Question: I have implemented this AVL tree code but as i have posted i am getting exception i dont know how to fix it can you
I have implemented this AVL tree code but as i have posted i am getting exception i dont know how to fix it can you help me this implementation work? 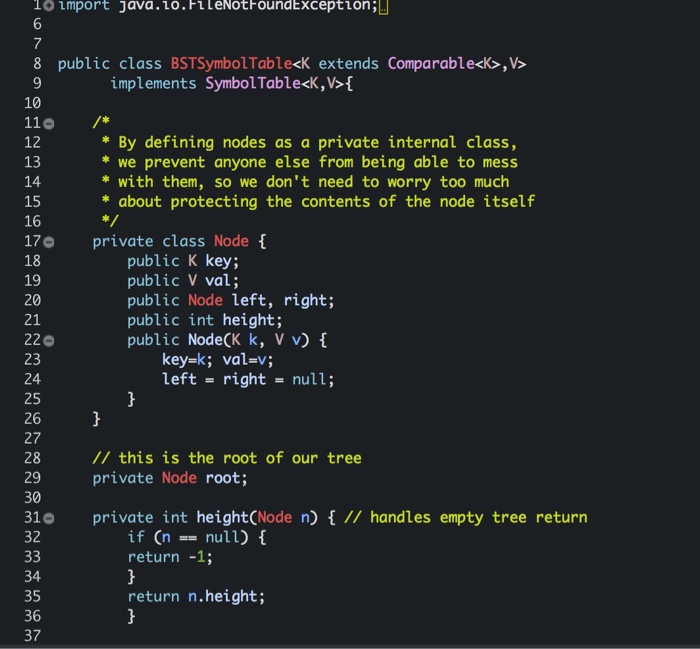
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Vector;
public class BSTSymbolTable,V>
implements SymbolTable{
/*
* By defining nodes as a private internal class,
* we prevent anyone else from being able to mess
* with them, so we don't need to worry too much
* about protecting the contents of the node itself
*/
private class Node {
public K key;
public V val;
public Node left, right;
public int height;
public Node(K k, V v) {
key=k; val=v;
left = right = null;
}
}
// this is the root of our tree
private Node root;
private int height(Node n) { // handles empty tree return
if (n == null) {
return -1;
}
return n.height;
}
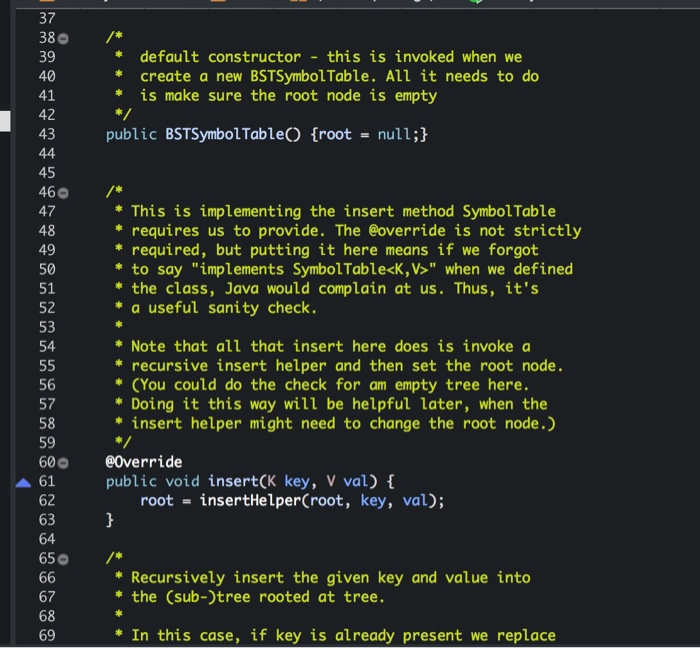
/*
* default constructor - this is invoked when we
* create a new BSTSymbolTable. All it needs to do
* is make sure the root node is empty
*/
public BSTSymbolTable() {root = null;}
/*
* This is implementing the insert method SymbolTable
* requires us to provide. The @override is not strictly
* required, but putting it here means if we forgot
* to say "implements SymbolTable" when we defined
* the class, Java would complain at us. Thus, it's
* a useful sanity check.
*
* Note that all that insert here does is invoke a
* recursive insert helper and then set the root node.
* (You could do the check for am empty tree here.
* Doing it this way will be helpful later, when the
* insert helper might need to change the root node.)
