Question: Help with this very long extra credit assignment!!! Will leave a like after!!!! Thank you if you do! need help with this. what do you

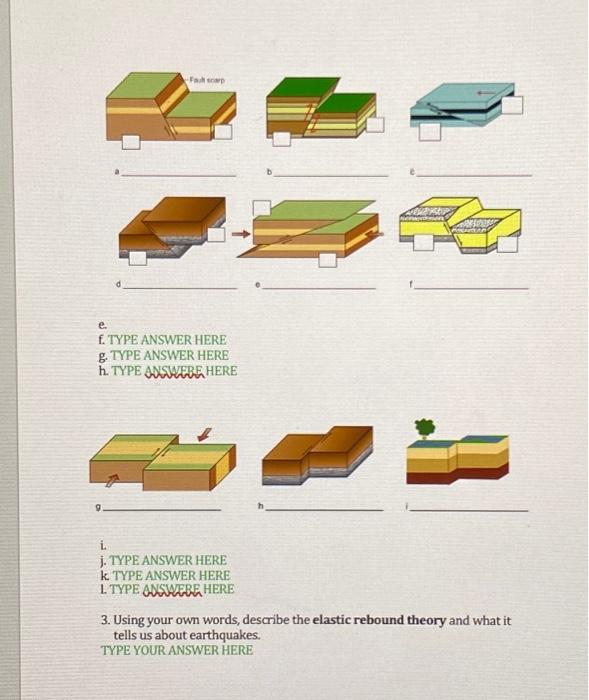










Chapter 3 Concepts - Earthquakes 1. Describe the motions of the two fault types listed below. a. Dip-slip Fault - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE b. Strike-slip Fault - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 2. Identify the type of faults shown below on the line below each image. When necessary label the hanging walls (bwo) and footwalls (fwo) in the white square provided on the fault blocks. (use the DRAW MENU in Microsoft Word to draw on the images and label the hanging and foot walls) a. b. TYPE ANSWER HERE c. TYPE ANSWER HERE d. TYPE ANSWERE HERE e. f. TYPE ANSWER HERE g. TYPE ANSWER HERE h. TYPE ANSWERE HERE g h i. j. TYPE ANSWER HERE K. TYPE ANSWER HERE LTYPE ANSULER HERE 3. Using your own words, describe the elastic rebound theory and what it tells us about earthquakes. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 4. Match the seismic wave type with the correct descriptions (there may be more than one description that fit some of the wave types). Body wave LETTEB Surface wave LETTEB S-wave LETTEB P-wave LETTER a The slowest of the body waves b. Can move through both solids and liquids c. Has an up and down motion d. Has a side to side motion (like a serpent) e. Can only move through solids f. The fastest of all seismic waves 2. Has a push pull motion (front to back like a slinky) h. Only moves through rocks at the surface of the Earth 5. What is the difference between the focus and the epicenterof an earthquake? TYPE YOURANSWER HERE 6. Match the following terms about measuring earthquakes with the correct description (there may be more than one description that fit some of the terms). Mercalli Intensity Scale LEITER Moment of Magnitude Scale LFTTEB Seismograph LETTEB Seismogram LETTEB Richter Scale HETTEB a Instrument that records vibrations b. Scale used to determine earthquake strength c. Uses a scale of I-XII for dassification d. Out dated earthquake intensity scale e Recordings of P and S wave arrival times f Scale used to measure earthquake damage g. Uses a scale of 1-10 for classification 7. List all the hazards that can be triggered (caused) by an earthquake. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 8. On the image below, highlight areas which would NOT be at a high risk for an earthquake? (use the DRAW MENU in Microsoft Word to draw on the image) 9. What are the hazards associated with earthquakes? For each hazard explain how we can mitigate or minimize damage from each. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 10. Explain in detail, two ways that there can be a magnitude 7 earthquake which doesn't cause a lot of damage. List a few ways that use human involvement and a few that do not. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 11. On the image below, highlight the ring of fire. (use the DRAW MENU in Microsoft Word to draw on the image) 12. What process do all the boundaries along the ring of fire have in common? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 13. Explain how hot spot volcanism is different than a volcanic island/continental arc. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 14. Give a description of each of the observations that we can use to predict when a volcanic eruption might occur: History - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Earthquakes - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Gas emissions - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Remote Monitoring - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 15. What is the difference between magma and lava? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 16. What is viscosity? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 17. Explain what will happen to a lavas viscosity as we begin to increase its temperature? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 18. Match the type of volcano with the images below. Composite/StGTOLETTER Shield LETTER Caldera LETTER 19. Give a detailed description for each of the volcano listed below. Include where these would fall (approximately) on the Volcanic Explesivitx Index (VEI). TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Composite/Stsata-TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Shield - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Cinder Cone - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE SUper - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 20. Explain how the viscosity of different types of lava (felsiGvs. mafis) lead to volcanoes of different shapes. Make sure to tie in composition of the lava and the shape of the types of volcanoes. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 21. Match the following volcanic hazards with the correct description. Gasses LETMEBB a. Ash mixed and mud that produces a concrete like slurry b. Volcanic rock that cools in the air to look like a football c. Fast moving cloud of ash and gasses d. CO,CO,SO, etc. that suffocate anyone in their path e. Crumbly and blocky lava flow f. Fine grained, sand-sized material g. Smooth and ropey lava flow h. Volcanic material that is ejected as a large, jagged block i. Massive cloud of ash that's ejected into the atmosphere 22. What are the best ways to mitigate damage from volcanoes? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 23. What are some benefits of volcanoes? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Chapter 5 Concepts - Mass Wasting 24. Differentiate between the two types of weathering below (in your own words). c. Physical - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE d. Chemical - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 25. Describe each process below and identify what type of weathering (physical or chemical) it is. a. Ice-wedging - (physical or chemical) TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE b. Root-wedging - (physical or chemical) TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE c. Water interaction - (physical or chemical) TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE d. Carbonic Acid Interaction - (physical or chemical) TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE e. Oxidation - (physical or chemical) TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 26. What factors contribute to how a rock will weather? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 27. Explain what mass wasting is. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 28. What is subsidence and why does it qualify as a type of mass wasting? