Question: Implement the bodies of the following classes using Java. Instructions and starter code are given below. Please use the following starter code for the four


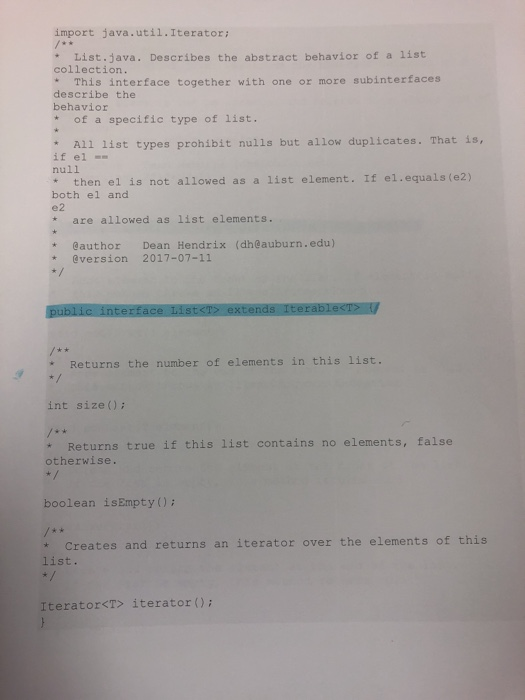




Implementing List Collections with Performance Constraints Problem Description This assignment focuses on applying the two collection implementation patterns that we've discussed: use data structures based on static memory (arrays) or dynamic memory (linked nodes). The dealing with are two very different List collections that are specified in a small interface hierarchy collections we're In addition to implementing the functional speciication (i.e., the method behavior), you must also meet non-funetional performance constraints. s always, you must closely adhere to the API as specified in the provided interfces. Deviation from any aspect of the API specified in these interfaces, or the items listed below, will result in a significant deduction of points. Performance Constraints The interface methods that you implement must meet the following performance constraints expressed in terms of big-oh. Remember that big-oh is an upper bound; therefore, your actual performance can perhaps be faster. . RandomizedList - All interface methods must have O(1) worst-case time complexity iterator, which can be O(N). The iterator methods themselves (hasNext 0, next 0) must be O(l). Amortization is allowable in O(1) times. The data memory proportional to the current number of elements in the list. Each iterator created by this class structure that you implement must use can also use a linear amount of memory with respect the number of elements in the list. . DoubleEndedList-All interface methods, with no exceptions, must have 0(1) worst-case time must use memory complexity, but amortization is allowable. The data structure that you implement proportional to the current number of elements in the list. Each iterator created by this class can only use a constant amount of memory, not a linear amount. API and Other Constraints You have been provided the code for the interfaces and a factory class'. While you have a measure of freedom in exactly how you design and build the implementing classes, you are subject to the following constraints. . You must not change (add, delete, modify) any provided interface in any way. You can only change the factory class by illing in a correct return value in the factory methods. You may not make any other changes to that class. The implementing classes that you create must be based on either an array data structure or a linked chain of nodes. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pactory.nethod.pattern Implementing List Collections with Performance Constraints Problem Description This assignment focuses on applying the two collection implementation patterns that we've discussed: use data structures based on static memory (arrays) or dynamic memory (linked nodes). The dealing with are two very different List collections that are specified in a small interface hierarchy collections we're In addition to implementing the functional speciication (i.e., the method behavior), you must also meet non-funetional performance constraints. s always, you must closely adhere to the API as specified in the provided interfces. Deviation from any aspect of the API specified in these interfaces, or the items listed below, will result in a significant deduction of points. Performance Constraints The interface methods that you implement must meet the following performance constraints expressed in terms of big-oh. Remember that big-oh is an upper bound; therefore, your actual performance can perhaps be faster. . RandomizedList - All interface methods must have O(1) worst-case time complexity iterator, which can be O(N). The iterator methods themselves (hasNext 0, next 0) must be O(l). Amortization is allowable in O(1) times. The data memory proportional to the current number of elements in the list. Each iterator created by this class structure that you implement must use can also use a linear amount of memory with respect the number of elements in the list. . DoubleEndedList-All interface methods, with no exceptions, must have 0(1) worst-case time must use memory complexity, but amortization is allowable. The data structure that you implement proportional to the current number of elements in the list. Each iterator created by this class can only use a constant amount of memory, not a linear amount. API and Other Constraints You have been provided the code for the interfaces and a factory class'. While you have a measure of freedom in exactly how you design and build the implementing classes, you are subject to the following constraints. . You must not change (add, delete, modify) any provided interface in any way. You can only change the factory class by illing in a correct return value in the factory methods. You may not make any other changes to that class. The implementing classes that you create must be based on either an array data structure or a linked chain of nodes. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pactory.nethod.pattern
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


