Question: Here is the condensed 2021 balance sheet for Skye Computer Company (in thousands of dollars): begin{tabular}{lr} & 2021 hline Current assets & $1,750
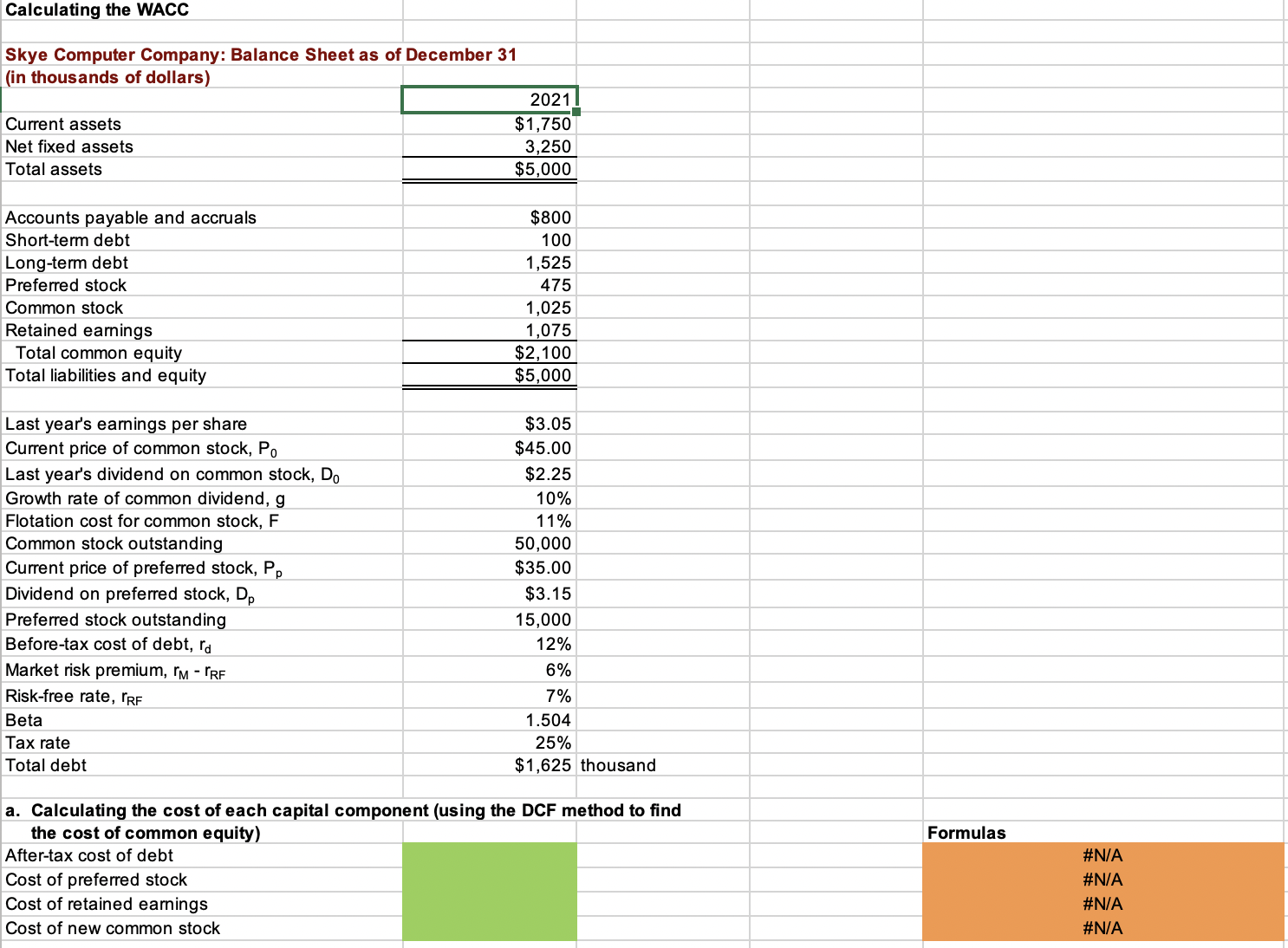
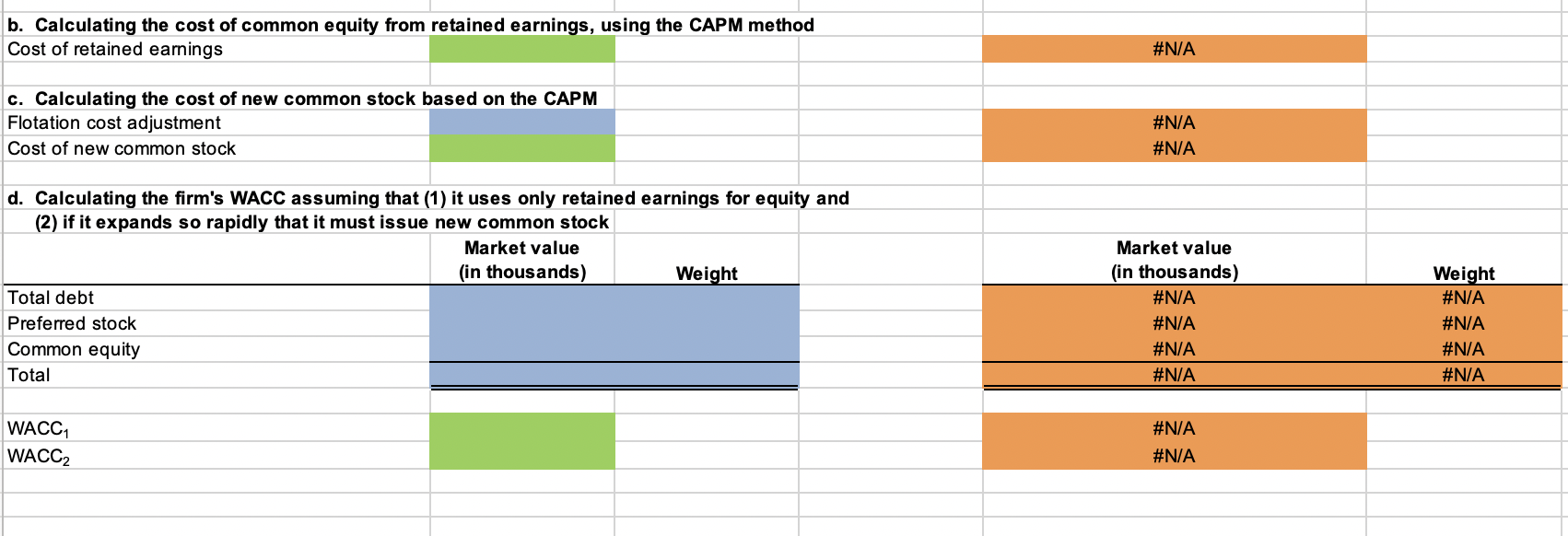
Here is the condensed 2021 balance sheet for Skye Computer Company (in thousands of dollars): \begin{tabular}{lr} & 2021 \\ \hline Current assets & $1,750 \\ Net fixed assets & 3,250 \\ Total assets & $5,000 \\ & \\ Accounts payable and accruals & $800 \\ Short-term debt & 100 \\ Long-term debt & 1,525 \\ Preferred stock (15,000 shares) & 475 \\ Common stock (50,000 shares) & 1,025 \\ Retained earnings & 1,075 \\ \multicolumn{1}{c}{ Total common equity } & $2,100 \\ Total liabilities and equity & $5,000 \end{tabular} million. Download spreadsheet Calculating the WACC-fb24d2.xlsX After-tax cost of debt: Cost of preferred stock: Cost of retained earnings: Cost of new common stock: b. Now calculate the cost of common equity from retained earnings, using the CAPM method. c. What is the cost of new common stock based on the CAPM? (Hint: Find the difference between re and rs as determined by the DCF method, and add that differential to the CAPM value for rs.) obtained under the two methods in calculating WACC.) WACC 1 : WACC 2 : Calculating the WACC Skye Computer Company: Balance Sheet as of December 31 (in thousands of dollars) Current assets Net fixed assets Total assets Accounts payable and accruals Short-term debt Long-term debt Preferred stock Common stock Retained earnings Total common equity Total liabilities and equity Last year's earnings per share Current price of common stock, P0 