Question: Implement a detect motion class for python Question 3: Build the class MotionDetection. 1 ### Question 3: Implement the MotionDetection class 3 class MotionDetection(object): def
Implement a detect motion class for python
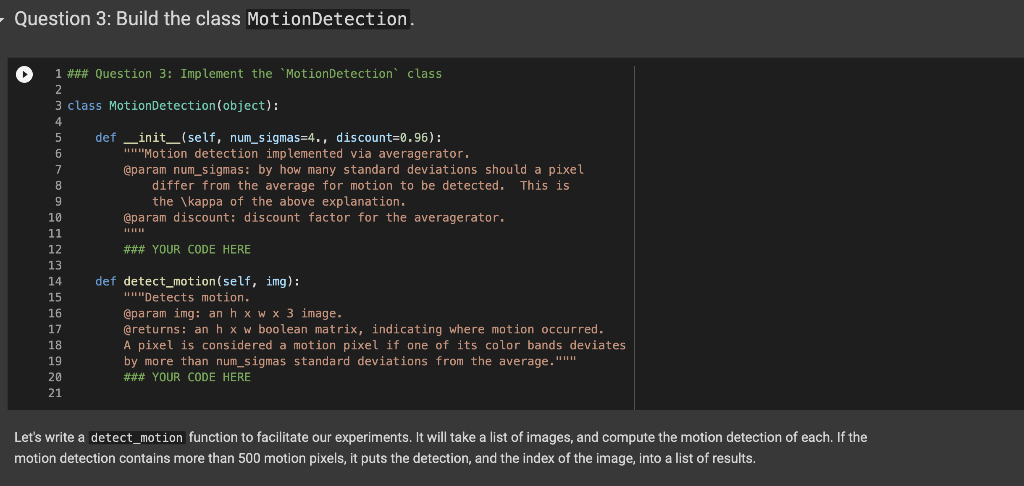
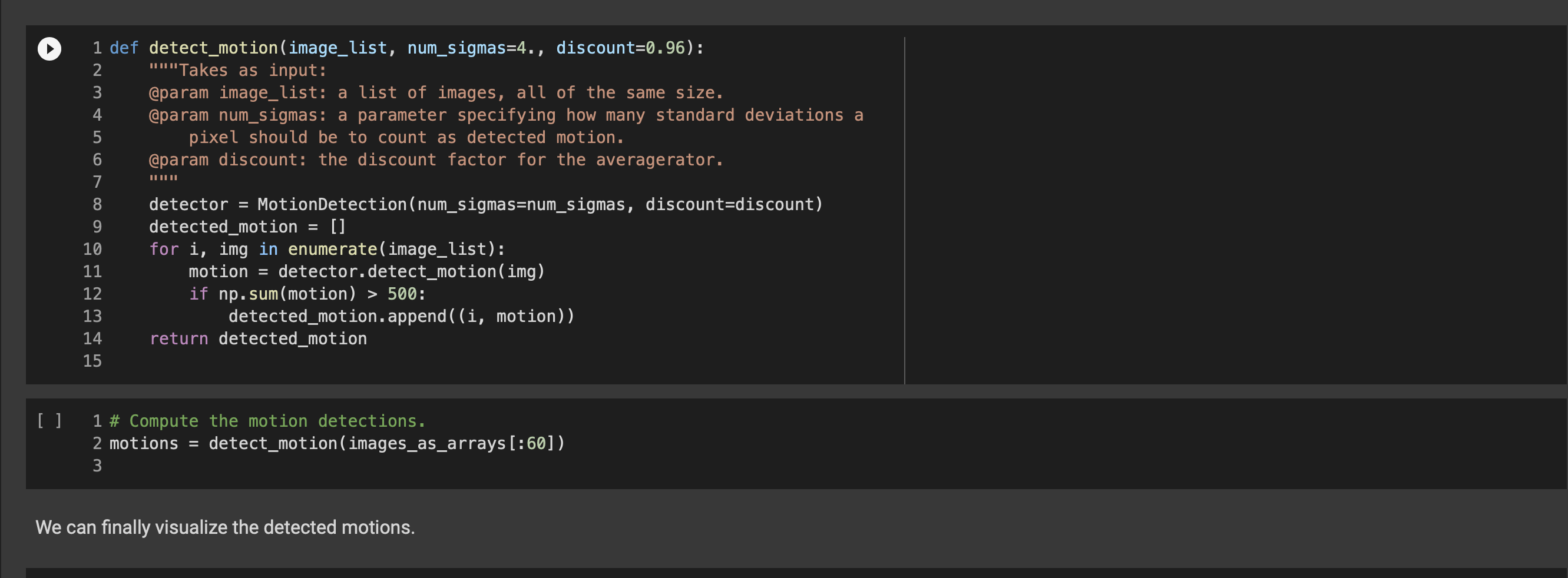
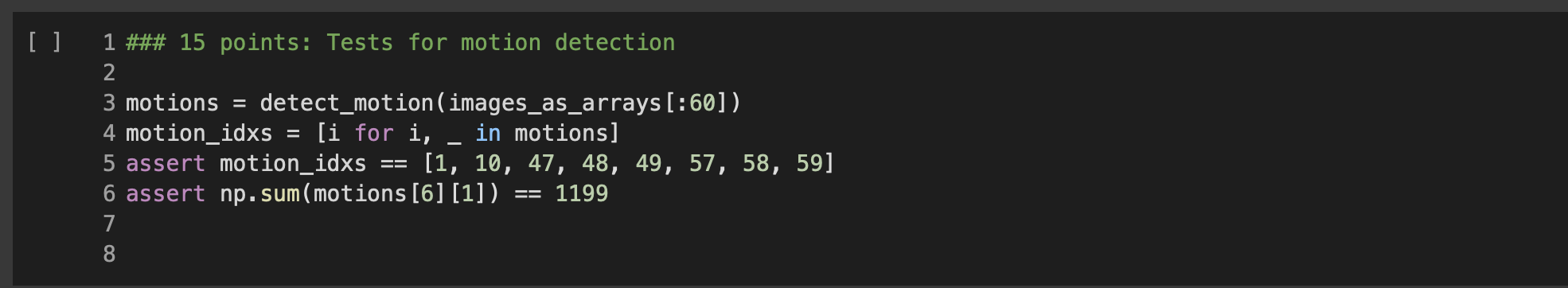
Question 3: Build the class MotionDetection. 1 ### Question 3: Implement the "MotionDetection class 3 class MotionDetection(object): def _init__(self, num_sigmas=4., discount=0.96): Motion detection implemented via averagerator. @param num_sigmas: by how many standard deviations should a pixel differ from the average for motion to be detected. This is the \kappa of the above explanation. @param discount: discount factor for the averagerator. ### YOUR CODE HERE 10 11 12 12 13 15 14 15 15 16 16 17 17 18 19 20 21 def detect_motion(self, img): "Detects motion. @param img: an h x w x 3 image. @returns: an hxw boolean matrix, indicating where motion occurred. A pixel is considered a motion pixel if one of its color bands deviates by more than num_sigmas standard deviations from the average." ### YOUR CODE HERE Let's write a detect_motion function to facilitate our experiments. It will take a list of images, and compute the motion detection of each. If the motion detection contains more than 500 motion pixels, it puts the detection, and the index of the image, into a list of results. 0 0 + WN 1 def detect_motion(image_list, num_sigmas=4., discount=0.96): 2 ""Takes as input: 3 @param image_list: a list of images, all of the same size. 4 @param num_sigmas: a parameter specifying how many standard deviations a 5 pixel should be to count as detected motion. 6 @param discount: the discount factor for the averagerator. 7 8 detector MotionDetection (num_sigmas=num_sigmas, discount=discount) 9 detected_motion = [] 10 for i, img in enumerate(image_list): 11 motion detector.detect_motion(img) 12 if np. sum(motion) > 500: 13 detected_motion.append((i, motion)) 14 return detected_motion 15 [] 1 # Compute the motion detections. 