Question: I. A statistician randomly sampled 25 observations from a normally distributed population. The descriptive statistics are given below: n = 25, X = 10, s
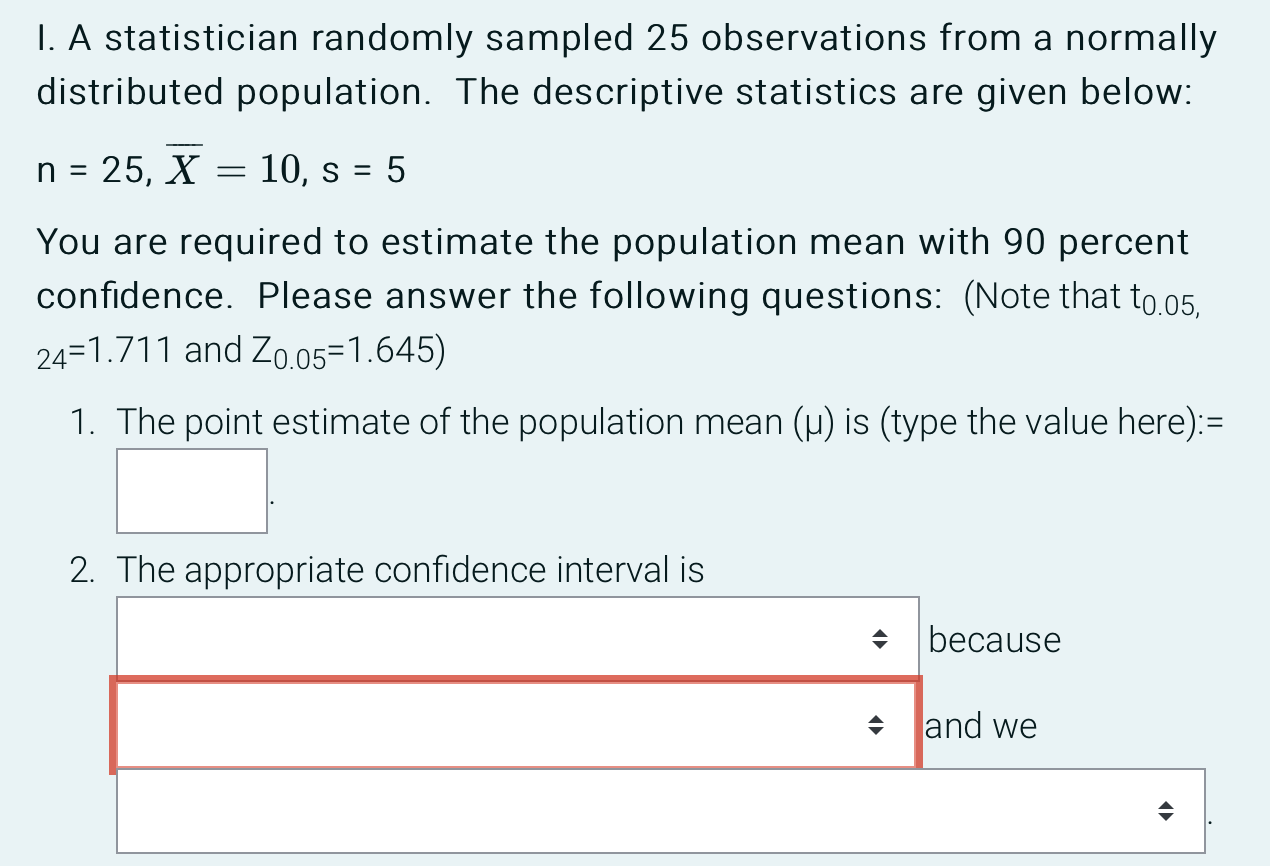
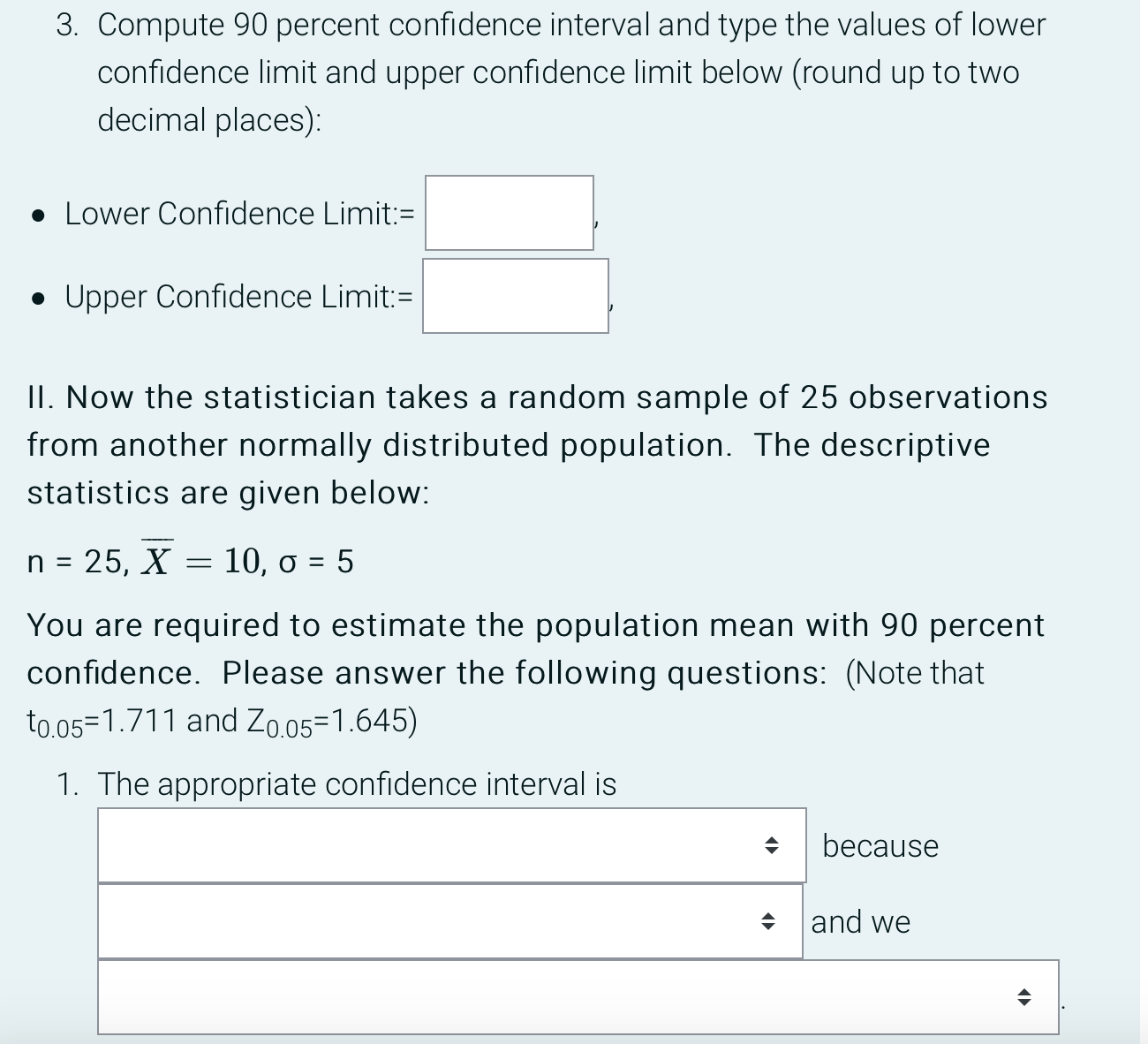

I. A statistician randomly sampled 25 observations from a normally distributed population. The descriptive statistics are given below: n = 25, X = 10, s = 5 You are required to estimate the population mean with 90 percent confidence. Please answer the following questions: (Note that to.05, 24=1.711 and Zo.05=1.645) 1. The point estimate of the population mean () is (type the value here): = 2. The appropriate confidence interval is because and we3. Compute 90 percent confidence interval and type the values of lower confidence limit and upper confidence limit below (round up to two decimal places): . Lower Confidence Limit:= . Upper Confidence Limit:= Il. Now the statistician takes a random sample of 25 observations from another normally distributed population. The descriptive statistics are given below: n = 25, X = 10, 0 = 5 You are required to estimate the population mean with 90 percent confidence. Please answer the following questions: (Note that to.05=1.711 and Zo.05=1.645) 1. The appropriate confidence interval is because and we2. Compute the 90 percent confidence interval and type the values of lower confidence limit and upper confidence limit below (round up to two decimal places): . Lower Confidence Limit:= . Upper Confidence Limit:= Ill. From the confidence intervals estimated in part (1) and (11): The t-interval estimated is wider than z-interval. The extent to which t- distribution is more spread out than the z-distribution is determined by
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


