Question: I Need my code to accept lower case letters as it states in level 1: so if 'i' is entered then it will output 1.
I Need my code to accept lower case letters as it states in level 1: so if 'i' is entered then it will output 1.

#include
#include
using namespace std;
int value(char r){
if (r == 'I') return 1; if (r == 'V') return 5; if (r == 'X') return 10; if (r == 'L') return 50; if (r == 'C') return 100; if (r == 'D') return 500; if (r == 'M') return 1000; return -1; }
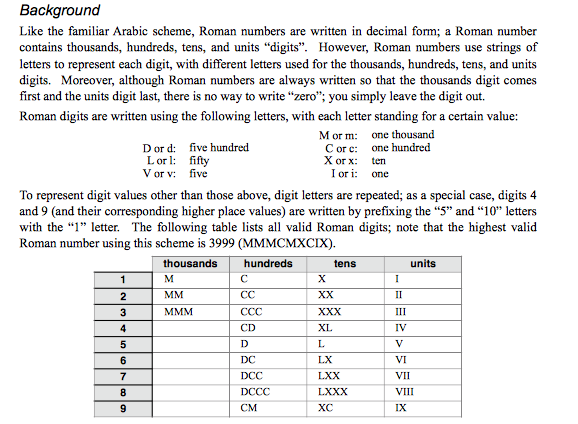
int romantoArabic(string &str){ int res = 0; for (int i=0; i int s1 = value(str[i]); if (i+1 int s2 = value(str[i+1]); if (s1 >= s2) { res = res + s1; } else { res = res + s2 - s1; i++; // Value of current symbol is } } else { res = res + s1; i++; } } return res; } int main(){ string str; cout>str; cout Background Like the familiar Arabic scheme, Roman numbers are written in decimal form; a Roman number contains thousands, hundreds, tens, and units "digits". However, Roman numbers use strings of letters to represent each digit, with different letters used for the thousands, hundreds, tens, and units digits. Moreover, although Roman numbers are always written so that the thousands digit comes first and the units digit last, there is no way to write "zero"; you simply leave the digit out. Roman digits are written using the following letters, with each letter standing for a certain value: one thousand one hundred M orm: D or d: five hundred Corc: Xorx ten L or fifty Vorv five I ori one To represent digit values other than those above, digit letters are repeated; as a special case, digits 4 and 9 (and their corresponding higher place values) are written by prefixing the "5" and "10" letters with the "1" letter. The following table lists all valid Roman digits; note that the highest valid Roman number using this scheme is 3999 (MMMCMXCIX). thousands hundreds units IV L. 6 DC VII VIII IX DCCC Xc
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


