Question: Here are given some instructions on self-exciting processes: Write a simulation algorithm and simulate and plot the trajectory of the self-exciting process, t > N(t),
Here are given some instructions on self-exciting processes:

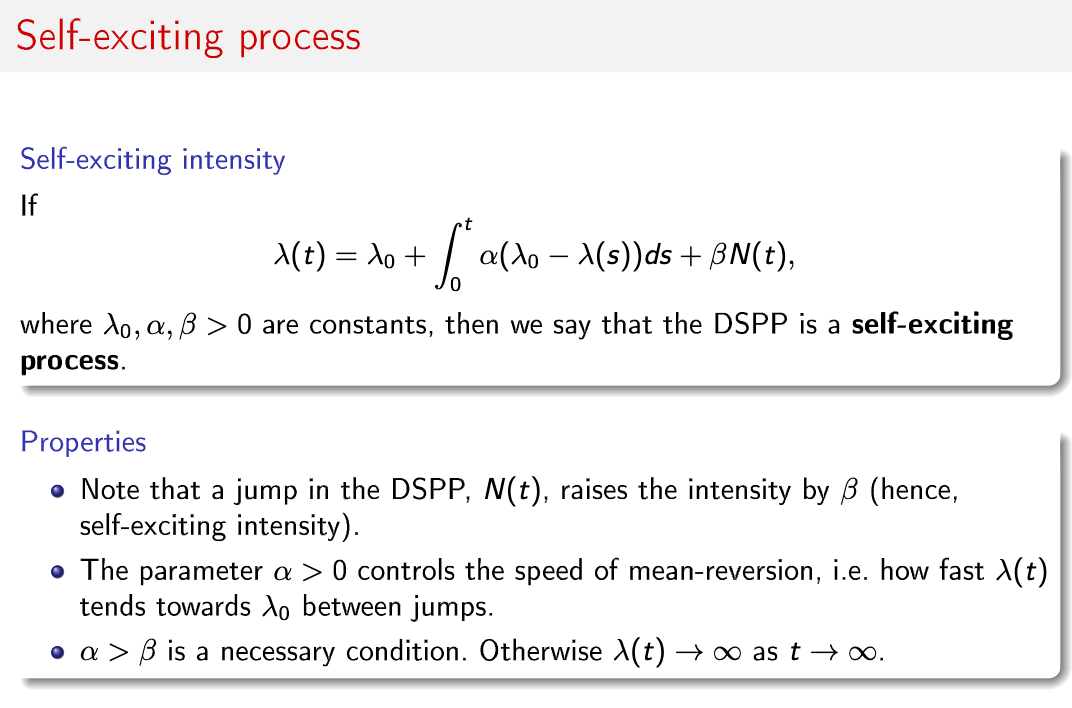

Write a simulation algorithm and simulate and plot the trajectory of the self-exciting process, t > N(t), together with the corresponding intensity process t > Mt), on the unit interval [0, 1]. The intensity formula / lnction is named and given in one of the instruction photos where 10, (1, [3 > 0 are constants and o: > [3, and N(t) is the self-exciting counting process. In the code you can use the following given parameters: to =10,B = 10, and B/u=0.1. Selfexciting process Selfexciting intensity If m) = A0 + /: aw A(s))ds + amt), where An, 05,3 > 0 are constants, then we say that the DSPP is a self-exciting process. Properties 0 Note that a jump in the DSPP, N(t), raises the intensity by ,8 (hence, selfexciting intensity). 0 The parameter a > 0 controls the speed of meanreversion, i.e. how fast Mt) tends towards A0 between jumps. 0 0: > is a necessary condition. Otherwise Mt) > 00 as t > oo. Simulation of selfexciting process It holds that A(t) = A0 + 3 Z emit-Th), Tkst where Tk are the arrival times of N(t). Thinning algorithm to simulate arrival times, Tk, on [0, T] 0 Let t = U. 0 Let )1 = Mt). 0 Generate an exponential random variable X having rate 3. 0 If t+X > T, then stop. Else, if t+X g T, set 1\" = t+X, generate a uniform random variable U on [0,1] and accept the arrival time t if U S A(t)/)\\. Return to step 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


