Question: Implement the BinarySearchTree ADT in bst.cpp exactly as shown below. // bst.cpp #ifndef BST_H #define BST_H #include #include #include using namespace std; template class BinarySearchTree
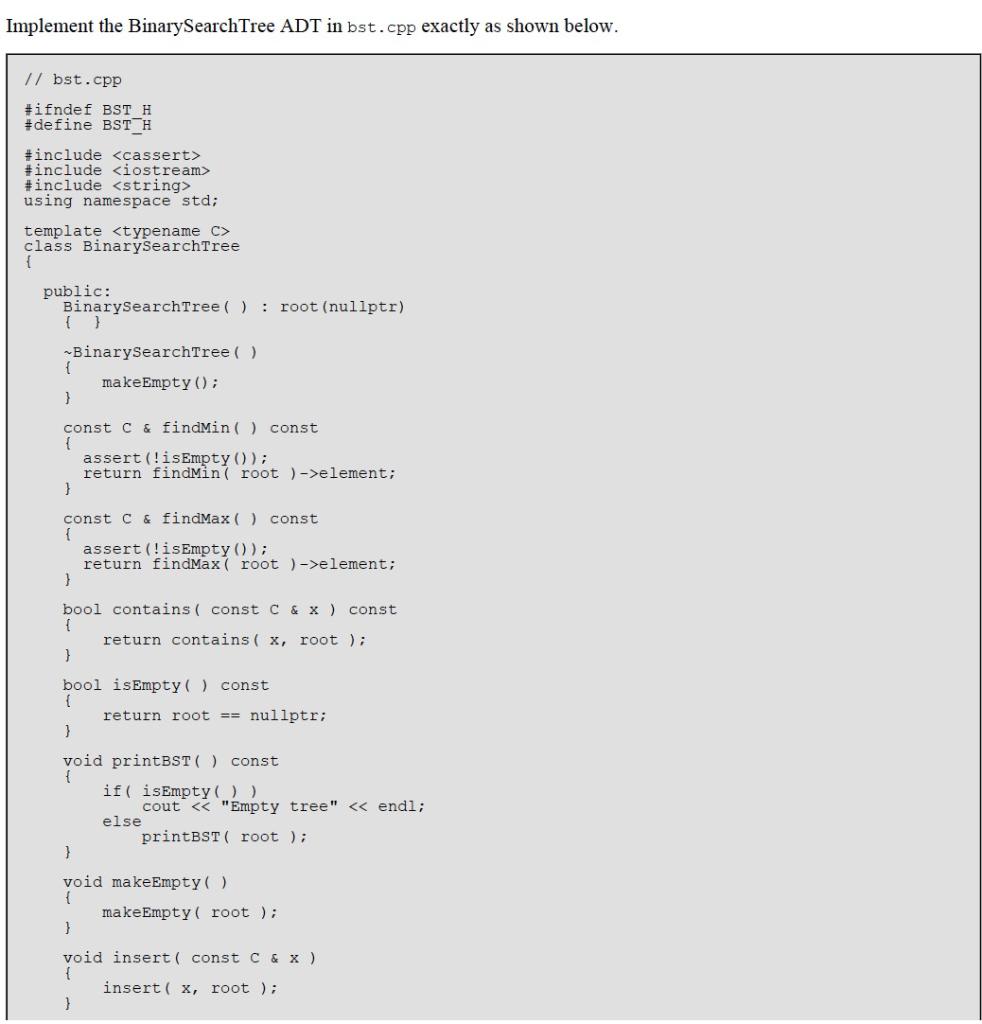

Implement the BinarySearchTree ADT in bst.cpp exactly as shown below.
