Question: How to finish this java?! Exercises #5, 6, 7, and 8 You are to implement all four classes described in the four exercises. For the
How to finish this java?!
Exercises #5, 6, 7, and 8 You are to implement all four classes described in the four exercises. For the classes that have advanced date requirements for the price of the ticket, the call to the Constructor must include, besides the ticket number, the days in advance the ticket is being purchased. You are to utilize the instructors client test program, Project10_EventTickets.java, to test your solution. The output is shown on the next page.

The java file is:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Project10_EventTickets {
public static void main(String[] args) { // Create ticket objects of the three ticket types WalkupTicket walkup = new WalkupTicket(1); AdvanceTicket advance1 = new AdvanceTicket(2, 12); AdvanceTicket advance2 = new AdvanceTicket(3, 5); StudentAdvanceTicket student1 = new StudentAdvanceTicket(4, 15); StudentAdvanceTicket student2 = new StudentAdvanceTicket(5,3); // Create an array of references to event Tickets, the element references // to the sub-class ticket objects created above Ticket[] tickets = { walkup, advance1, advance2, student1, student2 };
// Describe the Project Solution to the User introduction();
// Now iterate the list, displaying the ticket number and price for (Ticket ticket : tickets) System.out.println(ticket); } // End method: main(String[])
private static void introduction() { // Construct the first line of the Introduction: The Project # String line1 = "CS-" + COURSE_NUMBER + ": Project #" + PROJECT_NUMBER + " Solution"; // Construct the second line of the Introduction: Chapter, Exercise(s) // and the page number in the text // Start the second line with the text Chapter number and page number String line2 = "Chapter " + CHAPTER_NUMBER + ", page " + PAGE_NUMBER + ", Exercise"; // Now add the Exercise number(s) if (EXERCISE_NUMBERS.length == 1) { // Only 1 Exercise number line2 += (" #" + EXERCISE_NUMBERS[0]); } else { // Multiple Exercise numbers to display... line2 += "s "; // Add the 's' to "Exercise" // Now add the Exercise number(s) to the second line for (int index = 0; index 0) System.out.println(nextLine); System.out.println(" "); } // Class Private "static", constant "final" Values // Project Description items // 1. CS Course Number private static final int COURSE_NUMBER = 210; // 2. Textbook Project Number, Chapter Number, Page Number, and Exercise Number(s) private static final int PROJECT_NUMBER = 10; private static final int CHAPTER_NUMBER = 9; private static final int PAGE_NUMBER = 643; private static int[] EXERCISE_NUMBERS = { 5, 6, 7, 8 }; // 3. Description text private static String DESCRIPTION_TEXT = "This program tests the implementation of the abstract \"Ticket\" class " + "and its derived, concrete classes \"WalkupTicket\", \"AdvanceTicket\", and " + "\"StudentAdvanceTicket\", which is derived from \"AdvanceTicket\".";
private static final int CONSOLE_LINE_LENGTH = 68; private static final int LINE_LENGTH_TOLERANCE = 5; } // End class definition: Project10_EventTickets
The output is:
Exercises #5, #6, #7, and #8
This program tests the implementation of the abstract "Ticket" class and its derived, concrete classes "WalkupTicket", "AdvanceTicket", and "StudentAdvanceTicket", which is derived from "AdvanceTicket". Number: 1, Price: 50.0 Number: 2, Price: 30.0 Number: 3, Price: 40.0 Number: 4, Price: 15.0 (ID required) Number: 5, Price: 20.0 (ID required)
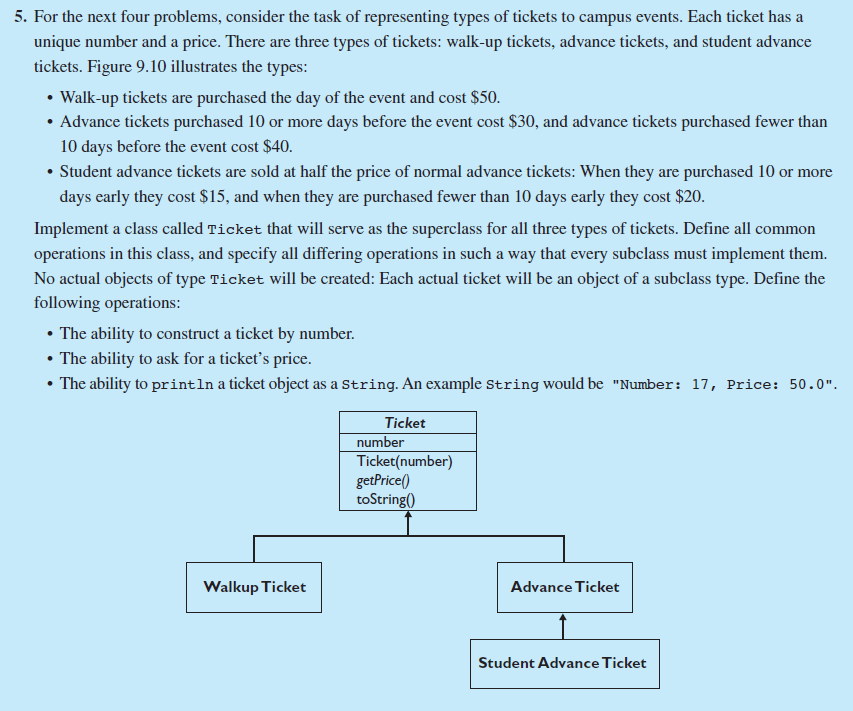
5. For the next four problems, consider the task of representing types of tickets to campus events. Each ticket has a unique number and a price. There are three types of tickets: walk-up tickets, advance tickets, and student advance tickets. Figure 9.10 illustrates the types: Walk-up tickets are purchased the day of the event and cost $50. Advance tickets purchased 10 or more days before the event cost $30, and advance tickets purchased fewer than 10 days before the event cost $40. Student advance tickets are sold at half the price of normal advance tickets: When they are purchased 10 or more days early they cost $15, and when they are purchased fewer than 10 days early they cost $20 Implement a class called Ticket that will serve as the superclass for all three types of tickets. Define all common operations in this class, and specify all differing operations in such a way that every subclass must implement them. No actual objects of type Ticket will be created: Each actual ticket will be an object of a subclass type. Define the following operations: The ability to construct a ticket by number. The ability to ask for a ticket's price. The ability to println a ticket object as a string. An example string would be "Number: 17, Price: 50.0". Ticket number Ticket number getPrice0 toString( Advance Ticket Walkup Ticket Student AdvanceTicket
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


