Question: I need help with writing a code to solve these using python. Thank you. Data is given below. Here are the data for co2Cp.csv that
I need help with writing a code to solve these using python. Thank you. Data is given below.
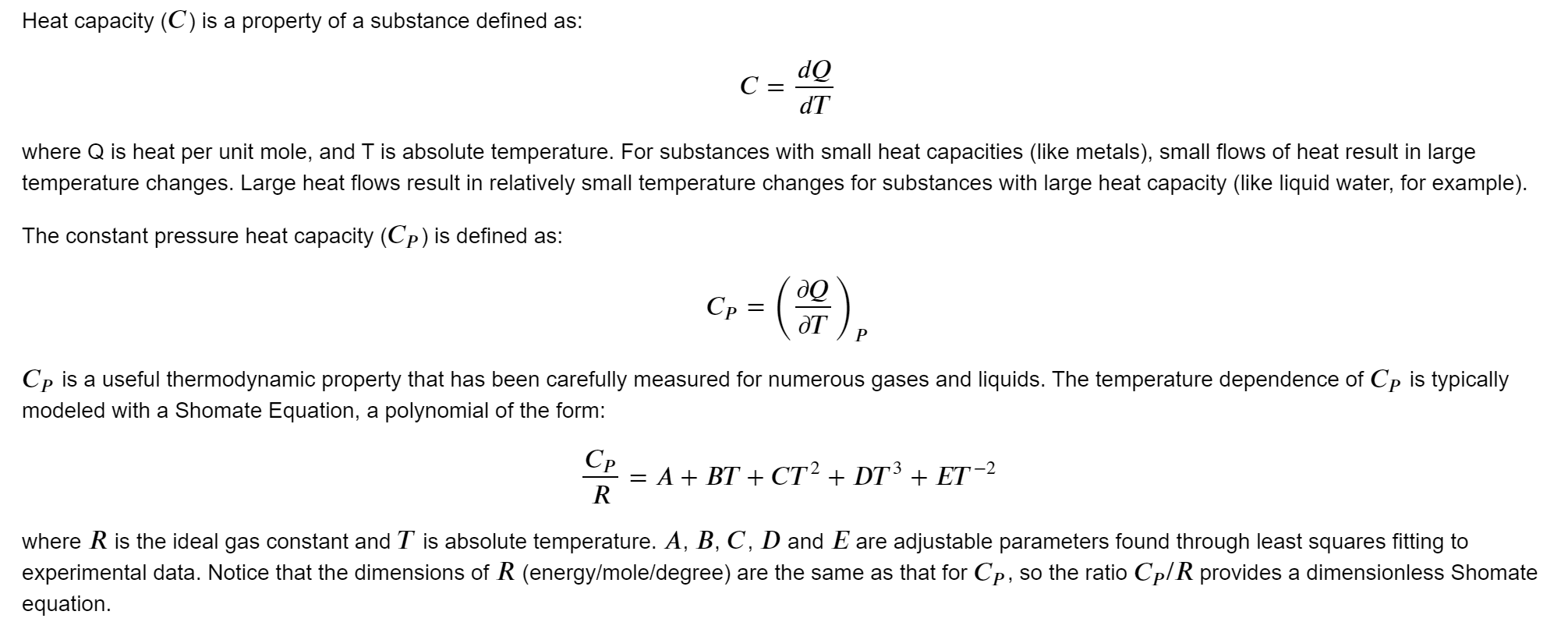

Here are the data for "co2Cp.csv" that you can paste in excel. Thanks.