// bst.cpp
#ifndef BST_H
#define BST_H
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
template
class BinarySearchTree
{
public:
BinarySearchTree( ) : root(nullptr)
{ }
~BinarySearchTree( )
{
makeEmpty();
}
const C & findMin( ) const
{
assert(!isEmpty());
return findMin( root )->element;
}
const C & findMax( ) const
{
assert(!isEmpty());
return findMax( root )->element;
}
bool contains( const C & x ) const
{
return contains( x, root );
}
bool isEmpty( ) const
{
return root == nullptr;
}
void printBST( ) const
{
if( isEmpty( ) )
cout
else
printBST( root );
}
void makeEmpty( )
{
makeEmpty( root );
}
void insert( const C & x )
{
insert( x, root );
}
CSE 2020 Lab 08 Binary Search Trees
bst.html[1/10/21, 11:54:20 PM]
void remove( const C & x )
{
remove( x, root );
}
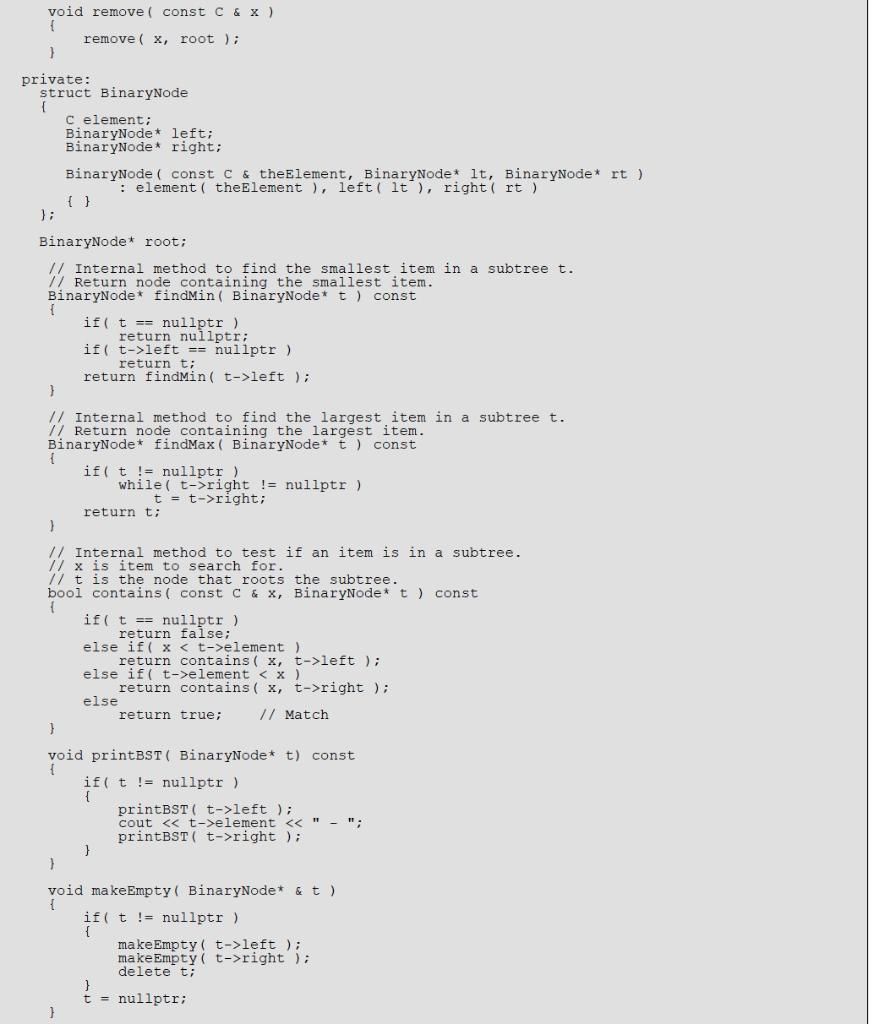
private:
struct BinaryNode
{
C element;
BinaryNode* left;
BinaryNode* right;
BinaryNode( const C & theElement, BinaryNode* lt, BinaryNode* rt )
: element( theElement ), left( lt ), right( rt )
{ }
};
BinaryNode* root;
// Internal method to find the smallest item in a subtree t.