2 motions = detect_motion(images_as_arrays [:60]) 3 We can finally visualize the detected motions. [] 1 ### 15 points: Tests for motion detection 2 3 motions = detect_motion(images_as_arrays [:60]) 4 motion_idxs = [i for i, in motions] 5 assert motion_idxs [1, 10, 47, 48, 49, 57, 58, 59] 6 assert np. sum(motions [6] [1]) 1199 == 8 Question 3: Build the class MotionDetection. 1 ### Question 3: Implement the "MotionDetection class 3 class MotionDetection(object): def _init__(self, num_sigmas=4., discount=0.96): Motion detection implemented via averagerator. @param num_sigmas: by how many standard deviations should a pixel differ from the average for motion to be detected. This is the \kappa of the above explanation. @param discount: discount factor for the averagerator. ### YOUR CODE HERE 10 11 12 12 13 15 14 15 15 16 16 17 17 18 19 20 21 def detect_motion(self, img): "Detects motion. @param img: an h x w x 3 image. @returns: an hxw boolean matrix, indicating where motion occurred. A pixel is considered a motion pixel if one of its color bands deviates by more than num_sigmas standard deviations from the average." ### YOUR CODE HERE Let's write a detect_motion function to facilitate our experiments. It will take a list of images, and compute the motion detection of each. If the motion detection contains more than 500 motion pixels, it puts the detection, and the index of the image, into a list of results. 0 0 + WN 1 def detect_motion(image_list, num_sigmas=4., discount=0.96): 2 ""Takes as input: 3 @param image_list: a list of images, all of the same size. 4 @param num_sigmas: a parameter specifying how many standard deviations a 5 pixel should be to count as detected motion. 6 @param discount: the discount factor for the averagerator. 7 8 detector MotionDetection (num_sigmas=num_sigmas, discount=discount) 9 detected_motion = [] 10 for i, img in enumerate(image_list): 11 motion detector.detect_motion(img) 12 if np. sum(motion) > 500: 13 detected_motion.append((i, motion)) 14 return detected_motion 15 [] 1 # Compute the motion detections. 2 motions = detect_motion(images_as_arrays [:60]) 3 We can finally visualize the detected motions. [] 1 ### 15 points: Tests for motion detection 2 3 motions = detect_motion(images_as_arrays [:60]) 4 motion_idxs = [i for i, in motions] 5 assert motion_idxs [1, 10, 47, 48, 49, 57, 58, 59] 6 assert np. sum(motions [6] [1]) 1199 == 8
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


