 2 2.84xos 1. Loxios 80cm / 1.68x103 Jucm3 2.000 2.10 x 10 3 3 Solm 2.8x103 121 5) 500 1.676 to Yoom 3.18 3.13 x 103 65 2. Determine a value for the cell constant. Use this value to obtain the conductivity values for each of the acid solutions. Hen obtain the molar conductivity of each solution. 3. On the separate sheet provided fill in the values for (a) The concentration of the acid (b) The acid dissociation constant (c) The cell constant of your conductance cell
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