// Return node containing the smallest item.
BinaryNode* findMin( BinaryNode* t ) const
{
if( t == nullptr )
return nullptr;
if( t->left == nullptr )
return t;
return findMin( t->left );
}
// Internal method to find the largest item in a subtree t.
// Return node containing the largest item.
BinaryNode* findMax( BinaryNode* t ) const
{
if( t != nullptr )
while( t->right != nullptr )
t = t->right;
return t;
}
// Internal method to test if an item is in a subtree.
// x is item to search for.
// t is the node that roots the subtree.
bool contains( const C & x, BinaryNode* t ) const
{
if( t == nullptr )
return false;
else if( x element )
return contains( x, t->left );
else if( t->element
return contains( x, t->right );
else
return true; // Match
}
void printBST( BinaryNode* t) const
{
if( t != nullptr )
{
printBST( t->left );
cout element
printBST( t->right );
}
}
void makeEmpty( BinaryNode* & t )
{
if( t != nullptr )
{
makeEmpty( t->left );
makeEmpty( t->right );
delete t;
}
t = nullptr;
}
// Internal method to insert into a subtree.
// x is the item to insert.
// t is the node that roots the subtree.
CSE 2020 Lab 08 Binary Search Trees
bst.html[1/10/21, 11:54:20 PM]
// Set the new root of the subtree.
void insert( const C & x, BinaryNode* & t )
{
if( t == nullptr )
t = new BinaryNode( x, nullptr, nullptr );
else if( x element )
insert( x, t->left );
else if( t->element
insert( x, t->right );
else
; // Duplicate; do nothing
}
// Internal method to remove from a subtree.
// x is the item to remove.
// t is the node that roots the subtree.
// Set the new root of the subtree.
void remove( const C & x, BinaryNode* & t )
{
if( t == nullptr )
return; // Item not found; do nothing
if( x element )
remove( x, t->left );
else if( t->element
remove( x, t->right );
else if( t->left != nullptr && t->right != nullptr ) // Two children
{
t->element = findMin( t->right )->element;
remove( t->element, t->right );
}
else
{
BinaryNode* oldNode = t;
if ( t->left == nullptr )
t = t->right;
else
t = t->left;
delete oldNode;
}
}
};
#endif
Exercise 2:
Program your own file lab08.cpp in which your main() function will test the new data structure. The main() function,
Declares an instance of BinarySearchTree (short: BST) suitable to hold integer values.
Prompts user to enter a random sequence of integer values, inserts these values into the binary search tree (the entered
values should NOT be in sorted order).
Calls the printBST() member function to print out the values of the binary search tree.
Prompts user to enter a random sequence of integer values, remove these values from your binary search tree. Print
out the reduced binary search tree.
Declares an instance of BinarySearchTree suitable to hold strings.
Prompts user to enter a random sequence of string,
inserts these strings into the binary search tree (the entered values
should NOT be in sorted order).
Calls the printBST() member function to print out the string in the binary search tree.