*/
@Override
public void insert(K key, V val) {
root = insertHelper(root, key, val);
}
/*
* Recursively insert the given key and value into
* the (sub-)tree rooted at tree.
*
* In this case, if key is already present we replace
* the old (key, value) pair with the new ones.
* Why would we want to replace the key, too?
*/
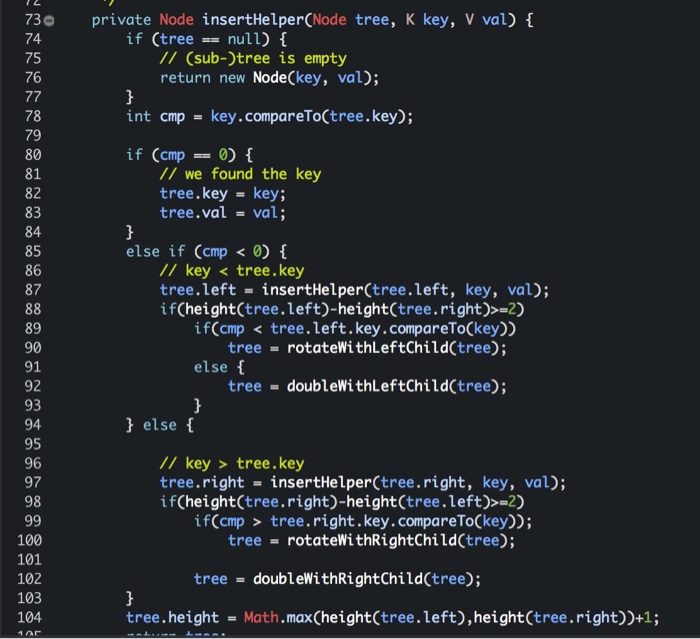
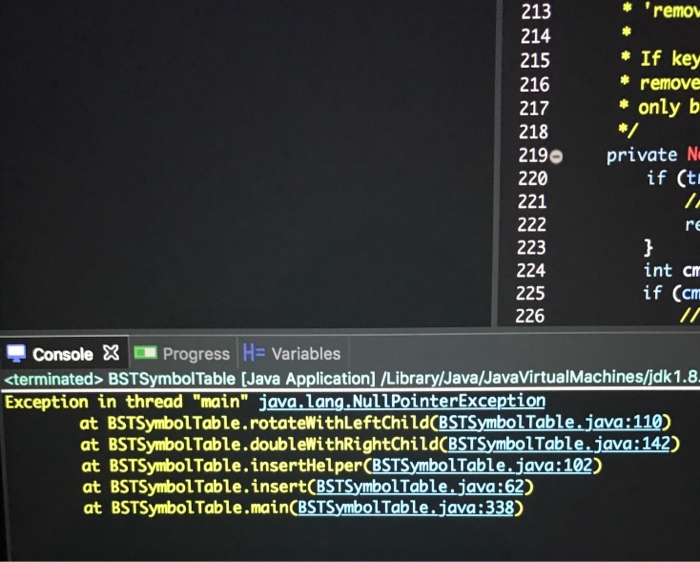
private Node insertHelper(Node tree, K key, V val) {
if (tree == null) {
// (sub-)tree is empty
return new Node(key, val);
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(tree.key);
if (cmp == 0) {
// we found the key
tree.key = key;
tree.val = val;
}
else if (cmp
// key
tree.left = insertHelper(tree.left, key, val);
if(height(tree.left)-height(tree.right)>=2)
if(cmp
tree = rotateWithLeftChild(tree);
else {
tree = doubleWithLeftChild(tree);
}
} else {
// key > tree.key
tree.right = insertHelper(tree.right, key, val);
if(height(tree.right)-height(tree.left)>=2)
if(cmp > tree.right.key.compareTo(key));
tree = rotateWithRightChild(tree);
tree = doubleWithRightChild(tree);
}
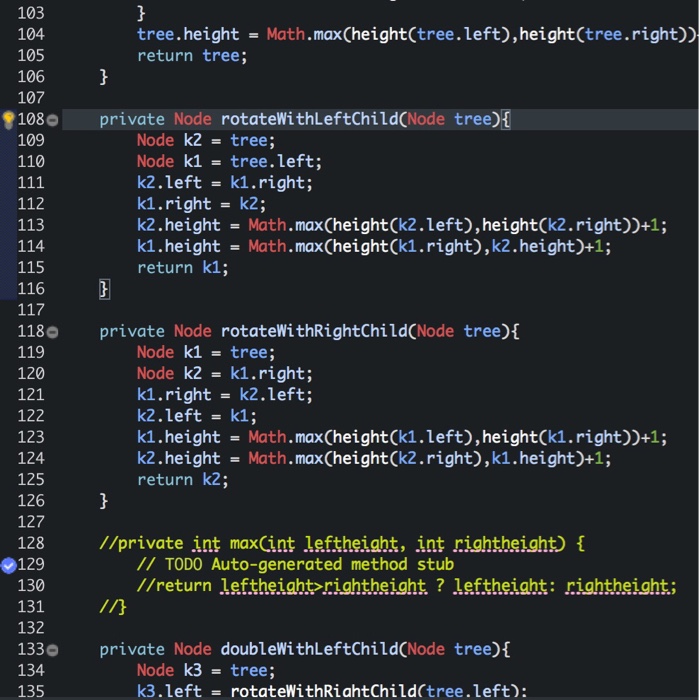
