Question: import ctypes class DynamicArray(object): def __init__(self): self._n = 0 self._capacity = 1 self._A = self._make_array(self._capacity) def _make_array(self, c): return (c * ctypes.py_object)() # creates an
import ctypes
class DynamicArray(object):
def __init__(self): self._n = 0 self._capacity = 1 self._A = self._make_array(self._capacity)
def _make_array(self, c): return (c * ctypes.py_object)() # creates an "array" of pointers # http://docs.python.org/3/c-api/structures.html#c.PyObject
def __len__(self): return self._n
def __getitem__(self, item): if not 0
# GROW THE ARRAY DYNAMICALLY def _resize(self, c): # c should be larger that the original array B = self._make_array(c) for k in range(self._n): B[k] = self._A[k] self._A = B self._capacity = c
def append(self, obj): if self._n == self._capacity: # list is full self._resize(2 * self._capacity) # grow the "list" by twice its size self._A[self._n] = obj self._n += 1
# Insert... # assume 0
for j in range(self._n, k, -1): # shift rightmost object first self._A[j] = self._A[j-1]
self._A[k] = value self._n += 1
def pop(self): if self._n > 1: self._A[self._n - 1] = None # help garbage collection self._n -= 1
# optimize memory usage by shrinking the capacity if self._n
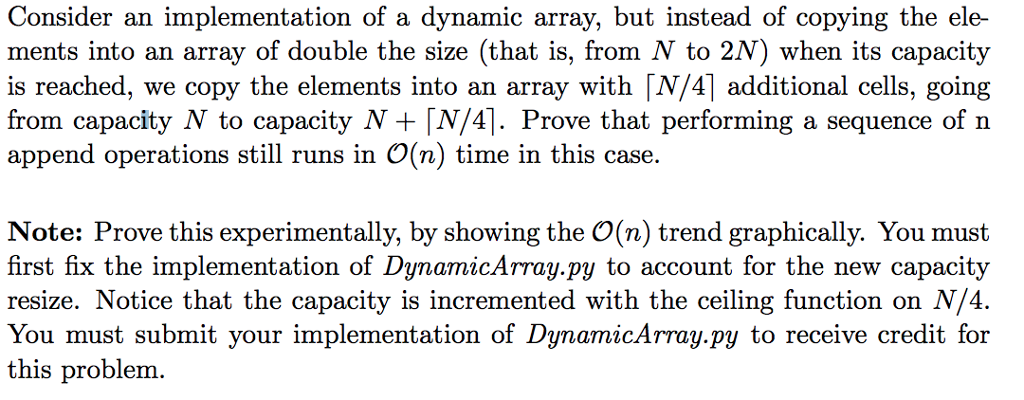
Consider an implementation of a dynamic array, but instead of copying the ele- ments into an array of double the size (that is, from N to 2N) when its capacity is reached, we copy the elements into an array withN/41 additional cells, going from capacity N to capacity N+N/41. Prove that performing a sequence of n append operations stil runs in O(n) time in this case. Note: Prove this experimentally, by showing the O(n) trend graphically. You must first fix the implementation of DynamicArray.py to account for the new capacity resize. Notice that the capacity is incremented with the ceiling function on N/4. You must submit your implementation of DynamicArray.py to receive credit for this problem. Consider an implementation of a dynamic array, but instead of copying the ele- ments into an array of double the size (that is, from N to 2N) when its capacity is reached, we copy the elements into an array withN/41 additional cells, going from capacity N to capacity N+N/41. Prove that performing a sequence of n append operations stil runs in O(n) time in this case. Note: Prove this experimentally, by showing the O(n) trend graphically. You must first fix the implementation of DynamicArray.py to account for the new capacity resize. Notice that the capacity is incremented with the ceiling function on N/4. You must submit your implementation of DynamicArray.py to receive credit for this
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