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 29. What are the three criteria we use to classify mass wasting? CRITERIA ONE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE CRITERIA TWO: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE CRITERIA THREE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 30. Match the term below with the correct description on the right. Soil TYPELETTER HERE Rock TYPE LETTER HERE Submarine TYPE LETTER HERE Subaerial TYPE LETTER HERE Regolith TYPE LETTER HERE a. Mass wasting that occurs underwater b. Loose organic material c. Solid, un-weathered material d. Weathered rock and mineral fragments e. Mass wasting that occurs on land 31. What are the factors that influence mass wasting and describe how they contribute to slope stability or instability of an area? FACTOR ONE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR TWO: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR THREE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR FOUR: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR FIVE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR SIX: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR SEVEN: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR EIGHT: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 32. Highlight areas that have the highest mass wasting risk on the map below. (USE THE DRAW MENU IN MICROSOFT WORD TO HIGHLIGHT THESE) 33. What do we mean by the term trigger in reference to landslides and subsidence? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 34. What are some landslide and subsidence triggers? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 35. Match the type of slope movement with the correct definition given below. Slide TYPEL LETER HERE Flow TYPELETTER HERE Fall TYPE L WTTER HERE a Exertall of material b. Movement of unconsolidated material c Movement of material as a coherent, solid block 36. What are some ways we can mitigate the mass wasting hazard? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 38. List the common tsunami triggers and explain how they create a tsunami. TRIGGER ONE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE TRIGGER TWO: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE TRIGGER THREE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE TRIGGER FOUR: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 39. Explain why coastlines surrounding the Pacific Ocean have a higher tsunami risk than those around the Atlantic Ocean. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 40. What should you do to prepare yourself for the tsunami hazard? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 41. List the four parts of the development of a tsunami wave in order below. 43. Describe what happens if the trough of a tsunami is the first part to reach a coastal area. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 44. List and describe the different ways can we mitigate the tsunami hazard. MITIGATION TECHNIQUE ONE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE MITIGATION TECHNIQUE TWO: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE MITIGATION TECHNIQUE THREE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE MITIGATION TECHNIQUE FOUR: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE MITIGATION TECHNIQUE FIVE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Chapter 3 Concepts - Earthquakes 1. Describe the motions of the two fault types listed below. a. Dip-slip Fault - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE b. Strike-slip Fault - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 2. Identify the type of faults shown below on the line below each image. When necessary label the hanging walls (bwo) and footwalls (fwo) in the white square provided on the fault blocks. (use the DRAW MENU in Microsoft Word to draw on the images and label the hanging and foot walls) a. b. TYPE ANSWER HERE c. TYPE ANSWER HERE d. TYPE ANSWERE HERE e. f. TYPE ANSWER HERE g. TYPE ANSWER HERE h. TYPE ANSWERE HERE g h i. j. TYPE ANSWER HERE K. TYPE ANSWER HERE LTYPE ANSULER HERE 3. Using your own words, describe the elastic rebound theory and what it tells us about earthquakes. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 4. Match the seismic wave type with the correct descriptions (there may be more than one description that fit some of the wave types). Body wave LETTEB Surface wave LETTEB S-wave LETTEB P-wave LETTER a The slowest of the body waves b. Can move through both solids and liquids c. Has an up and down motion d. Has a side to side motion (like a serpent) e. Can only move through solids f. The fastest of all seismic waves 2. Has a push pull motion (front to back like a slinky) h. Only moves through rocks at the surface of the Earth 5. What is the difference between the focus and the epicenterof an earthquake? TYPE YOURANSWER HERE 6. Match the following terms about measuring earthquakes with the correct description (there may be more than one description that fit some of the terms). Mercalli Intensity Scale LEITER Moment of Magnitude Scale LFTTEB Seismograph LETTEB Seismogram LETTEB Richter Scale HETTEB a Instrument that records vibrations b. Scale used to determine earthquake strength c. Uses a scale of I-XII for dassification d. Out dated earthquake intensity scale e Recordings of P and S wave arrival times f Scale used to measure earthquake damage g. Uses a scale of 1-10 for classification 7. List all the hazards that can be triggered (caused) by an earthquake. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 8. On the image below, highlight areas which would NOT be at a high risk for an earthquake? (use the DRAW MENU in Microsoft Word to draw on the image) 9. What are the hazards associated with earthquakes? For each hazard explain how we can mitigate or minimize damage from each. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 10. Explain in detail, two ways that there can be a magnitude 7 earthquake which doesn't cause a lot of damage. List a few ways that use human involvement and a few that do not. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 11. On the image below, highlight the ring of fire. (use the DRAW MENU in Microsoft Word to draw on the image) 12. What process do all the boundaries along the ring of fire have in common? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 13. Explain how hot spot volcanism is different than a volcanic island/continental arc. