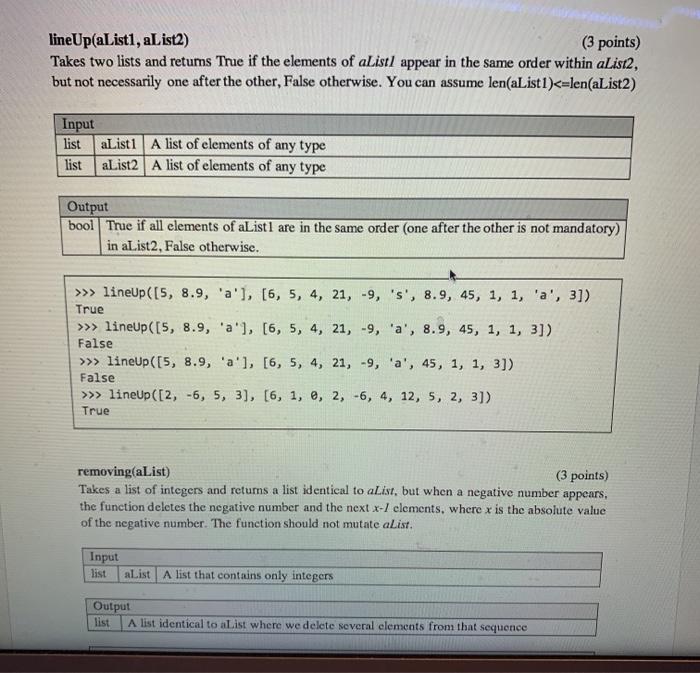
Question: how do you complete this lineUp(aList1, al ist2) (3 points) Takes two lists and retums True if the elements of aListl appear in the same
![21, -9, 's', 8.9, 45, 1, 1, 'a', 3]) True >>> lineup](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3b6b5083b3_05266f3b6b49595e.jpg)
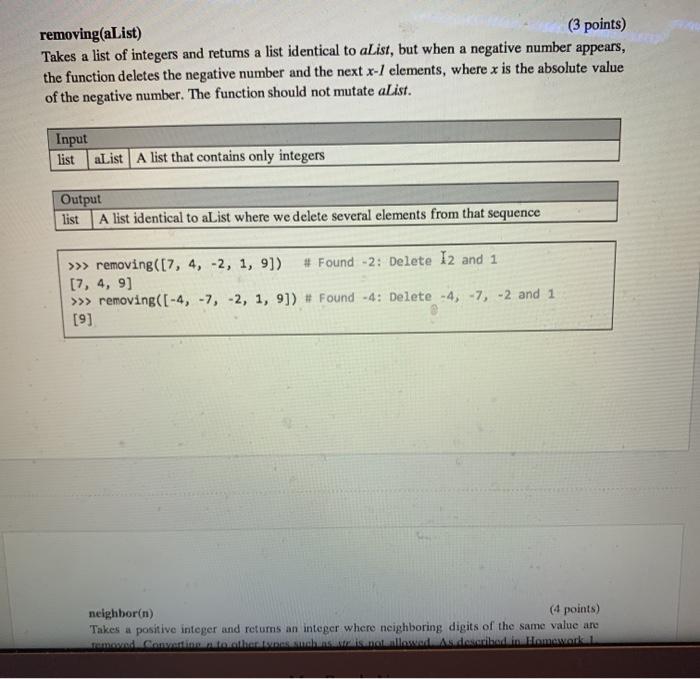
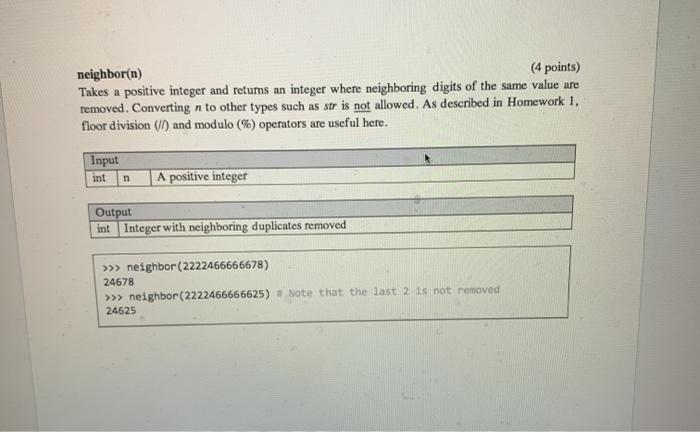
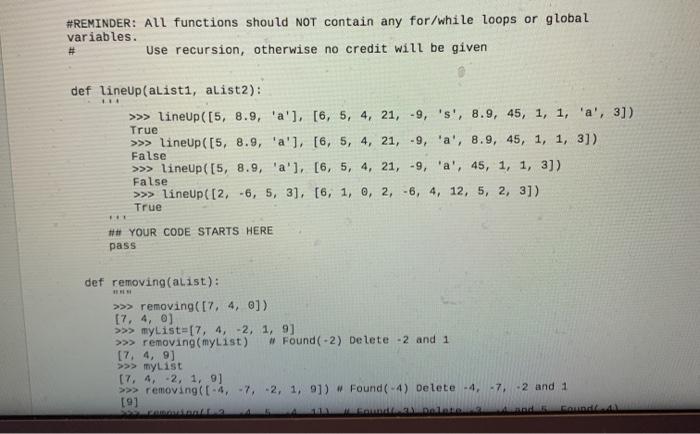
lineUp(aList1, al ist2) (3 points) Takes two lists and retums True if the elements of aListl appear in the same order within aList2, but not necessarily one after the other, False otherwise. You can assume len(aList1)>> lineUp([5, 8.9, 'a'), (6, 5, 4, 21, -9, 's', 8.9, 45, 1, 1, 'a', 3]) True >>> lineup ([5, 8.9, 'a'), (6, 5, 4, 21, -9, 'a', 8.9, 45, 1, 1, 3]) False >>> lineUp ([5, 8.9, 'a'], [6, 5, 4, 21, -9, 'a', 45, 1, 1, 3]) False >>> lineUp([2, -6, 5, 3), (6, 1, 0, 2, -6, 4, 12, 5, 2, 3]) True removing(aList) (3 points) Takes a list of integers and returns a list identical to aList, but when a negative number appears, the function deletes the negative number and the next x-/ elements, where x is the absolute value of the negative number. The function should not mutate alist. Input list aList A list that contains only integers Output list A list identical to aList where we delete several elements from that sequence removing(aList) (3 points) Takes a list of integers and retums a list identical to aList, but when a negative number appears, the function deletes the negative number and the next x-1 elements, where x is the absolute value of the negative number. The function should not mutate alist. Input list aList