Question: Implement these OCAML functions using only Higher Order Functions such as List.map, List.filter, List.fold_right, and List.fold_left. Please don't use any other built-in OCAML functions or
Implement these OCAML functions using only Higher Order Functions such as List.map, List.filter, List.fold_right, and List.fold_left. Please don't use any other built-in OCAML functions or the ^ or @ operator. NEED ASAP THANK YOU!!!
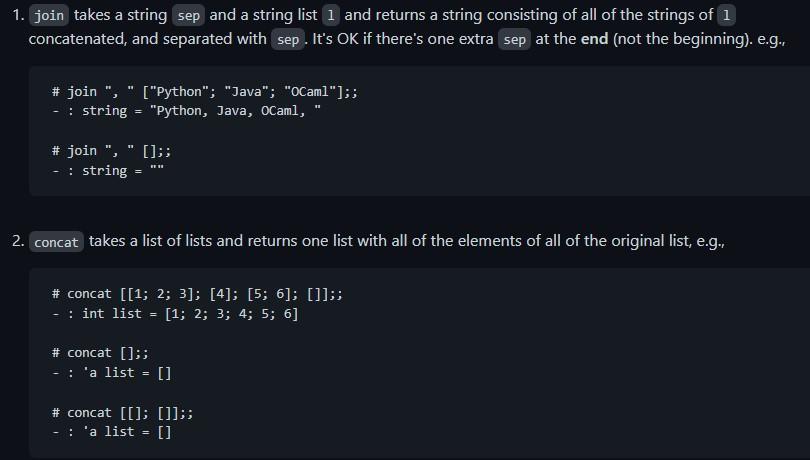
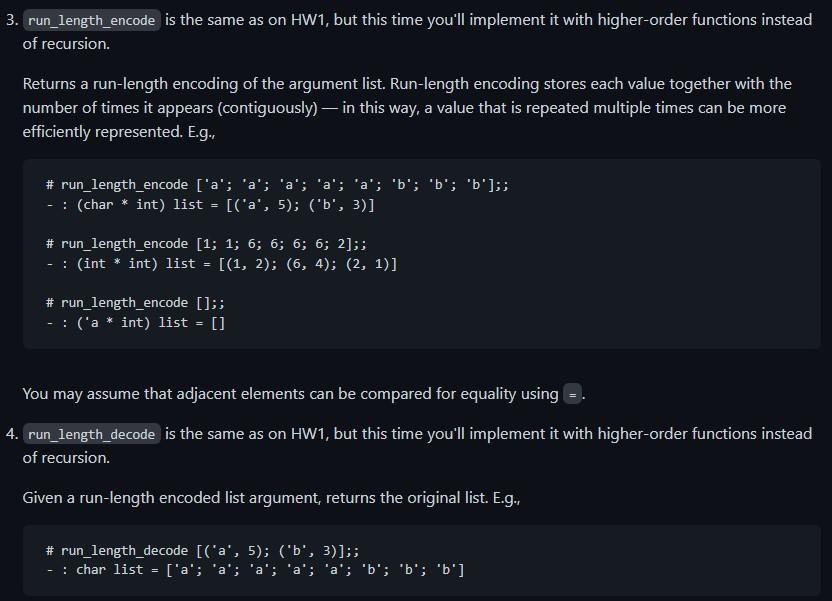
1. join takes a string sep and a string list 1 and returns a string consisting of all of the strings of 1 concatenated, and separated with sep. It's OK if there's one extra sep at the end (not the beginning). e.g.r \# join ", " ["Python"; "Java"; "OCaml" ]; - : string = "Python, Java, OCaml, " \# join ", " [];; - : string = "" 2. concat takes a list of lists and returns one list with all of the elements of all of the original list, e.g., \# concat [[1;2;3];[4];[5;6];[]]; : int list =[1;2;3;4;5;6] \# concat []; : 'a list = [] \# concat [[];[]]; : a list =[] 3. run_length_encode is the same as on HW1, but this time you'll implement it with higher-order functions instead of recursion. Returns a run-length encoding of the argument list. Run-length encoding stores each value together with the number of times it appears (contiguously) - in this way, a value that is repeated multiple times can be more efficiently represented. E.g.r You may assume that adjacent elements can be compared for equality using =. 4. run_length_decode is the same as on HW1, but this time you'll implement it with higher-order functions instead of recursion. Given a run-length encoded list argument, returns the original list. E.g
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