tree.height = Math.max(height(tree.left),height(tree.right))+1;
return tree;
}
private Node rotateWithLeftChild(Node tree){
Node k2 = tree;
Node k1 = tree.left;
k2.left = k1.right;
k1.right = k2;
k2.height = Math.max(height(k2.left),height(k2.right))+1;
k1.height = Math.max(height(k1.right),k2.height)+1;
return k1;
}
private Node rotateWithRightChild(Node tree){
Node k1 = tree;
Node k2 = k1.right;
k1.right = k2.left;
k2.left = k1;
k1.height = Math.max(height(k1.left),height(k1.right))+1;
k2.height = Math.max(height(k2.right),k1.height)+1;
return k2;
}
//private int max(int leftheight, int rightheight) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//return leftheight>rightheight ? leftheight: rightheight;
//}
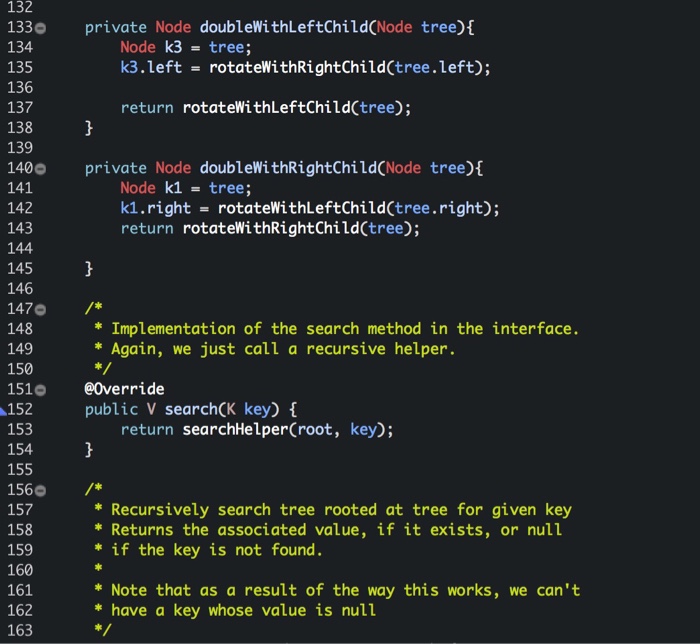
private Node doubleWithLeftChild(Node tree){
Node k3 = tree;
k3.left = rotateWithRightChild(tree.left);
return rotateWithLeftChild(tree);
}
private Node doubleWithRightChild(Node tree){
Node k1 = tree;
k1.right = rotateWithLeftChild(tree.right);
return rotateWithRightChild(tree);
}
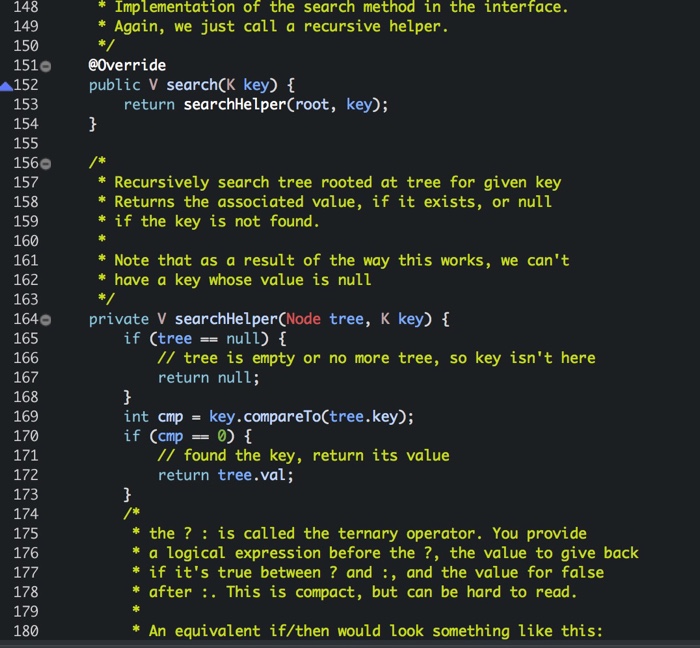
/*
* Implementation of the search method in the interface.
