Question: I need help with this. Submit an improved HashSet.java as described below (plus all the other extras you desire). The textbook provided Class for hashing
I need help with this.Submit an improved HashSet.java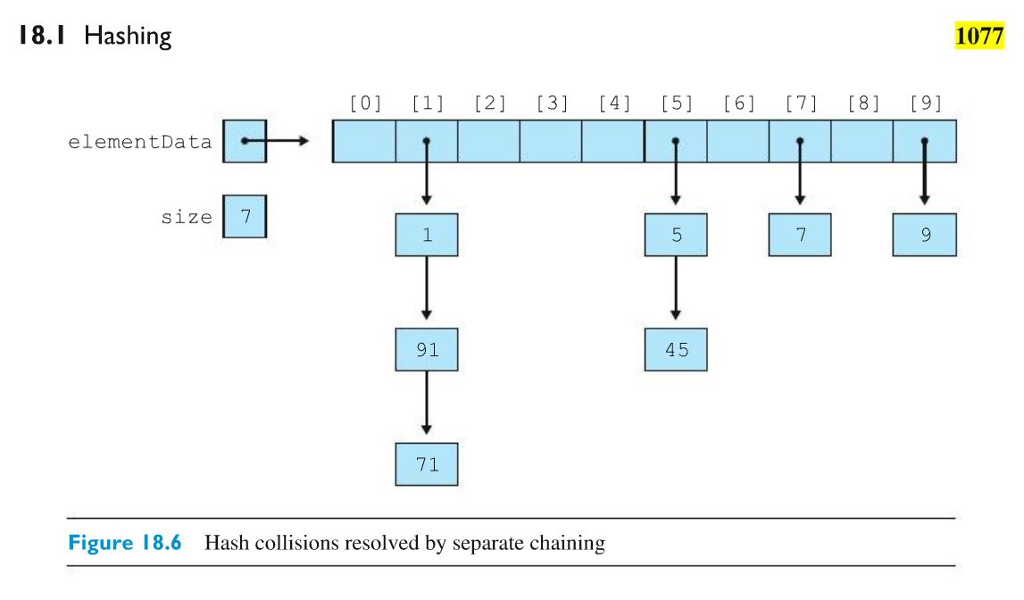 as described below (plus all the other extras you desire).
as described below (plus all the other extras you desire).
The textbook provided Class for hashing HashSet.java has a toString() that does NOT display the true structure of the Set.
Alternatively, I'd like to see what the author shows in our textbook:
Write a method (or more) in the provided HashSet.java that is called .toString2() which provides a String return that will print similar to above display. This means your return String will need spaces and line feeds to achieve the desired result. Keep your data left-justified under each index, and assume a fixed spacing of 10 char is enough for the display of each piece of data.
For the example shown above {1,91,71,5,45,7,9} has seven pieces of data, so adding a couple more elements will force it to re-hash and create a very different output.
public class HashSet {
private static final double MAX_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75;
private HashEntry[] elementData;
private int size;
// Constructs an empty set.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public HashSet() {
elementData = new HashEntry[10];
size = 0;
}
// ADD METHODS HERE for exercise solutions:
// Adds the given element to this set, if it was not already
// contained in the set.
public void add(E value) {
if (!contains(value)) {
if (loadFactor() >= MAX_LOAD_FACTOR) {
rehash();
}
// insert new value at front of list
int bucket = hashFunction(value);
elementData[bucket] = new HashEntry(value, elementData[bucket]);
size++;
}
}
// Removes all elements from the set.
public void clear() {
for (int i = 0; i
elementData[i] = null;
}
size = 0;
}
// Returns true if the given value is found in this set.
public boolean contains(E value) {
int bucket = hashFunction(value);
HashEntry current = elementData[bucket];
while (current != null) {
if (current.data.equals(value)) {
return true;
}
current = current.next;
}
return false;
}
// Returns true if there are no elements in this queue.
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// Removes the given value if it is contained in the set.
// If the set does not contain the value, has no effect.
public void remove(E value) {
int bucket = hashFunction(value);
if (elementData[bucket] != null) {
// check front of list
if (elementData[bucket].data.equals(value)) {
elementData[bucket] = elementData[bucket].next;
size--;
} else {
// check rest of list
HashEntry current = elementData[bucket];
while (current.next != null && !current.next.data.equals(value)) {
current = current.next;
}
// if the element is found, remove it
if (current.next != null && current.next.data.equals(value)) {
current.next = current.next.next;
size--;
}
}
}
}
// Returns the number of elements in the queue.
public int size() {
return size;
}
// Returns a string representation of this queue, such as "[10, 20, 30]";
// The elements are not guaranteed to be listed in sorted order.
public String toString() {
String result = "[";
boolean first = true;
if (!isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 0; i
HashEntry current = elementData[i];
while (current != null) {
if (!first) {
result += ", ";
}
result += current.data;
first = false;
current = current.next;
}
}
}
return result + "]";
}
// Returns the preferred hash bucket index for the given value.
private int hashFunction(E value) {
return Math.abs(value.hashCode()) % elementData.length;
}
private double loadFactor() {
return (double) size / elementData.length;
}
// Resizes the hash table to twice its former size.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void rehash() {
// replace element data array with a larger empty version
HashEntry[] oldElementData = elementData;
elementData = new HashEntry[2 * oldElementData.length];
size = 0;
// re-add all of the old data into the new array
for (int i = 0; i
HashEntry current = oldElementData[i];
while (current != null) {
add((E)current.data);
current = current.next;
}
}
}
// Represents a single value in a chain stored in one hash bucket.
@SuppressWarnings("hiding")
private class HashEntry {
public E data;
public HashEntry next;
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public HashEntry(E data) {
this(data, null);
}
public HashEntry(E data, HashEntry next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
I 8.I Hashing 1077 [0] [1] [2] 3 4 [5] [6] 7 [8] [9] element Data size 7 91 71 Figure 18.6 Hash collisions resolved by separate chaining I 8.I Hashing 1077 [0] [1] [2] 3 4 [5] [6] 7 [8] [9] element Data size 7 91 71 Figure 18.6 Hash collisions resolved by separate chainingStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


