Question: I have the problem below, and the code I have so far is this. Can someone help? #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std;
I have the problem below, and the code I have so far is this. Can someone help?
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//void accept(int intArray[], long int s);
//void display(int intArray[], long int s);
void bubbleSort(int intArray[], long int s);
void insertionSort(int intArray[], long int s);
//void ssort(int intArray[], long int s);
void quickSort(int intArray[], int low, long int high);
int partition(int intArray[], int low, long int high);
void swap(int* a, int* b);
void mergeSort(int *a, int low, long int high);
void merge(int *a, int low, long int high, long int mid);
void findMaxHeap(int a[], int i, long int n);
void heapSort(int a[], long int n);
//void generateMaxHeap(int a[], long int n);
/* Method to perform bubble sort */
void bubbleSort(int intArray[], long int s) {
int i, j, Temp;
for (i = 0; i
for (j = 0; j
if (intArray[j]>intArray[j + 1]) {
Temp = intArray[j];
intArray[j] = intArray[j + 1];
intArray[j + 1] = Temp;
}
}
}
/* Method to perform insertion sort */
void insertionSort(int intArray[], long int s){
int i, j;
int Temp;
for (i = 1; i
Temp = intArray[i];
j = i - 1;
while ((Temp
intArray[j + 1] = intArray[j];
j--;
}
intArray[j + 1] = Temp;
}
}
// Method to perform merge sort via merging divided array
void merge(int *a, int low, long int high, long int mid) {
long int i, j, k;
long int temp[10000000];
i = low;
k = 0;
j = mid + 1;
while (i
if (a[i]
temp[k] = a[i];
k++;
i++;
}
else {
temp[k] = a[j];
k++;
j++;
}
}
while (i
temp[k] = a[i];
k++;
i++;
}
while (j
temp[k] = a[j];
k++;
j++;
}
for (i = low; i
a[i] = temp[i - low];
}
}
// Mergesort method to divide array
void mergeSort(int *a, int low, long int high) {
long int mid;
if (low
mid = (low + high) / 2;
mergeSort(a, low, mid);
mergeSort(a, mid + 1, high);
merge(a, low, high, mid);
}
}
/* Partition function for quick sort */
int partition(int intArray[], int low, long int high){
int i, p;
int firsthigh = low;
p = high;
for (i = 1; i
if (intArray[i]
swap(&intArray[i], &intArray[firsthigh]);
firsthigh++;
}
swap(&intArray[p], &intArray[firsthigh]);
return firsthigh;
}
/* Method to swap positions */
void swap(int* a, int* b){
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
/*
int pivot = intArray[high];
int i = (low - 1);
for (int j = low; j
if (intArray[j]
i++;
swap(&intArray[i], &intArray[j]);
}
}
swap(&intArray[i + 1], &intArray[high]);
return (i + 1);
*/
/* Method to perform quick sort */
void quickSort(int intArray[], int low, int long high){
if (low
int part = partition(intArray, low, high);
quickSort(intArray, low, part - 1);
quickSort(intArray, part + 1, high);
}
}
/* Method to find max heap */
void findMaxHeap(int a[], int i, long int n){
long int j, temp;
temp = a[i];
j = 2 * i;
while (j
if (j a[j])
j = j + 1;
if (temp > a[j])
break;
else if (temp
a[j / 2] = a[j];
j = 2 * j;
}
}
a[j / 2] = temp;
return;
}
/* Method to perform heap sort */
void heapSort(int a[], long int n){
long int i, temp;
for (i = n; i >= 2; i--){