| T (Kelvin) | Cp (J/mol K) |
| 298.15 | 37.129 |
| 300 | 37.221 |
| 400 | 41.325 |
| 500 | 44.627 |
| 600 | 47.321 |
| 700 | 49.564 |
| 800 | 51.434 |
| 900 | 52.999 |
| 1000 | 54.308 |
| 1100 | 55.409 |
| 1200 | 56.342 |
| 1300 | 57.137 |
| 1400 | 57.802 |
| 1500 | 58.379 |
| 1600 | 58.886 |
| 1700 | 59.317 |
| 1800 | 59.701 |
| 1900 | 60.049 |
| 2000 | 60.35 |
| 2100 | 60.622 |
| 2200 | 60.865 |
| 2300 | 61.086 |
| 2400 | 61.287 |
| 2500 | 61.471 |
| 2600 | 61.647 |
| 2700 | 61.802 |
| 2800 | 61.952 |
| 2900 | 62.095 |
| 3000 | 62.229 |
| 3100 | 62.347 |
| 3200 | 62.462 |
| 3300 | 62.573 |
| 3400 | 62.681 |
| 3500 | 62.785 |
| 3600 | 62.884 |
| 3700 | 62.98 |
| 3800 | 63.074 |
| 3900 | 63.166 |
| 4000 | 63.254 |
| 4100 | 63.341 |
| 4200 | 63.426 |
| 4300 | 63.509 |
| 4400 | 63.588 |
| 4500 | 63.667 |
| 4600 | 63.745 |
| 4700 | 63.823 |
| 4800 | 63.893 |
| 4900 | 63.968 |
| 5000 | 64.046 |
| 5100 | 64.128 |
| 5200 | 64.22 |
| 5300 | 64.312 |
| 5400 | 64.404 |
| 5500 | 64.496 |
| 5600 | 64.588 |
| 5700 | 64.68 |
| 5800 | 64.772 |
| 5900 | 64.865 |
| 6000 | 64.957 |
Heat capacity (C) is a property of a substance defined as: dQ C= d where Q is heat per unit mole, and T is absolute temperature. For substances with small heat capacities (like metals), small flows of heat result in large temperature changes. Large heat flows result in relatively small temperature changes for substances with large heat capacity (like liquid water, for example). The constant pressure heat capacity (Cp) is defined as: Q Cp = OT P Cp is a useful thermodynamic property that has been carefully measured for numerous gases and liquids. The temperature dependence of Cp is typically modeled with a Shomate Equation, a polynomial of the form: Cp = A + BT + CT2 + DT3 + ET-2 R where R is the ideal gas constant and T is absolute temperature. A, B, C, D and E are adjustable parameters found through least squares fitting to experimental data. Notice that the dimensions of R (energy/mole/degree) are the same as that for Cp, so the ratio Cp/R provides a dimensionless Shomate equation. Problem 4 The data file "co2Cp.csv" contains values for Cp of carbon dioxide measured at various temperatures at a fixed pressure of 1 bar. The first column is the measured heat capacity in units of Joules/mole/Kelvin. The second column is the absolute temperature in Kelvin. The Shomate equation does not fit carbon dioxide over the entire temperature range as it did for methane in the previous problem. The proposed solution is to divide the data into two temperature ranges: (1) T1200 K, then fit the Shomate equation to each of the two temperature ranges. Calculate the root mean square percent error in predicting Cp/R when using a single Shomate equation fit over the entire temperature range compared to that obtained by splitting into two temperature ranges and fitting each range separately. The root mean square percent error is defined as: 1/2 error i=1 RMSE = 11 where n is the number of data points over the entire temperature range. The perecent error (called "error" here) is defined for each data point as described above In [ ]: N Problem 5 Using data from the previous problem, plot the percent error in predicted Cp/R values obtained by fitting a single equation over the entire temperature range compared to that obtained by splitting the data into two ranges for fitting. In [ ]: Heat capacity (C) is a property of a substance defined as: dQ C= d where Q is heat per unit mole, and T is absolute temperature. For substances with small heat capacities (like metals), small flows of heat result in large temperature changes. Large heat flows result in relatively small temperature changes for substances with large heat capacity (like liquid water, for example). The constant pressure heat capacity (Cp) is defined as: Q Cp = OT P Cp is a useful thermodynamic property that has been carefully measured for numerous gases and liquids. The temperature dependence of Cp is typically modeled with a Shomate Equation, a polynomial of the form: Cp = A + BT + CT2 + DT3 + ET-2 R where R is the ideal gas constant and T is absolute temperature. A, B, C, D and E are adjustable parameters found through least squares fitting to experimental data. Notice that the dimensions of R (energy/mole/degree) are the same as that for Cp, so the ratio Cp/R provides a dimensionless Shomate equation. Problem 4 The data file "co2Cp.csv" contains values for Cp of carbon dioxide measured at various temperatures at a fixed pressure of 1 bar. The first column is the measured heat capacity in units of Joules/mole/Kelvin. The second column is the absolute temperature in Kelvin. The Shomate equation does not fit carbon dioxide over the entire temperature range as it did for methane in the previous problem. The proposed solution is to divide the data into two temperature ranges: (1) T1200 K, then fit the Shomate equation to each of the two temperature ranges. Calculate the root mean square percent error in predicting Cp/R when using a single Shomate equation fit over the entire temperature range compared to that obtained by splitting into two temperature ranges and fitting each range separately. The root mean square percent error is defined as: 1/2 error i=1 RMSE = 11 where n is the number of data points over the entire temperature range. The perecent error (called "error" here) is defined for each data point as described above In [ ]: N Problem 5 Using data from the previous problem, plot the percent error in predicted Cp/R values obtained by fitting a single equation over the entire temperature range compared to that obtained by splitting the data into two ranges for fitting. In [ ]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