* Again, we just call a recursive helper.
*/
@Override
public V search(K key) {
return searchHelper(root, key);
}
/*
* Recursively search tree rooted at tree for given key
* Returns the associated value, if it exists, or null
* if the key is not found.
*
* Note that as a result of the way this works, we can't
* have a key whose value is null
*/
private V searchHelper(Node tree, K key) {
if (tree == null) {
// tree is empty or no more tree, so key isn't here
return null;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(tree.key);
if (cmp == 0) {
// found the key, return its value
return tree.val;
}
/*
* the ? : is called the ternary operator. You provide
* a logical expression before the ?, the value to give back
* if it's true between ? and :, and the value for false
* after :. This is compact, but can be hard to read.
*
* An equivalent if/then would look something like this:
* V ret;
* if(cmp
* ret = searchHelper(tree.left, key);
* }
* else {
* ret = searchHelper(tree.right, key);
* }
* return ret;
*/
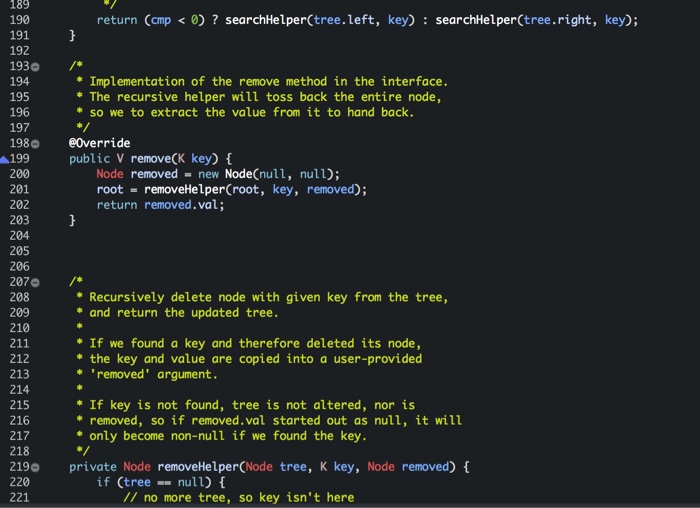
return (cmp
}
/*
* Implementation of the remove method in the interface.
* The recursive helper will toss back the entire node,
* so we to extract the value from it to hand back.
*/
@Override
public V remove(K key) {
Node removed = new Node(null, null);
root = removeHelper(root, key, removed);
return removed.val;
}
/*
* Recursively delete node with given key from the tree,
* and return the updated tree.
*
* If we found a key and therefore deleted its node,
* the key and value are copied into a user-provided
* 'removed' argument.
*
* If key is not found, tree is not altered, nor is
* removed, so if removed.val started out as null, it will
* only become non-null if we found the key.
*/
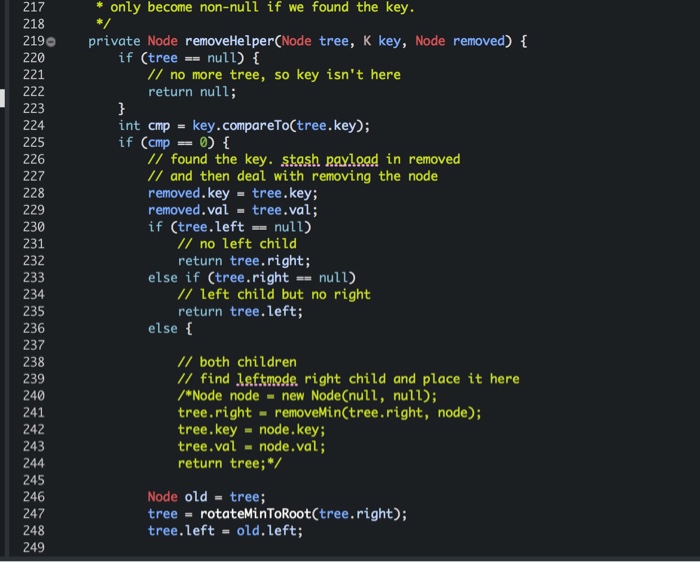
private Node removeHelper(Node tree, K key, Node removed) {
if (tree == null) {
// no more tree, so key isn't here
return null;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(tree.key);
if (cmp == 0) {
// found the key. stash payload in removed
// and then deal with removing the node
removed.key = tree.key;
removed.val = tree.val;
if (tree.left == null)
// no left child
return tree.right;
else if (tree.right == null)
// left child but no right
return tree.left;
else {
// both children
// find leftmode right child and place it here
/*Node node = new Node(null, null);
tree.right = removeMin(tree.right, node);
tree.key = node.key;
tree.val = node.val;
return tree;*/
Node old = tree;
tree = rotateMinToRoot(tree.right);
tree.left = old.left;
}
} else if (cmp
// key
tree.left = removeHelper(tree.left, key, removed);
} else {
// key > tree.key
tree.right = removeHelper(tree.right, key, removed);
}
return tree;
}
/*
* Helper to locate the smallest (leftmost) node
* in a tree and remove it, returning the updated tree.
