Question: i dont get the last part One pathway for the destruction of ozone in the upper atmosphere is O3(g)+NO(g)NO2(g)+O2(g)SlowNO2(g)+O(g)NO(g)+O2(g)Fast Overall reaction: O3(g)+O(g)2O2(g) Identify the correct
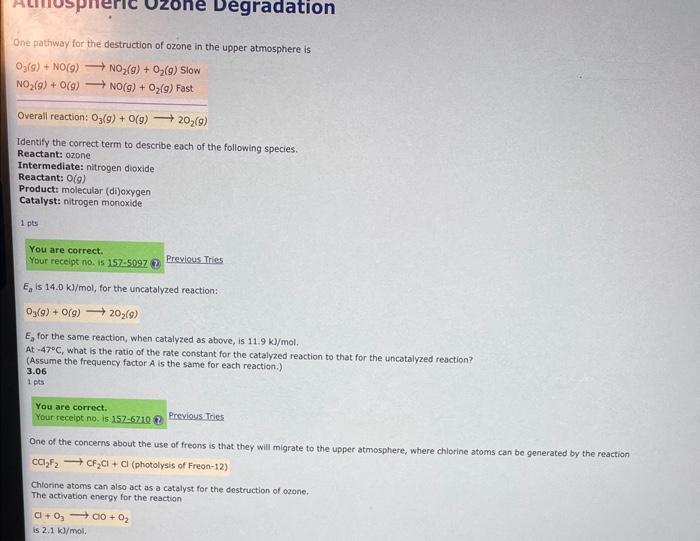


One pathway for the destruction of ozone in the upper atmosphere is O3(g)+NO(g)NO2(g)+O2(g)SlowNO2(g)+O(g)NO(g)+O2(g)Fast Overall reaction: O3(g)+O(g)2O2(g) Identify the correct term to describe each of the following species. Reactant: ozone Intermediate: nitrogen dioxide Reactant: O(g) Product: molecular (di)oxygen Catalyst: nitrogen monoxide 1.pts Previous Tries Ea is 14.0kJ/mol, for the uncatalyzed reaction: O3(g)+O(g)2O2(9) Ea for the same reaction, when catalyzed as above, is 11.9kJ/mol. At 47C, what is the ratio of the rate constant for the catalyzed reaction to that for the uncatalyzed reaction? (Assume the frequency factor A is the same for each reaction.) 3.06 1 pis Previous. Tnies One of the concerns about the use of freons is that they will migrate to the upper atmosphere, where chlorine atoms can be generated by the reaction Chlorine atoms can also act as a catalyst for the destruction of ozone. The activation energy for the reaction +O3CO+O2 Freriavitines One of the cancerns about the use of freons is thut they nill migrote to the upper atmosphere, where chlorine atomi can be gtherates by the reaction CO2F2Cr2C+C(ohotolyesofFreon-12) Chlorine atoms can also act as a catalys for the dethuction of orone. The activation energy for the resction C+O3oD+Oj is 2.1k/mal. Cis repenerates ty the fast reachion Co+OO2+C desertied in the ortivious quention. Cl+O3ClO+O2 is 2.1kg/mol. O is regenerated by the fast reaction ClO+OO2+O If the frequency factors are the same and both catalysts are in equal concentrabon, how many times faster, at 28C, does the G catalysed reaction proceed combsred to the reaction cotalysed as described in the arevious question. Ifts One pathway for the destruction of ozone in the upper atmosphere is O3(g)+NO(g)NO2(g)+O2(g)SlowNO2(g)+O(g)NO(g)+O2(g)Fast Overall reaction: O3(g)+O(g)2O2(g) Identify the correct term to describe each of the following species. Reactant: ozone Intermediate: nitrogen dioxide Reactant: O(g) Product: molecular (di)oxygen Catalyst: nitrogen monoxide 1.pts Previous Tries Ea is 14.0kJ/mol, for the uncatalyzed reaction: O3(g)+O(g)2O2(9) Ea for the same reaction, when catalyzed as above, is 11.9kJ/mol. At 47C, what is the ratio of the rate constant for the catalyzed reaction to that for the uncatalyzed reaction? (Assume the frequency factor A is the same for each reaction.) 3.06 1 pis Previous. Tnies One of the concerns about the use of freons is that they will migrate to the upper atmosphere, where chlorine atoms can be generated by the reaction Chlorine atoms can also act as a catalyst for the destruction of ozone. The activation energy for the reaction +O3CO+O2 Freriavitines One of the cancerns about the use of freons is thut they nill migrote to the upper atmosphere, where chlorine atomi can be gtherates by the reaction CO2F2Cr2C+C(ohotolyesofFreon-12) Chlorine atoms can also act as a catalys for the dethuction of orone. The activation energy for the resction C+O3oD+Oj is 2.1k/mal. Cis repenerates ty the fast reachion Co+OO2+C desertied in the ortivious quention. Cl+O3ClO+O2 is 2.1kg/mol. O is regenerated by the fast reaction ClO+OO2+O If the frequency factors are the same and both catalysts are in equal concentrabon, how many times faster, at 28C, does the G catalysed reaction proceed combsred to the reaction cotalysed as described in the arevious question. Ifts
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