A list that contains only integers Output list A list identical to alist where we delete several elements from that sequence >>> removing([7, 4, -2, 1, 9]) # Found-2: Delete 12 and 1 [7, 4, 9] >>> removing([-4, -7, -2, 1, 9]) # Found -4: Delete -4, -7, -2 and 1 [9] neighbor(n) (4 points) Takes a positive integer and returns an integer where neighboring digits of the same value are rumored Conwettino danes mehndinellosid Asi described in Homework neighbor(n) (4 points) Takes a positive integer and returns an integer where neighboring digits of the same value are removed. Converting n to other types such as str is not allowed. As described in Homework 1. floor division () and modulo (%) operators are useful here. Input int A positive integer Output int Integer with neighboring duplicates removed >>> neighbor (2222466666678) 24678 >>> neighbor (2222466666625) . Note that the last 2 is not removed 24625 #REMINDER: All functions should NOT contain any for/while loops or global variables. # Use recursion, otherwise no credit will be given def lineUp(alisti, alist2): >>> lineup([5, 8.9, 'a'], [6, 5, 4, 21,-9, 's', 8.9, 45, 1, 1, 'a', 3]) True >>> lineup ([5, 8.9, 'a']. [6, 5, 4, 21, 19, 'a', 8.9, 45, 1, 1, 3]) False >>> lineup ([5, 8.9, 'a'], [6, 5, 4, 21, -9, 'a', 45, 1, 1, 3]) False >>> lineup ([2, -6, 5, 3), [6, 1, 0, 2, -6, 4, 12, 5, 2, 3]) True # YOUR CODE STARTS HERE pass def removing(alist): >>> removing([7, 4, 0]) [7, 4, 0] >> myList=7, 4, -2, 1, 9] >>> removing(mylist) # Found(-2) Delete -2 and 1 (7,4, 9) >>> Ty 19t [7, 4, 2, 1,9 >>> removing (-4, 7, 2, 1, 9]) Found(-4) Delete -4, 27, 2 and 1 [9] Do Forum
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


