Question: I only need help with questions B, C, D, and E - all highlighted in yellow. I have already solved question A on my own.
I only need help with questions B, C, D, and E - all highlighted in yellow. I have already solved question A on my own.
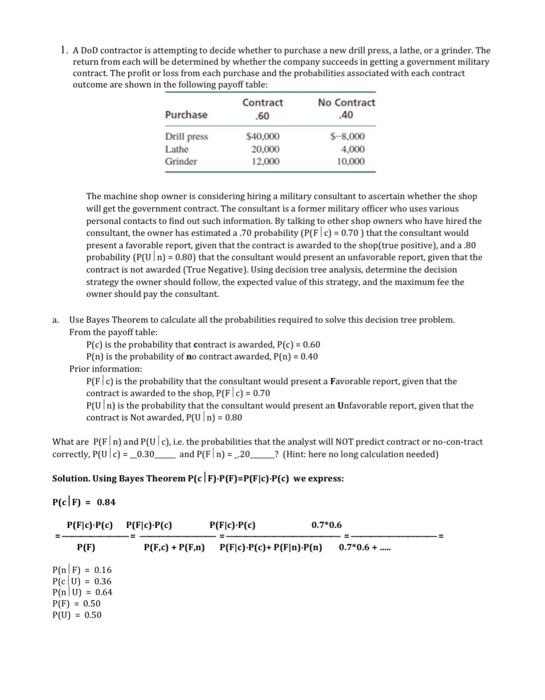
1. A DoD contractor is attempting to decide whether to purchase a new drill press, a lathe, or a grinder. The return from each will be determined by whether the company succeeds in getting a government military contract. The profit or loss from each purchase and the probabilities associated with each contract outcome are shown in the following payoff table: Contract No Contract Purchase .60 40 Drill press S40,000 5-8,000 Lathe 20.000 4,000 Grinder 12.000 10,000 The machine shop owner is considering hiring a military consultant to ascertain whether the shop will get the government contract. The consultant is a former military officer who uses various personal contacts to find out such information. By talking to other shop owners who have hired the consultant, the owner has estimated a 70 probability (P(F c) = 0.70 ) that the consultant would present a favorable report, given that the contract is awarded to the shop(true positive), and a 80 probability (P(uln) = 0.80) that the consultant would present an unfavorable report, given that the contract is not awarded (True Negative). Using decision tree analysis, determine the decision strategy the owner should follow the expected value of this strategy, and the maximum fee the owner should pay the consultant. Use Bayes Theorem to calculate all the probabilities required to solve this decision tree problem. From the payoff table: PCC) is the probability that contract is awarded, PCC) = 0.60 P[n) is the probability of no contract awarded, P(n) = 0.40 Prior information: P(Fle) is the probability that the consultant would present a Favorable report, given that the contract is awarded to the shop, P(FIC) = 0.70 P(Uin) is the probability that the consultant would present an Unfavorable report, given that the contract is Not awarded PU In) = 0.80 What are P(Fin) and P(UIC), ie the probabilities that the analyst will NOT predict contract or no-con-tract correctly. PU1C) = _0.30_ and P(Fin) =_20__? (Hint: here no long calculation needed) Solution. Using Bayes Theorem P(c|F)-P(F)=P(FIC)-P(c) we express: Pe | F) = 0.84 P(FIC)-PC) P(Fe)-PC) P(FIC)-PCC) 0.7*0.6 P(F) P(5.c) + P(F.) P(FIC)-P(c)+ P(F]n)-P(n) 0.7*0.6 + P(nF) = 0.16 PC U) - 0.36 P[n U) = 0.64 P(F) = 0.50 PU) 0.50 b. With these probabilities, create and draw a decision tree for this problem. Follow discussion and example we went over in class on Thursday, c. Should the owner of the shop hire the military consultant? (ie the value of consultants expertise worth $ 17,500). d. What is the maximum amount that the owner would be willing to pay to the consultant for the expert advice? e. What is the efficiency of the sample information