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[1];
a[1] = temp;
findMaxHeap(a, 1, i - 1);
}
}
/* Method to generate max heap */
/*void generateMaxHeap(int a[], long int n){
long int i;
for (i = n / 2; i >= 1; i--)
findMaxHeap(a, i, n);
}*/
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int a, i = 0;
long int n;
int *intArray;
string sortType, sortName;
string inputFileName, outputFileName;
sortType = argv[1];
inputFileName = argv[2];
outputFileName = argv[3];
cin >> sortType >> inputFileName>> outputFileName;
fstream inputFile(inputFileName);
inputFile >> n;
intArray = new int[n];
ofstream outputfile(outputFileName);
while (inputFile >> a) {
intArray[i] = a;
i++;
}
int start_s = clock();
if (sortType == "B") {
outputfile
sortName = "Bubble Sort";
}
else if (sortType == "I") {
insertionSort(intArray, n);
sortName = "Insertion Sort";
}
else if (sortType == "M") {
mergeSort(intArray, 0, n);
sortName = "Merge Sort";
}
else if (sortType == "H") {
heapSort(intArray, n - 1);
sortName = "Heap Sort";
}
else if (sortType == "Q") {
quickSort(intArray, 0, n);
sortName = "Quick Sort";
}
else {
cout
}
int stop_s = clock();
cout
return 0;
}
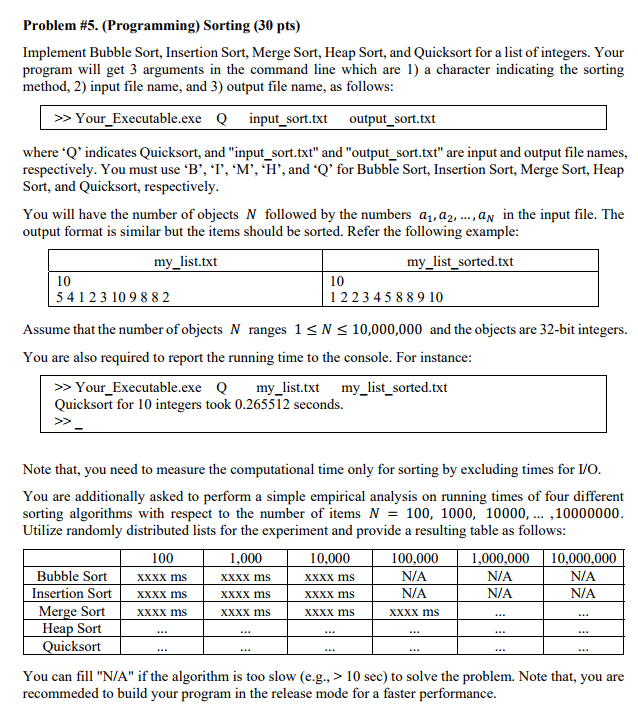
Problem #5. (Programming) Sorting (30 pts) Implement Bubble Sort, Insertion Sort, Merge Sort, Heap Sort, and Quicksort for a list of integers. Your program will get 3 arguments in the command line which are 1) a character indicating the sorting method, 2) input file name, and 3) output file name, as follows: >> Your_Executable.exe Qinput_sort.txt output_sort.txt where 'Q' indicates Quicksort, and "input_sort.txt" and "output_sort.txt" are input and output file names, respectively. You must use B', I', M", ,, and Q' for Bubble Sort, Insertion Sort, Merge Sort, Heap Sort, and Quicksort, respectively You will have the number of objects N followed by the numbers a,a2, .., av in the input file. The output format is similar but the items should be sorted. Refer the following example: my_list.txt my_list sorted.txt 10 1 223 45889 10 54123 10988 2 Assume that the number of objects N ranges 1sN 10,000,000 and the objects are 32-bit integers. You are also required to report the running time to the console. For instance >> Your_Executable.exe Qmy list.txt my list sorted.txt Quicksort for 10 integers took 0.265512 seconds. Note that, you need to measure the computational time only for sorting by excluding times for I/O. You are additionally asked to perform a simple empirical analysis on running times of four different sorting algorithms with respect to the number of items N = 100, 1000, 10000, 10000000 Utilize randomly distributed lists for the experiment and provide a resulting table as follows 100 1,000 Xxxx ms Xxxx ms XxxX ms 10,000 Xxxx ms Xxxx ms XxxX ms 100,000 N/A N/A 1,000,000 10,000,000 N/A NIA N/A N/A Bubble SorXxxx ms Insertion SortXxxx ms Merge Sort Heap Sort uicksort You can fill "N/A" if the algorithm is too slow (e.g., > 10 sec) to solve the problem. Note that, you are recommeded to build your program in the release mode for a faster performance
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


