Question: I need the code for counting_queue_getitem(self,n) and it must follow the exact parameters. It must pass the tests given. def counting_queue_getitem(self, n): ### YOUR CODE
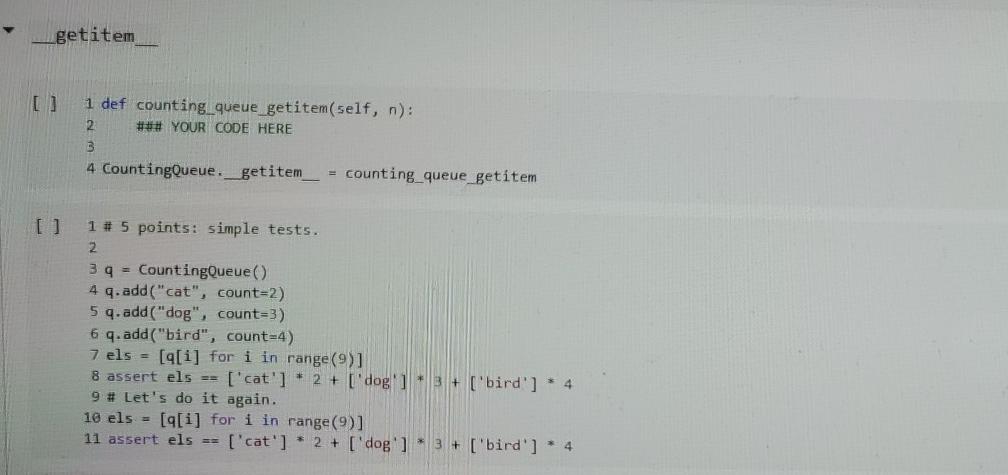
I need the code for counting_queue_getitem(self,n) and it must follow the exact parameters. It must pass the tests given.
def counting_queue_getitem(self, n):
### YOUR CODE HERE
CountingQueue.__getitem__ = counting_queue_getitem
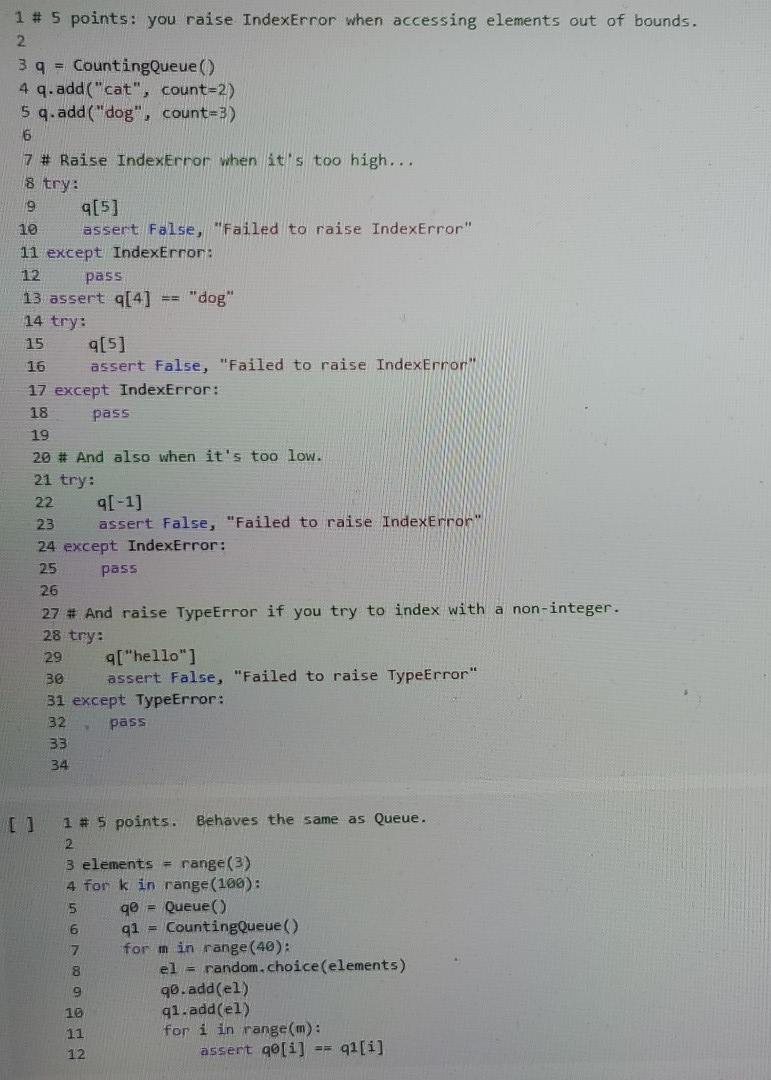
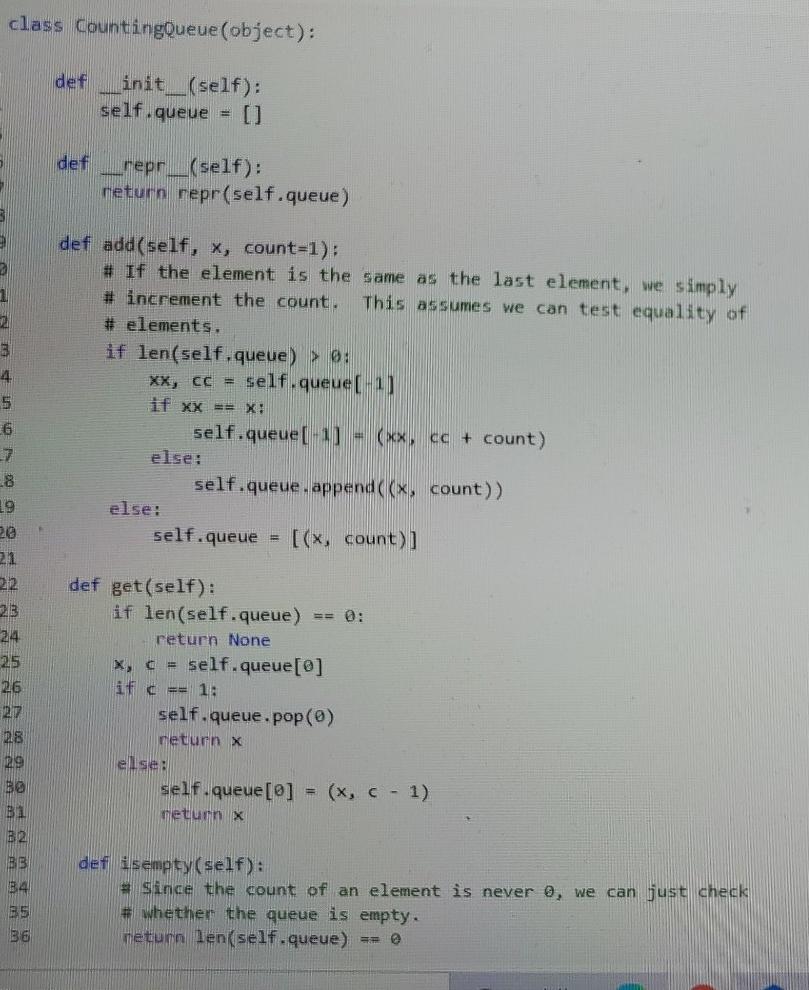
getitem 1 def counting queue getitem(self, n): 2 ### YOUR CODE HERE 3 4 CountingQueue._getitem = counting queue getitem [] 1 # 5 points: simple tests. 2 3 4 = CountingQueue () 4 q.add("cat", count=2) 5 q.add("dog", count=3) 6 q.add("bird", count=4) 7 els = [q[i] for i in range (9) 8 assert els == ['cat'] * 2+ ['dog'] + 3 + ['bird'] * 4 9 # Let's do it again. 10 els = [[i] for i in range (9)] 11 assert els == ['cat'] + 2 + ['dog'] * 3+ ['bird'] + 4 1 # 5 points: you raise IndexError when accessing elements out of bounds. 2 3 9 = CountingQueue 4 q.add("cat", count=2) 5 q.add("dog", count=3) 6 7 # Raise IndexError when it's too high... 8 try: 9 9[5] 10 assert False, "Failed to raise IndexError" 11 except IndexError: 12 pass 13 assert q[4] == "dog" 14 try: 15 9[5] 16 assert False, "Failed to raise IndexError 17 except IndexError: 18 pass 19 20 # And also when it's too low. 21 try: 22 9[-1] 23 assert False, "Failed to raise IndexError 24 except IndexError: 25 pass 26 27 # And raise TypeError if you try to index with a non-integer. 28 try: 29 9["hello"] BO assert False, "Failed to raise TypeError" 31 except TypeError: 32 pass 33 34 1 # 5 points. Behaves the same as Queue. 2 3 elements = range (3) 4 for k in range (100): 5 90 = Queue 6 q1 = CountingQueue () 7 for min range (40): 8 el = random.choice(elements) 9 90.add(el) 10 qi.add(el) 11 for i in range(m): assert q[1] 91[1] 12 class countingQueue (object): det ___init__(self): self.queue = 0) def repr__(self): return repr(self.queue) 3 3 1 2 3 4 5 def add(self, x, count=1); # If the element is the same as the last element, we simply # increment the count. This assumes we can test equality of # elements. if len(self.queue) > 0: XX, cc = self.queue(-1) if xx == X: self.queue[-1) = (xx, ce + count) else: self.queue.append((x, count)) else: self.queue [(x, count)) 6 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 def get(self): if len(self.queue) return None x, c = self.queue[@] if c == 1: self.queue.pop() return x else: self.queue[] (x, c - 1) eturn x 327 28 29 BO B1 B2 BB B4 35 36 def isempty(self): # Since the count of an element is never , we can just check # whether the queue is empty. return len(self.queue) -- @
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