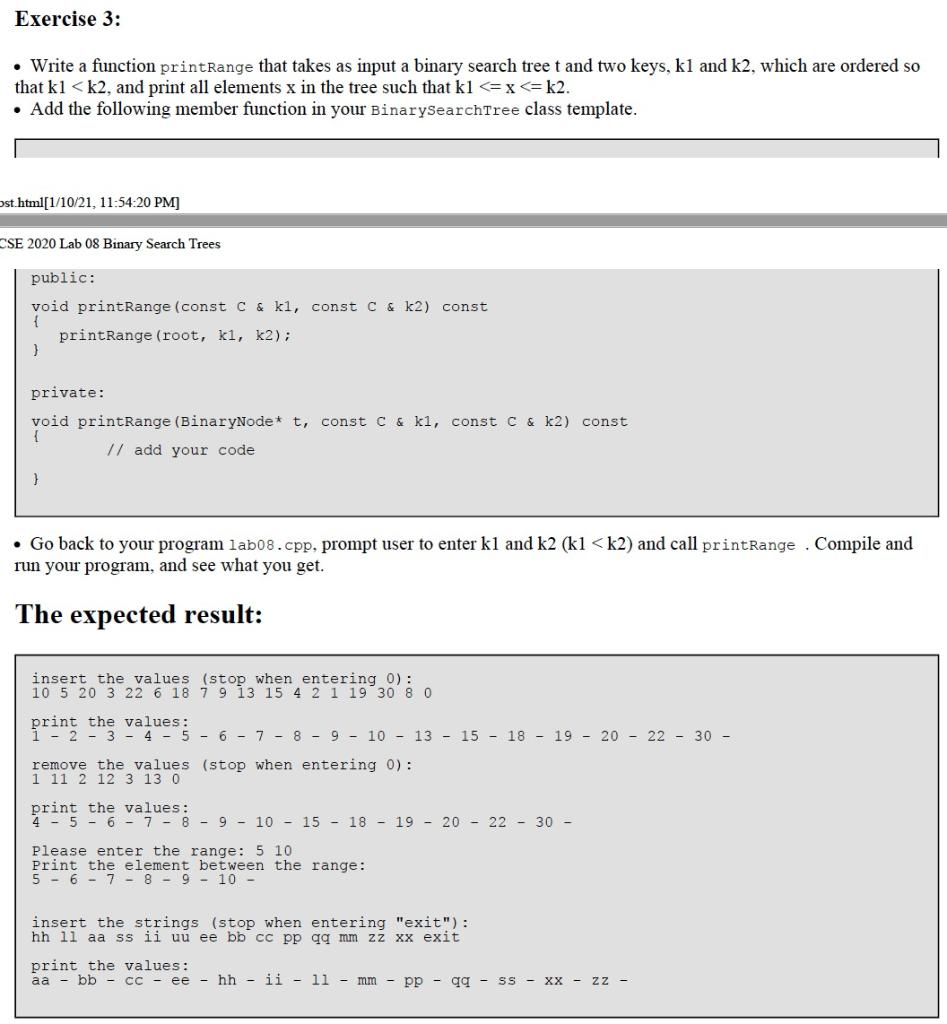
Exercise 3:
Write a function printRange that takes as input a binary search tree t and two keys, k1 and k2, which are ordered so
that k1
Add the following member function in your BinarySearchTree class template.
CSE 2020 Lab 08 Binary Search Trees
bst.html[1/10/21, 11:54:20 PM]
public:
void printRange(const C & k1, const C & k2) const
{
printRange(root, k1, k2);
}
private:
void printRange(BinaryNode* t, const C & k1, const C & k2) const
{
// add your code
}
Go back to your program lab08.cpp, prompt user to enter k1 and k2 (k1
Compile and
run your program, and see what you get.
The expected result:
insert the values (stop when entering 0):
10 5 20 3 22 6 18 7 9 13 15 4 2 1 19 30 8 0
print the values:
1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7 - 8 - 9 - 10 - 13 - 15 - 18 - 19 - 20 - 22 - 30 -
remove the values (stop when entering 0):
1 11 2 12 3 13 0
print the values:
4 - 5 - 6 - 7 - 8 - 9 - 10 - 15 - 18 - 19 - 20 - 22 - 30 -
Please enter the range: 5 10
Print the element between the range:
5 - 6 - 7 - 8 - 9 - 10 -
insert the strings (stop when entering "exit"):
hh ll aa ss ii uu ee bb cc pp qq mm zz xx exit
print the values:
aa - bb - cc - ee - hh - ii - ll - mm - pp - qq - ss - xx - zz -
Implement the BinarySearch Tree ADT in bst.cpp exactly as shown below. // bst.cpp #ifndef BST H #define BST H #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