* The key and value of the minimum node are passed back
* through a user-supplied 'min' argument.
*
* Note: requires tree != null
*/
private Node rotateMinToRoot(Node tree) {
if (tree.left != null) {
// found the minimum
tree.left = rotateMinToRoot(tree.left);
tree = rotateWithLeftChild(tree);
}
return tree;
}
/*
* This method is not part of the symbol table interface
* Instead, it lets us convert the BSTSymbolTable into a
* form that's easy to hand off for display.
* This works by traversing the tree (with a helper) and
* shoving information about its nodes into a vector we
* can pass off later.
*/
public Vector serialize() {
Vector vec = new Vector();
serializeHelper(root, vec);
return vec;
}
/*
* Perform a (recursive) pre-order traversal and
* store node information into a provided vector of strings.
* Note that we add ":black" to the end of the node's key.
* This is because the TreePrinter will happily work on
* Red-Black trees, where color is significant, so we fill
* in a default.
*/
private void serializeHelper(Node tree, Vector vec) {
if (tree == null)
vec.addElement(null);
else {
vec.addElement(tree.key.toString() + ":black");
serializeHelper(tree.left, vec);
serializeHelper(tree.right, vec);
}
}
/*
* This main provides a relatively simple test harness for
* the BSTSymbolTable, by randomly adding some nodes, removing
* a few, and then invoking the TreePrinter to get a picture
* of the tree.
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
/*
* Normally you'd probably want to use a SymbolTable on
* the left here, but because we want to use .serialize(),
* which is part of BSTSymbolTable but not SymbolTable, it's
* easier to just call it a BSTSymbolTable to begin with, rather
* than doing a cast.
*/
BSTSymbolTable symtab = new BSTSymbolTable();
/*
* This will insert 100 nodes with random values for us.
* We'll always get the same random sequence. If you want
* a different one, either remove the 1234, or replace it
* with something else.
*/
Random RNG = new Random(1234);
for (int i = 0; i
int r = (int) (RNG.nextDouble()*100);
symtab.insert(r,r);
}
// removing nodes using the SymbolTable interface.
symtab.remove(64);
symtab.remove(26);
symtab.remove(64);
/*
* this block interacts with the TreePrinter for us.
* First, we generate a vector of strings containing the
* serialized tree. Once that's done, use it to create
* a TreePrinter object, and then open a file and have
* the TreePrinter throw a picture of the tree into the file.
*
* If you're using Eclipse, tree.svg will end up in the project
* directory in your workspace. So, figure out where the source
* files are stored, and go up one from there.
*/
Vector st = symtab.serialize();
TreePrinter treePrinter = new TreePrinter(st);
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("tree.svg");
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(out);
treePrinter.printSVG(ps);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {}
}
}
public interface SymbolTable,V> {
void insert(K key, V val);
V search(K key);
V remove(K key);
}
import java.util.Vector; import java.io.*;
/** Class for pretty-printing binary trees using SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics). @author Wayne O. Cochran (wcochran@vancouver.wsu.edu) */ public class TreePrinter { private static class Node { public String str; public Node left, right; public int height; public float dx; public float x, y; public String color; public Node(String s, String c) { str = s; color = c; left = right = null; height = 0; dx = x = y = 0; } public Node(String s) {this(s, "purple");} } private Node root; private float[] xrange; private static class Scanner { private int next; private Vector vec; public Scanner(Vector serializedTree) { next = 0; vec = serializedTree; } public boolean hasNext() { return next
/** Constructor that loads a serialized tree for printing via the printSVG() method. Here is a code snippet that demonstrates how to serialize your trees so that they can be passed to this constructor.
