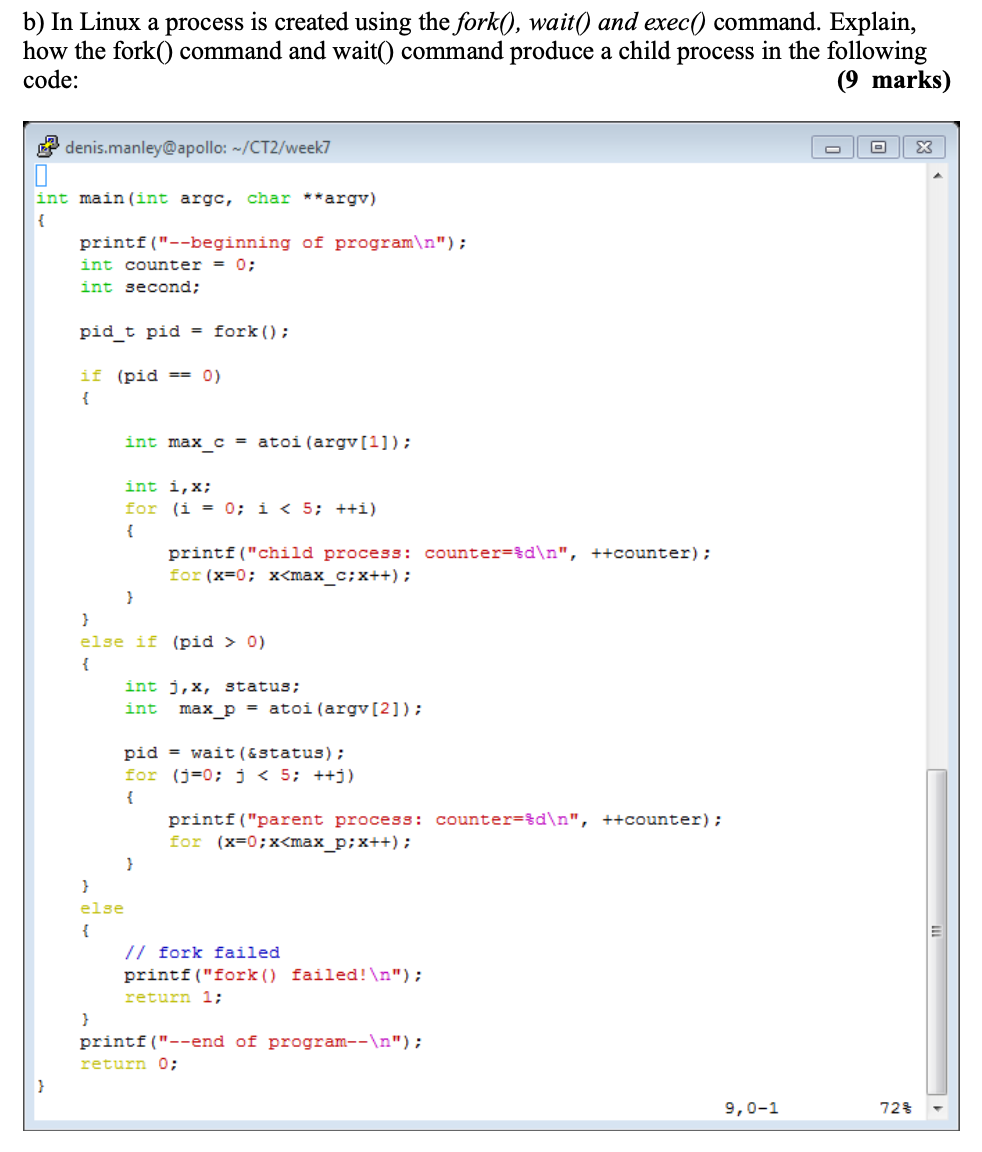
Question: how the fork ( ) command and wait ( ) command produce a child process in the following code: int main ( int argc, char
how the fork command and wait command produce a child process in the following code: int mainint argc, char argv printfbeginning of program
; int counter ; int second; pidt pid fork; if pid int maxc atoiargv; int ix; for i ; i i printfchild process: countersd
counter; for x; xmax c ; x ; else if pid int j x status; int maxp atoiargv; pid wait&status; for j ; j ;j printfparent process: countersd
counter; for x; x maxp; x ; else fork failed printffork failed!
; return ; printfend of program
; return ;
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


