Question: Homework 1.7 Progress saved Done Score: 0/4 0/4 answered Question 2 0/1 pt 9 3 7 19 0 Details Use Euler's method with step size
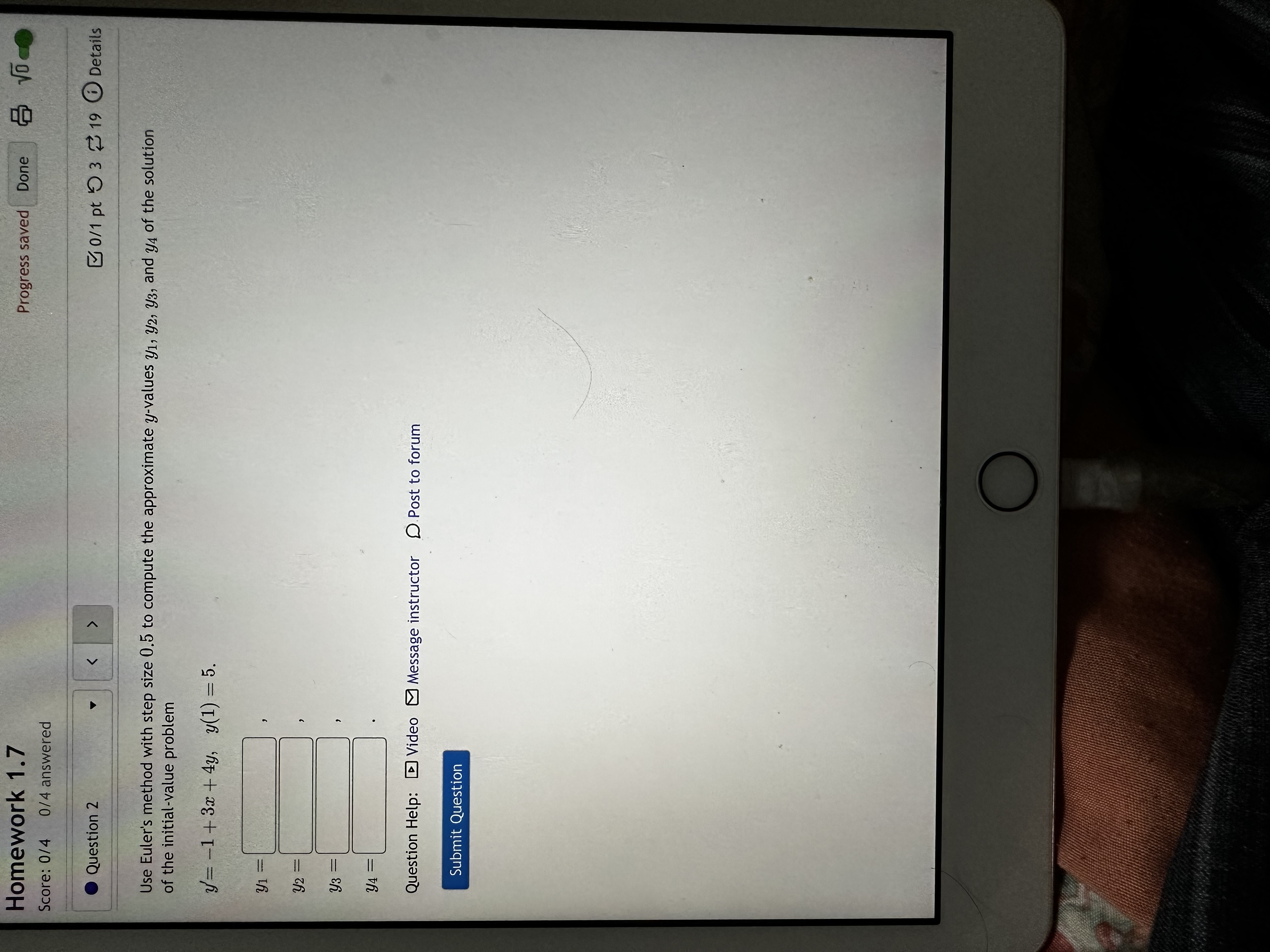
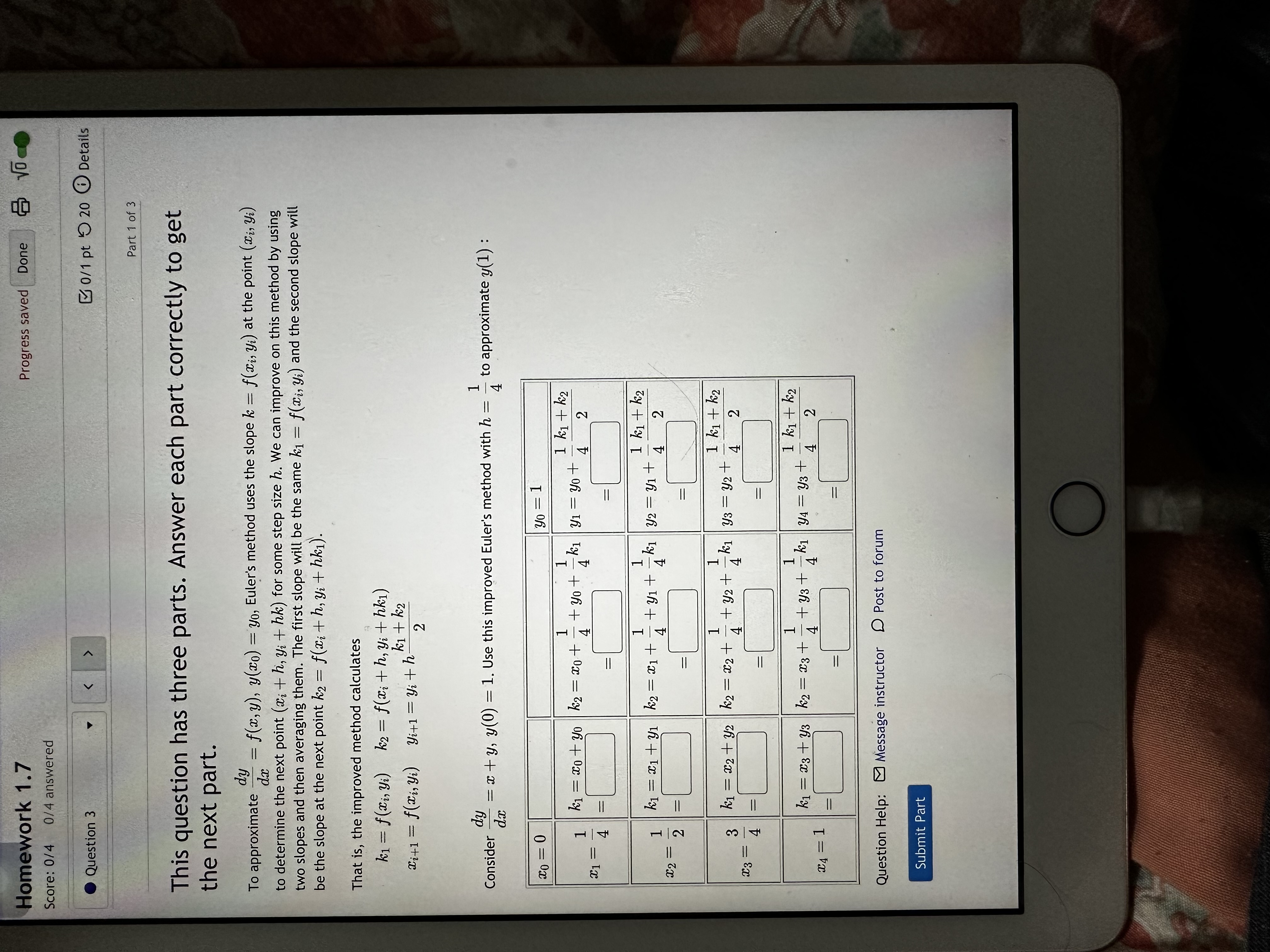
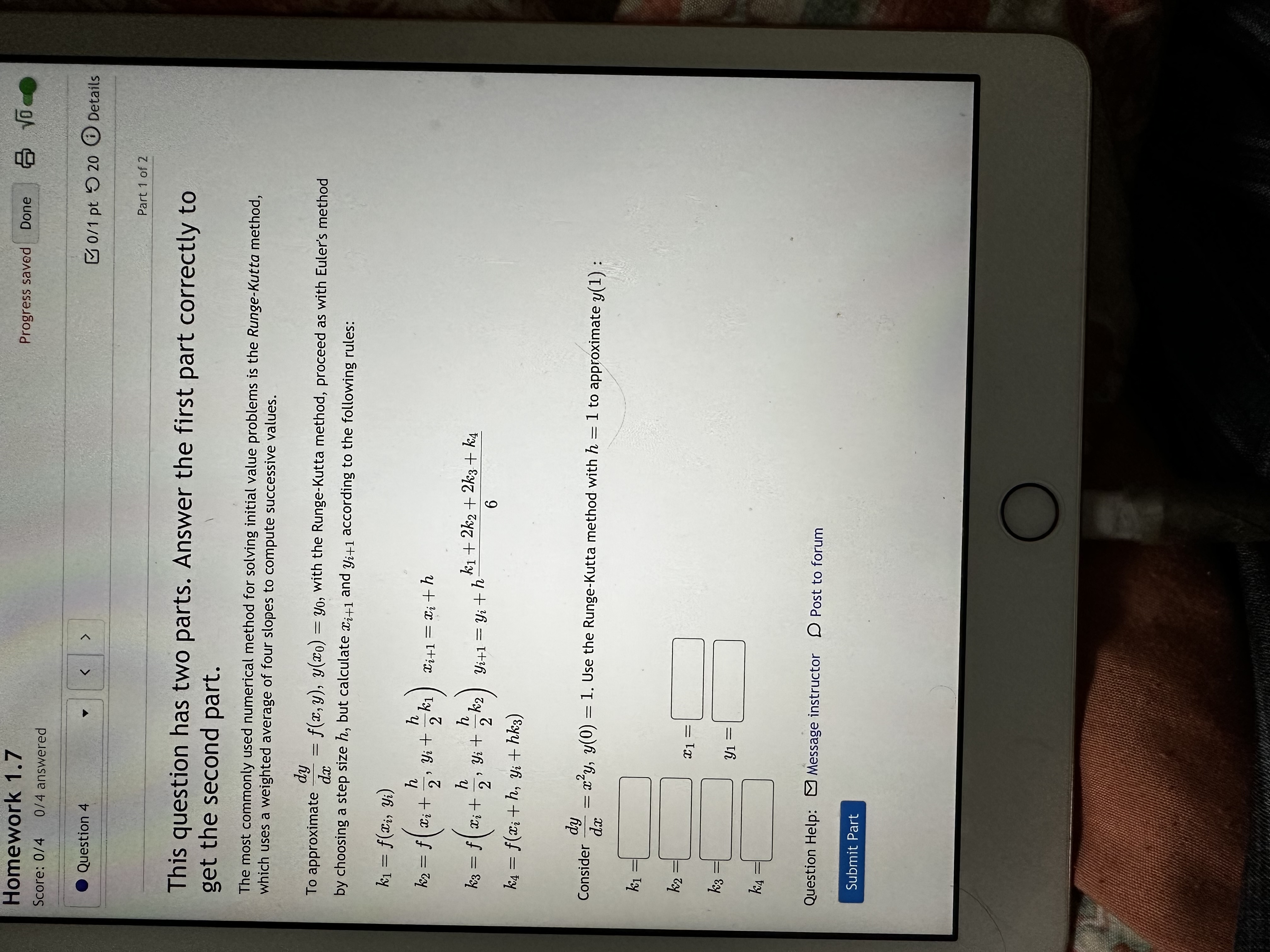
Homework 1.7 Progress saved Done Score: 0/4 0/4 answered Question 2 0/1 pt 9 3 7 19 0 Details Use Euler's method with step size 0.5 to compute the approximate y-values y1, y2, y3, and y4 of the solution of the initial-value problem y=-1+3x +4y, y(1) = 5. 21 y2 y3 = y4 Question Help: Video Message instructor D Post to forum Submit Question OHomework 1.7 Progress saved Done Score: 0/4 0/4 answered Question 3 0/1 pt 9 20 @ Details Part 1 of 3 This question has three parts. Answer each part correctly to get the next part. To approximate dx a = f(x, y), y(20) = yo, Euler's method uses the slope k = f(Tis