Question: how do you start this table DATA TABLE DATA ANALYSIS NOTE: for this experiment, you can convert the initial rate as measured in KPa2/ into
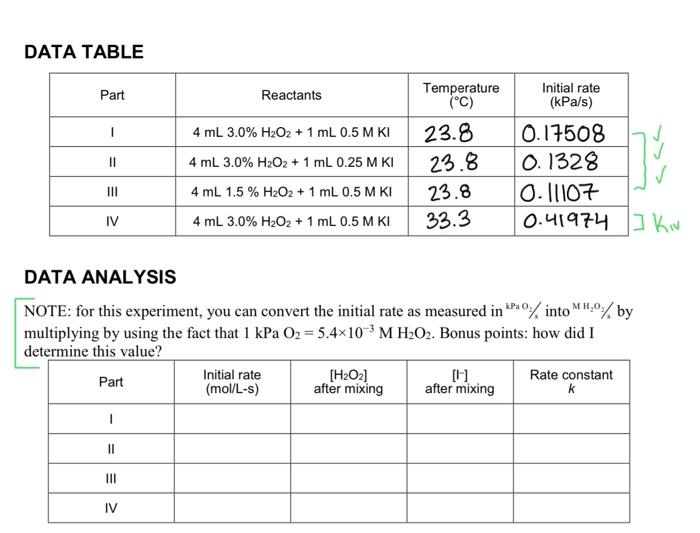

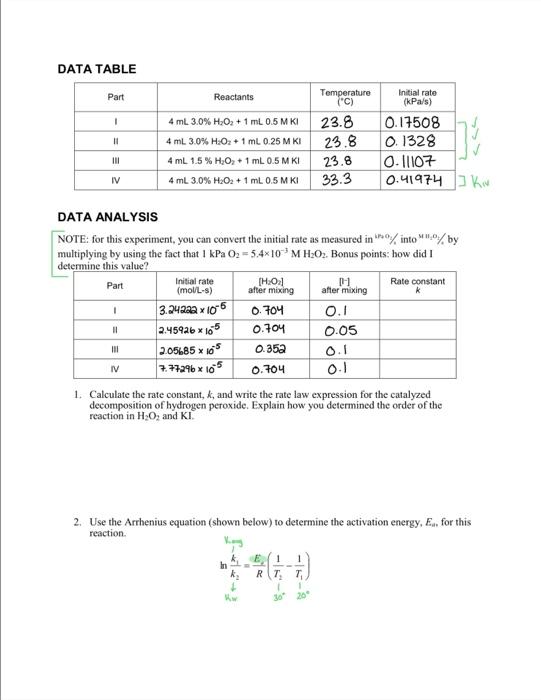
DATA TABLE DATA ANALYSIS NOTE: for this experiment, you can convert the initial rate as measured in KPa2/ into MH2O3/3 by multiplying by using the fact that 1kPaOO2=5.4103MH2O2. Bonus points: how did I determine this value? PRE-LAB EXERCISE The hydrogen peroxide solution that you are using in this experiment is labeled as a 3% solution, mass/volume (%g/mL). However, in order to complete the calculations, the concentration must be in molarity. Calculate the molarity of a 3% mass volume H2O2 solution (Part 1, II, and IV) and a 1.5% mass/volume H2O2 solution (Part III) and record these values in the table below. PROCEDURE PROCEDUREPartIDecompose3%H2O2solutionwith0.5MKisolutionat20C1.5gg1.Obtainandweargoggles. 2. Prepare the reagents for temperature equilibration. 0441 a. Obtain room-temperature water to set up a water bath to completely immerse the test tube. Use a thermometer or a Temperature Probe to measure the temperature of the bath. Record this temperature in your data table for Parts 1-3; presume that the water bath temperature remains constant throughout. b. Measure out 4mL of 3%H2O2 solution into the test tube. Seal the test tube with the rolid) rubber stopper and place the test tube in the water bath. c. Measure out 2mL of 0.5MKI solution in a graduated cylinder. Draw I mL of the KI solution into a graduated Beral pipet. Invert the pipet and immerse the reservoir end of the pipet in the water bath. 3. Connect the Gas Pressure Sensor to LabQuest and choose New from the File menu. If you have an older sensor that does not auto-ID, manually set up the sensor. 4. Use the plastic tubing to connect the one-hole rubber stopper to the Gas Pressure Sensor, as shown in Figure 1. About one-half tur of the fittings will secure the tubing tightly. 5. On the Meter sereen, tap Rate. Change the data-collection rate 60.1 samples/second znd the data-collection length to 300 seconds and select OK. 6. Prepare to run the reaction and collect pressure data. a. Remove the test tube from the water bath and remove the solid stopper. b. Remove the plastic Beral pipet from the water bath and quickly transfer the 1mL. of KI solution into the test tube. Tap or lightly shake the test tube to mix the reagents. c. Seal the test tube with the one-hole stopper connected to the Gas Pressure Sensor. d. Place the test tube back in the water bath. DATA TABLE DATA ANALYSIS multiplying by using the fact that 1kPaO2=5.4103MH2O2. Bonus points: how did 1 determine this value? 