Question: How do I write a put method in Array Dictionary. What is the contructor going to be like? package datastructures.concrete.dictionaries; import java.lang.reflect.Array; import datastructures.interfaces.IDictionary; import
How do I write a put method in Array Dictionary.
What is the contructor going to be like?
package datastructures.concrete.dictionaries;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import datastructures.interfaces.IDictionary; import misc.exceptions.NoSuchKeyException; import misc.exceptions.NotYetImplementedException;
/** * See IDictionary for more details on what this class should do */ public class ArrayDictionary
// You're encouraged to add extra fields (and helper methods) though!
public ArrayDictionary() { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Pair
/** * This method will return a new, empty array of the given size * that can contain Pair
}
@Override public void put(K key, V value) { }
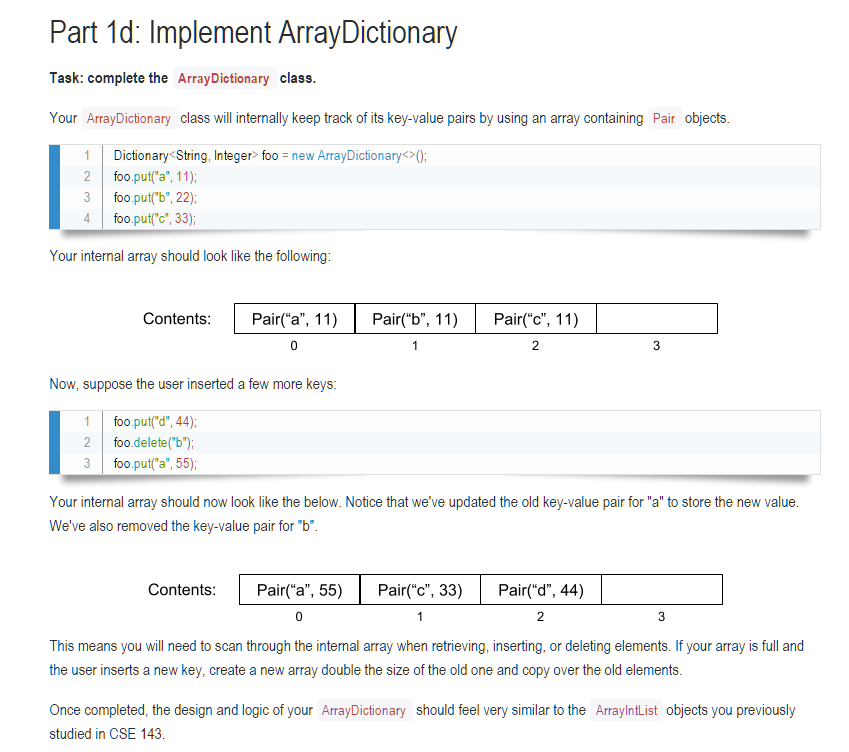
Part 1d: Implement ArrayDictionary Task: complete the ArrayDictionary class Your ArrayDictionary class will internally keep track of its key-value pairs by using an array containing Pair objects new ArrayDictionary>0; 1Dictionary String, Integer> foo 2foo.put"a", 11) 3foo.put"b", 22); foo put" 33); Your internal array should look like the following Contents: Pair("a", 11)Pair("b", 11) Pair("c", 11) 2 Now, suppose the user inserted a few more ke ys 1foo put'd,44) 2 foo.delete(b") 3foo.put"a", 55) Your internal array should now look like the below. Notice that we've updated the old key-value pair for "a" to store the new value We've also removed the key-value pair for "b Contents Pair("a", 55) Pair("c", 33)"d", 44) 2 This means you will need to scan through the internal array when retrieving, inserting, or deleting elements. If your array is full and the user inserts a new key, create a new array double the size of the old one and copy over the old elements Once completed, the design and logic of your ArrayDictionary should feel very similar to the ArraylntList objects you previously studied in CSE 143 Part 1d: Implement ArrayDictionary Task: complete the ArrayDictionary class Your ArrayDictionary class will internally keep track of its key-value pairs by using an array containing Pair objects new ArrayDictionary>0; 1Dictionary String, Integer> foo 2foo.put"a", 11) 3foo.put"b", 22); foo put" 33); Your internal array should look like the following Contents: Pair("a", 11)Pair("b", 11) Pair("c", 11) 2 Now, suppose the user inserted a few more ke ys 1foo put'd,44) 2 foo.delete(b") 3foo.put"a", 55) Your internal array should now look like the below. Notice that we've updated the old key-value pair for "a" to store the new value We've also removed the key-value pair for "b Contents Pair("a", 55) Pair("c", 33)"d", 44) 2 This means you will need to scan through the internal array when retrieving, inserting, or deleting elements. If your array is full and the user inserts a new key, create a new array double the size of the old one and copy over the old elements Once completed, the design and logic of your ArrayDictionary should feel very similar to the ArraylntList objects you previously studied in CSE 143
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