yi) at the point (is yi) to determine the next point (i + h, yi + hk) for some step size h. We can improve on this method by using two slopes and then averaging them. The first slope will be the same k1 = f(Ti, yi) and the second slope will be the slope at the next point k2 = f(xi + h, yi + hki). That is, the improved method calculates k1 = f(i, yi) k2 = f(xit h, yi + hk1) Ziti = f(is yi) yit1 = yit h ki + k2 2 Consider dx = x + y, y(0) =1. Use this improved Euler's method with h = 4 to approximate y(1) : CO = 0 yo = 1 1 K1 = Not yo k2 = xo+ + yo+ ki|y1 = got- 1 k1 + K2 1 4 C1 = 2 = 1 = city k2= 1+ + yit - k1 32 = y1+- 1 ki + k2 12 = 4 2 = K1 = x2+ 2 k2 = =2+-+92+- k1 |y3= yz+ 1 k1 + K2 C3 = 2 K1 = 3+ 23 K2 = 23 + + 93+ k 1 K1 y4 = 43 + 1 ki + k2 C4 = 1 4 2 = Question Help: Message instructor D Post to forum Submit Part OHomework 1.7 Progress saved Done Score: 0/4 0/4 answered Question 4 0/1 pt 9 20 @ Details Part 1 of 2 This question has two parts. Answer the first part correctly to get the second part. The most commonly used numerical method for solving initial value problems is the Runge-Kutta method, which uses a weighted average of four slopes to compute successive values. To approximate - wy = f(x, y), y(20) = yo, with the Runge-Kutta method, proceed as with Euler's method by choosing a step size h, but calculate Xi+1 and yi+1 according to the following rules: k1 = f(Ci, yi) 2' yit h ki Citl = with kg = f ( Dit ? ' yit 2 h kz) yitl = yith ki+ 2k2+ 2k3 + ka 6 KA = f(with, yit hkg) dy Consider dx = x y, y(0) = 1. Use the Runge-Kutta method with h = 1 to approximate y(1) : K1 K2 C1 K3 y1 = KA Question Help: Message instructor D Post to forum Submit Part O
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


