Question: I NEED 5-17 here is problem 5-13 5.17 17. Suppose that in problem 13 a Type 2 service objective of 95 percent is substituted for
I NEED 5-17
here is problem 5-13

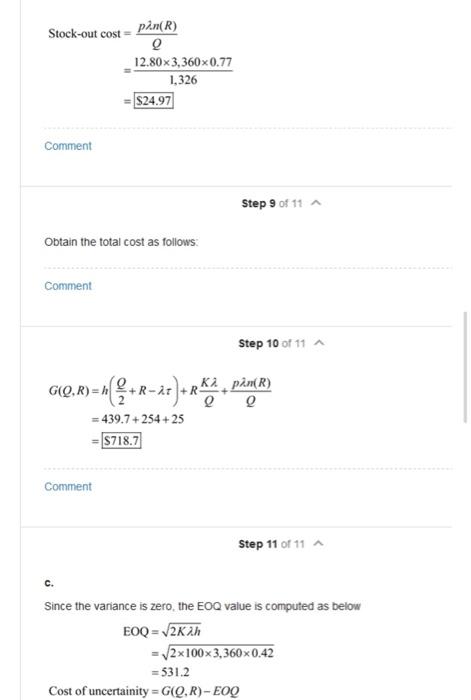

5.17 17. Suppose that in problem 13 a Type 2 service objective of 95 percent is substituted for the stock-out cost of $12.80. Find the resulting values of Q and R. Also, what is the imputed cost of shortage for this case? Here I have 5-13. 5-13. An automotive warehouse stocks a variety of parts that are sold at neighborhood stores. One particular part, a popular brand of oil filter, is purchased by the warehouse for $1.50 each. It is estimated that the cost of order processing and receipt is $100 per order. The company uses an inventory carrying charge based on a 28 percent annual interest rate. The monthly demand for the filter follows a normal distribution with mean 280 and standard deviation 77. Order lead time is assumed to be five months. Assume that if a filter is demanded when the warehouse is out of stock, then the demand is back ordered, and the cost assessed for each back-ordered demand is $12.80. Determine the following quantities. a. The optimal values of the order quantity and the reorder level. b. The average annual cost of holding, setup, and stock-out associated with this item assuming that an optimal policy is used. C. Evaluate the cost of uncertainty for this process. That is, compare the average annual cost you obtained in part (b) with the average annual cost that would be incurred if the lead time a. The optimal values of the order quantity and the reorder level. b. The average annual cost of holding, setup, and stock-out associated with this item assuming that an optimal policy is used. C. Evaluate the cost of uncertainty for this process. That is, compare the average annual cost you obtained in part (b) with the average annual cost that would be incurred if the lead time demand had zero variance. Lot size-reorder point system is one of the muti period models. This system is denoted by decision variables (QR). This multi period models are implemented when there is uncertain demand in inventory control However, in the simple EOQ model, demand is known and foed. But when the demand is random, these lot size-reorder point (0.) systems allow random demand There are two decision variables in a ( R) system Order quantity, and Reorder point, R The following costs are assumed in lot-size reordering Setup cost per order - K Holding costat per unit held per year h Proportional order cost of per item Stock - out cost per unit of unsatisfied demand =p lead time in a year mean lead - time demandu standard deviation of annual demand, standard deviation of leadtime-time demand=G, VE Service levels in (QR) systems Type 1 service: a Determine R to satisfy the equation F(a) = R-4 o b. Set QEOQ TYRE 2 service: Lot size-reorder point system is one of the multi period models. This system is denoted by decision variables (Q, R). This multi period models are implemented when there is uncertain demand in inventory control However, in the simple EOQ model, demand is known and faxed. But when the demand is random these lot size-reorder point [Q, R) systems allow random demand. There are two decision variables in a (Q.R) system Order quantity, Q and Reorder point, R The following costs are assumed in lot-size reordering Setup cost per order- Holding cost at per unit held per year = h Proportional order cost of per item=c Stock-out cost per unit of unsatisfied demand p lead time in a year mean lead-time demand uit standard deviation of annual demand = 0, standard deviation of leadtime - time demand = 6, Vt Service levels in (QR) systems Type 1 service: a Determine R to satisfy the equation F(a)=a. D Set Q=E0Q Type 2 service: (R) =1- Q (R) - EOQ(1-B) L(Z) =(1-B)Q/o R=0+ B = F(R) Consider the following information: Holding cost, h = $1.50x0.28 = $0.42 Setup cost, K = $100 Stock-out cost, p=$12.80 mean rate of demand, 2 = 280x12 = 3, 360 u=280x5 1,400 9, Vr = 77x5 = 172.17 Calculating optimal values of order quantity, considering 2001 and 2 until optimal value of reorder point is reached Iteration 1: E0Q-9,- 2K 2x100x 3,360 0.42 2. = 1,264.91 a 1,265 I-F(R)-ON p 1,265x0.42 12.803,360 =0.0123 Iteration 2 - = 2.24.L(3.) =0.004.1(R.) = 0.75 22 (K + pn[r)) 2x3,360 (100+12.80(0.75)) 0.42 =1.324.23 = 1,325 I-F(R.) OM pi 1,325 x 0.42 12.80 x 3,360 =0.012 Carrying the iteration one more step ahead Now, we have from above given formulas 3 = 2.23, L(5.)=0.0044,7(R) = 0.77 22 (K + p.(R)) 2x 3,360 (100+12.80(0.77) 0.42 Q = 1,325 23 2 1,326 As, both Q and R values are within one unit, we terminate the iteration R=0+ R=(172.17x2.23)+1400 Q 22 (K + p.n(R)) h 2x 3,360 (100+12.80(0.77)) 0.42 2 = 1,325.23 1,326 As, both Q and R values are within one unit, we terminate the iteration R= O2 + 1 R=(172.17X 2.23)+1400 R=1784 Therefore, the optimal (Q, R) = (1,326, 1,784). b. in the cost function, the average annual cost of holding is defined as below Holding cost = "+R-u) =0.42% (1,326 +1,784-1,400 439.7 Hence, the average cost holding is 718.7 Comments (3) Step 5 of 11 A Calculate the annual setup cost as follows: Comments (1) Step 6 of 11 A Setup cost K2 Q 100x 3,360 1,326 S253.4 Step 7 of 11 A Calculate the annual stock-out cost as follows: Stock-out cost = pan(R) 12.80X3,360x0.77 1,326 S24.97 Comment Step 9 of 11 Obtain the total cost as follows: Comment Step 10 of 11 A GIQ,R)="{$+R-27) +RK24 pn) 2 = 439.7 +254 +25 S718.7 Comment Step 11 of 11 A Since the variance is zero, the EOQ value is computed as below EOQ = 22h - 2x100x3,360x0.42 = 531.2 Cost of uncertainity = G(Q, R)- EOQ c. Since the variance is zero, the EOQ value is computed as below EOQ = V2K2h = 2x100x3,360x0.42 = 531.2 Cost of uncertainity = G(QR) - EOQ = 718.7 - 531.2 c. Since the variance is zero, the EOQ value is computed as below EOQ = V2Kih = /2x100x3, 360x0.42 = 531.2 Cost of uncertainity = G(Q,R) - EOQ = 718.7-531.2 =$187.5 per year Therefore, the cost of uncertainty for this process is $187.5