Last year's dividend on common stock, D0 Growth rate of common dividend, g Flotation cost for common stock, F Common stock outstanding Current price of preferred stock, Pp Dividend on preferred stock, Dp Preferred stock outstanding Before-tax cost of debt, rd Market risk premium, rMrRF Risk-free rate, rRF Beta Tax rate Total debt \begin{tabular}{|r|} \hline 2021 \\ \hline$1,750 \\ 3,250 \\ \hline$5,000 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{r|} \hline \hline$800 \\ 100 \\ 1,525 \\ 475 \\ 1,025 \\ 1,075 \\ \hline$2,100 \\ \hline$5,000 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|r|r|r|} \hline$3.05 & \\ \hline$45.00 & \\ \hline$2.25 & \\ \hline 10% & 11% & \\ \hline 50,000 & \\ \hline 35.00 & \\ \hline$3.15 & \\ \hline 15,000 & \\ \hline 12% & \\ \hline 6% & \\ \hline 7% & \\ \hline 25% & \\ \hline$1,625 & thousand \\ \hline \end{tabular} a. Calculating the cost of each capital component (using the DCF method to find the cost of common equity) After-tax cost of debt Cost of preferred stock Cost of retained earnings Cost of new common stock Formulas \#N/A \#N/A \#N/A \#N/A b. Calculating the cost of common equity from retained earnings, using the CAPM method Cost of retained earnings c. Calculating the cost of new common stock based on the CAPM Flotation cost adjustment Cost of new common stock d. Calculating the firm's WACC assuming that (1) it uses only retained earnings for equity and (2) if it expands so rapidly that it must issue new common stock Market value (in thousands) Weight Total debt Preferred stock Common equity Total WACC 1 WACC2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