private void serializeAux(Node tree, Vector vec) { if (tree == null) vec.addElement(null); else { vec.addElement(tree.key.toString() + ":black"); serializeAux(tree.left, vec); serializeAux(tree.right, vec); } }
public Vector serialize() { Vector vec = new Vector(); serializeAux(root, vec); return vec; }
@param serializedTree Binary tree that has been encoded into a vector of strings. */ public TreePrinter(Vector serializedTree) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(serializedTree); root = buildTree(scanner); childOffsets(root); xrange = new float[2]; assignCoordinates(root, 0, 0, xrange); } private static void rightContour(Node n, int y, float x, float contour[]) { if (n != null) { x += n.dx; if (x > contour[y]) contour[y] = x; rightContour(n.left, y+1, x, contour); rightContour(n.right, y+1, x, contour); } } private static void leftContour(Node n, int y, float x, float contour[]) { if (n != null) { x += n.dx; if (x
int lh = height(tree.left); float[] rcontour = new float[lh+1]; for (int i = 0; i
int rh = height(tree.right); float[] lcontour = new float[rh+1];; for (int i = 0; i
int yend = (lh
private void assignCoordinates(Node n, float x, float y, float[] xrange) { if (n != null) { n.x = x + n.dx; if (n.x xrange[1]) xrange[1] = n.x; n.y = y; assignCoordinates(n.left, n.x, y+1, xrange); assignCoordinates(n.right, n.x, y+1, xrange); } }
private void circleSVG(PrintStream stream, float x, float y, float radius, String color) { stream.println( " "\" stroke-width=\"3\" stroke=\"" + color + "\" fill=\"white\"/>"); }
private void lineSVG(PrintStream stream, float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, String color) { stream.println( " "\" style=\"stroke:" + color + ";stroke-width:3\"/>"); }
private void textSVG(PrintStream stream, float x, float y, int fontSize, String text) { stream.println( " "\" style=\"text-anchor: middle;dominant-baseline: central;\">" + text + ""); } void edgeSVG(PrintStream stream, float x0, float y0, float x1, float y1, float nodeRadius, String color) { float dx = x1 - x0; float dy = y1 - y0; float len =(float) Math.sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy); float u = dx/len; float v = dy/len; lineSVG(stream, x0 + nodeRadius*u, y0 + nodeRadius*v, x1 - nodeRadius*u, y1 - nodeRadius*v, color); } private void printSVG(PrintStream f, Node n, int fontSize, int nodeRadius, float scalex, float scaley, float dx, float dy) { if (n == null) return; float x = scalex*n.x + dx; float y = scaley*n.y + dy; // XXX String color = "black"; circleSVG(f, x, y, nodeRadius, n.color); textSVG(f, x, y, fontSize, n.str); if (n.left != null) { float x1 = scalex*n.left.x + dx; float y1 = scaley*n.left.y + dy; edgeSVG(f, x, y, x1, y1, nodeRadius, n.left.color); printSVG(f, n.left, fontSize, nodeRadius, scalex, scaley, dx, dy); } if (n.right != null) { float x1 = scalex*n.right.x + dx; float y1 = scaley*n.right.y + dy; edgeSVG(f, x, y, x1, y1, nodeRadius, n.right.color); printSVG(f, n.right, fontSize, nodeRadius, scalex, scaley, dx, dy); } }
/** Amount of border to place around resulting image. */ public float border = 30;
/** Horizontal scale factor. */ public float scalex = 20;
/** Vertical scale factor. */ public float scaley = 50;
/** Size of font to use for node strings. */ public int fontSize = 20;
/** Radius of circular nodes. */ public int nodeRadius = 14;
/** Prints SVG representation of tree to given stream. @param stream Output stream to print to. */ public void printSVG(PrintStream stream) {
float yshift = border; float xshift = -scalex*xrange[0] + border; int W = (int) (scalex*xrange[1] + xshift + border); int H = (int) (scaley*height(root) + yshift + border); stream.println( " " width=\"" + W + "\" height=\"" + H + "\">"); printSVG(stream, root, fontSize, nodeRadius, scalex, scaley, xshift, yshift); stream.println(" "); }
}
o import java.10.FiLeNotFoundException 8 public class implements SymbolTable
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


