Question: I will give thumb up Problem 1: (2 pts) Using LaTeX, typeset the analytic solution to the geometric growth model (model introduced in lecture 4,
I will give thumb up

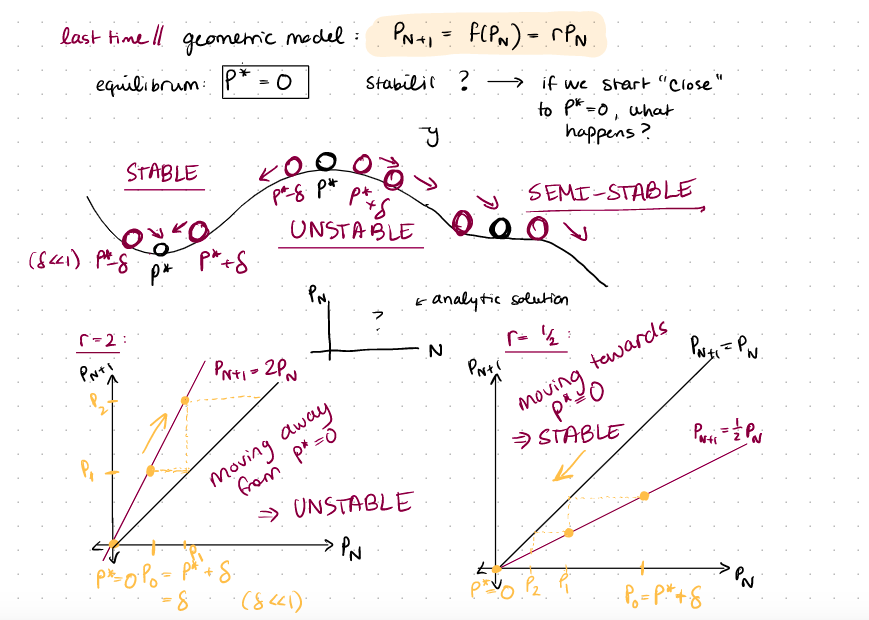
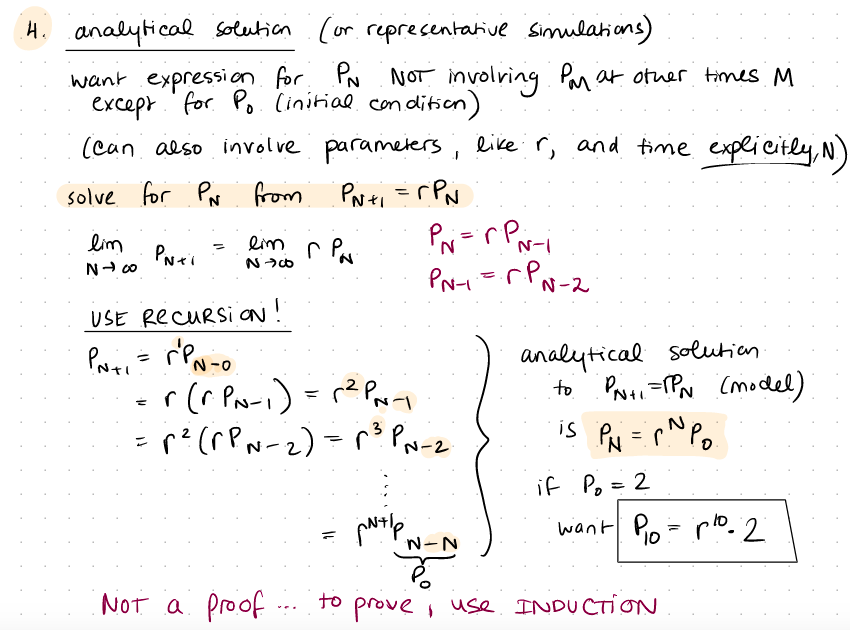
Problem 1: (2 pts) Using LaTeX, typeset the analytic solution to the geometric growth model (model introduced in lecture 4, analytic solution discussed in lecture 5). Be sure to execute the cell so that the LaTeX typesetting actually displays nicely, instead of showing the LaTeX syntax. last timell geometric model: PN+1 = F(PN) = NPN equilibrum P* - stabilic ? if we start "Close" to P*=o, what y happens? STABLE SEMI-STABLE ONSTABLE (841) pts P*+S Kanalytic solution K od -8 * P+ p* Pri = 2: rah N PNE=PN PNTI Prti = 2PN Poti tewards movimento > STABLE Parti a moving away > UNSTABLE + PN .p*o po- pt + S = 8 :(821) PP2 . Po=P*+8 H. analytical solution (or representative Simulations) want expression for Pa NOT involving Par at other times M except for Po. Cinitial condition) (can also involve parameters, liker, and time explicitly, N.) solve for PN from from PNti = RPN lim N00 = PN=rp Puti lim r Par N- N 00 = 3 PN-1=0.PN-2 USE Recursia! Poti = rpno analytical solution r(0.PN-1) = PPori to : Priti =PN (model) :r? (FPN-2) = r PN-2 is PM = PNP if .Po=2 want Pio plo. 2 Po Not a proof to prove use INDUCTION Antip W-N
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