1. Calculate the rate constant, k, and write the rate law expression for the catalyzed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. Explain how you determined the order of the reaction in H2O2 and KI. 2. Use the Arrhenius equation (shown below) to determine the activation energy, Ea, for this reaction. mnk2k1=REc(T21T11) DATA TABLE DATA ANALYSIS NOTE: for this experiment, you can convert the initial rate as measured in KPa2/ into MH2O3/3 by multiplying by using the fact that 1kPaOO2=5.4103MH2O2. Bonus points: how did I determine this value? PRE-LAB EXERCISE The hydrogen peroxide solution that you are using in this experiment is labeled as a 3% solution, mass/volume (%g/mL). However, in order to complete the calculations, the concentration must be in molarity. Calculate the molarity of a 3% mass volume H2O2 solution (Part 1, II, and IV) and a 1.5% mass/volume H2O2 solution (Part III) and record these values in the table below. PROCEDURE PROCEDUREPartIDecompose3%H2O2solutionwith0.5MKisolutionat20C1.5gg1.Obtainandweargoggles. 2. Prepare the reagents for temperature equilibration. 0441 a. Obtain room-temperature water to set up a water bath to completely immerse the test tube. Use a thermometer or a Temperature Probe to measure the temperature of the bath. Record this temperature in your data table for Parts 1-3; presume that the water bath temperature remains constant throughout. b. Measure out 4mL of 3%H2O2 solution into the test tube. Seal the test tube with the rolid) rubber stopper and place the test tube in the water bath. c. Measure out 2mL of 0.5MKI solution in a graduated cylinder. Draw I mL of the KI solution into a graduated Beral pipet. Invert the pipet and immerse the reservoir end of the pipet in the water bath. 3. Connect the Gas Pressure Sensor to LabQuest and choose New from the File menu. If you have an older sensor that does not auto-ID, manually set up the sensor. 4. Use the plastic tubing to connect the one-hole rubber stopper to the Gas Pressure Sensor, as shown in Figure 1. About one-half tur of the fittings will secure the tubing tightly. 5. On the Meter sereen, tap Rate. Change the data-collection rate 60.1 samples/second znd the data-collection length to 300 seconds and select OK. 6. Prepare to run the reaction and collect pressure data. a. Remove the test tube from the water bath and remove the solid stopper. b. Remove the plastic Beral pipet from the water bath and quickly transfer the 1mL. of KI solution into the test tube. Tap or lightly shake the test tube to mix the reagents. c. Seal the test tube with the one-hole stopper connected to the Gas Pressure Sensor. d. Place the test tube back in the water bath. DATA TABLE DATA ANALYSIS multiplying by using the fact that 1kPaO2=5.4103MH2O2. Bonus points: how did 1 determine this value? 1. Calculate the rate constant, k, and write the rate law expression for the catalyzed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. Explain how you determined the order of the reaction in H2O2 and KI. 2. Use the Arrhenius equation (shown below) to determine the activation energy, Ea, for this reaction. mnk2k1=REc(T21T11)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


