Question: Here it is. thanks.////// interface UnaryPredicate { public boolean test(T obj); } final class Algorithm { public static int countIf(Collection c, UnaryPredicate p) { int
Here it is. thanks.//////
interface UnaryPredicate {
public boolean test(T obj);
}
final class Algorithm {
public static int countIf(Collection c, UnaryPredicate p) {
int count = 0;
for (T elem : c)
if (p.test(elem))
++count;
return count;
}
}
class OddPredicate implements UnaryPredicate {
public boolean test(Integer i) {
return i % 2 != 0;
}
}
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection ci = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4);
int count = Algorithm.countIf(ci, new OddPredicate());
System.out.println("Number of odd integers = " + count);
}
}
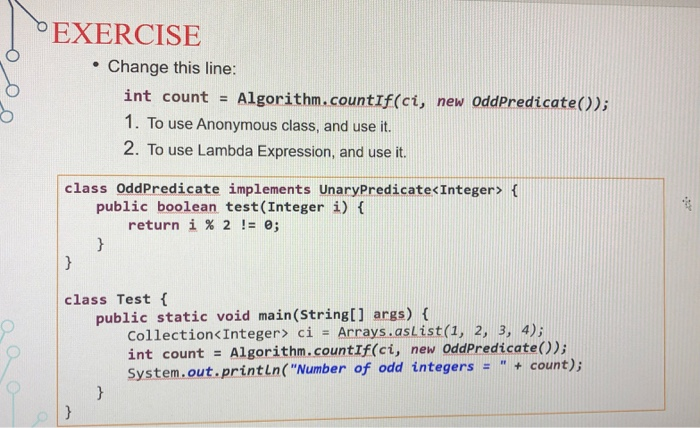
EXERCISE Change this line: int count = Algorithm.countIf(ci, new OddPredicate()); 1. To use Anonymous class, and use it. 2. To use Lambda Expression, and use it. class OddPredicate implements UnaryPredicate { public boolean test(Integer i) { return i % 2 != 0; class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Collections Integer> ci = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4); int count = Algorithm.countIf(ci, new OddPredicate()); System.out.println("Number of odd integers = " + count); EXERCISE Change this line: int count = Algorithm.countIf(ci, new OddPredicate()); 1. To use Anonymous class, and use it. 2. To use Lambda Expression, and use it. class OddPredicate implements UnaryPredicate { public boolean test(Integer i) { return i % 2 != 0; class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Collections Integer> ci = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4); int count = Algorithm.countIf(ci, new OddPredicate()); System.out.println("Number of odd integers = " + count)