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 14. Give a description of each of the observations that we can use to predict when a volcanic eruption might occur: History - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Earthquakes - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Gas emissions - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Remote Monitoring - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 15. What is the difference between magma and lava? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 16. What is viscosity? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 17. Explain what will happen to a lavas viscosity as we begin to increase its temperature? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 18. Match the type of volcano with the images below. Composite/StGTOLETTER Shield LETTER Caldera LETTER 19. Give a detailed description for each of the volcano listed below. Include where these would fall (approximately) on the Volcanic Explesivitx Index (VEI). TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Composite/Stsata-TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Shield - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Cinder Cone - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE SUper - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 20. Explain how the viscosity of different types of lava (felsiGvs. mafis) lead to volcanoes of different shapes. Make sure to tie in composition of the lava and the shape of the types of volcanoes. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 21. Match the following volcanic hazards with the correct description. Gasses LETMEBB a. Ash mixed and mud that produces a concrete like slurry b. Volcanic rock that cools in the air to look like a football c. Fast moving cloud of ash and gasses d. CO,CO,SO, etc. that suffocate anyone in their path e. Crumbly and blocky lava flow f. Fine grained, sand-sized material g. Smooth and ropey lava flow h. Volcanic material that is ejected as a large, jagged block i. Massive cloud of ash that's ejected into the atmosphere 22. What are the best ways to mitigate damage from volcanoes? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 23. What are some benefits of volcanoes? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE Chapter 5 Concepts - Mass Wasting 24. Differentiate between the two types of weathering below (in your own words). c. Physical - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE d. Chemical - TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 25. Describe each process below and identify what type of weathering (physical or chemical) it is. a. Ice-wedging - (physical or chemical) TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE b. Root-wedging - (physical or chemical) TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE c. Water interaction - (physical or chemical) TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE d. Carbonic Acid Interaction - (physical or chemical) TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE e. Oxidation - (physical or chemical) TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 26. What factors contribute to how a rock will weather? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 27. Explain what mass wasting is. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 28. What is subsidence and why does it qualify as a type of mass wasting? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 29. What are the three criteria we use to classify mass wasting? CRITERIA ONE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE CRITERIA TWO: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE CRITERIA THREE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 30. Match the term below with the correct description on the right. Soil TYPELETTER HERE Rock TYPE LETTER HERE Submarine TYPE LETTER HERE Subaerial TYPE LETTER HERE Regolith TYPE LETTER HERE a. Mass wasting that occurs underwater b. Loose organic material c. Solid, un-weathered material d. Weathered rock and mineral fragments e. Mass wasting that occurs on land 31. What are the factors that influence mass wasting and describe how they contribute to slope stability or instability of an area? FACTOR ONE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR TWO: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR THREE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR FOUR: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR FIVE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR SIX: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR SEVEN: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE FACTOR EIGHT: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 32. Highlight areas that have the highest mass wasting risk on the map below. (USE THE DRAW MENU IN MICROSOFT WORD TO HIGHLIGHT THESE) 33. What do we mean by the term trigger in reference to landslides and subsidence? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 34. What are some landslide and subsidence triggers? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 35. Match the type of slope movement with the correct definition given below. Slide TYPEL LETER HERE Flow TYPELETTER HERE Fall TYPE L WTTER HERE a Exertall of material b. Movement of unconsolidated material c Movement of material as a coherent, solid block 36. What are some ways we can mitigate the mass wasting hazard? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 38. List the common tsunami triggers and explain how they create a tsunami. TRIGGER ONE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE TRIGGER TWO: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE TRIGGER THREE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE TRIGGER FOUR: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 39. Explain why coastlines surrounding the Pacific Ocean have a higher tsunami risk than those around the Atlantic Ocean. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 40. What should you do to prepare yourself for the tsunami hazard? TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 41. List the four parts of the development of a tsunami wave in order below. 43. Describe what happens if the trough of a tsunami is the first part to reach a coastal area. TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE 44. List and describe the different ways can we mitigate the tsunami hazard. MITIGATION TECHNIQUE ONE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE MITIGATION TECHNIQUE TWO: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE MITIGATION TECHNIQUE THREE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE MITIGATION TECHNIQUE FOUR: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE MITIGATION TECHNIQUE FIVE: TYPE YOUR ANSWER HERE
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


