Question: import java.util.*; // implementing a doubly linked list class Node{ private int data; private Node nextNodePtr; private Node prevNodePtr; public Node(){} public void setData(int d){
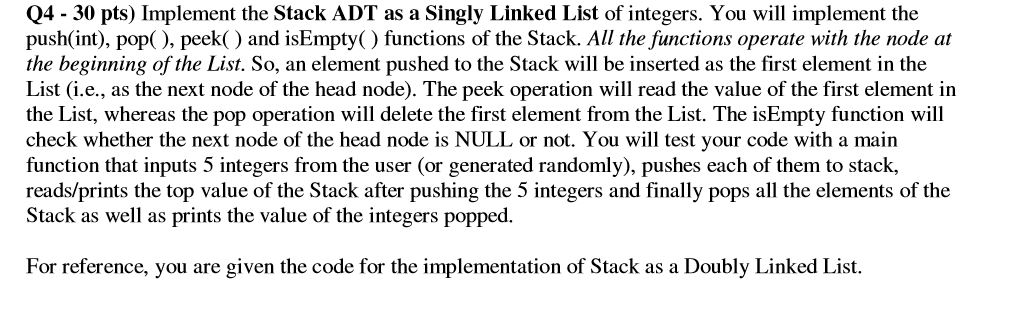
import java.util.*;
// implementing a doubly linked list
class Node{ private int data; private Node nextNodePtr; private Node prevNodePtr; public Node(){} public void setData(int d){ data = d; } public int getData(){ return data; } public void setNextNodePtr(Node nodePtr){ nextNodePtr = nodePtr; } public Node getNextNodePtr(){ return nextNodePtr; } public void setPrevNodePtr(Node nodePtr){ prevNodePtr = nodePtr; } public Node getPrevNodePtr(){ return prevNodePtr; } }
class Stack{
private Node headPtr; private Node tailPtr;
public Stack(){ headPtr = new Node(); tailPtr = new Node(); headPtr.setNextNodePtr(null); tailPtr.setPrevNodePtr(null); } public Node getHeadPtr(){ return headPtr; } public Node getTailPtr(){ return tailPtr; } public boolean isEmpty(){ if (headPtr.getNextNodePtr() == null) return true; return false; } public void push(int data){ Node newNodePtr = new Node(); newNodePtr.setData(data); newNodePtr.setNextNodePtr(null); Node lastNodePtr = tailPtr.getPrevNodePtr(); if (lastNodePtr == null){ headPtr.setNextNodePtr(newNodePtr); newNodePtr.setPrevNodePtr(null); } else{ lastNodePtr.setNextNodePtr(newNodePtr); newNodePtr.setPrevNodePtr(lastNodePtr); } tailPtr.setPrevNodePtr(newNodePtr); }
public int pop(){ Node lastNodePtr = tailPtr.getPrevNodePtr(); Node prevNodePtr = null; int poppedData = -100000; //empty stack if (lastNodePtr != null){ prevNodePtr = lastNodePtr.getPrevNodePtr(); poppedData = lastNodePtr.getData(); } else return poppedData; if (prevNodePtr != null){ prevNodePtr.setNextNodePtr(null); tailPtr.setPrevNodePtr(prevNodePtr); } else{ headPtr.setNextNodePtr(null); tailPtr.setPrevNodePtr(null); }
return poppedData; } public int peek(){ Node lastNodePtr = tailPtr.getPrevNodePtr(); if (lastNodePtr != null) return lastNodePtr.getData(); else return -100000; // empty stack } public void IterativePrint(){ Node currentNodePtr = headPtr.getNextNodePtr(); while (currentNodePtr != null){ System.out.print(currentNodePtr.getData() + " "); currentNodePtr = currentNodePtr.getNextNodePtr(); } System.out.println(); } public void ReversePrint(){ Node currentNodePtr = tailPtr.getPrevNodePtr(); while (currentNodePtr != null){ System.out.print(currentNodePtr.getData() + " "); currentNodePtr = currentNodePtr.getPrevNodePtr(); } System.out.println(); } }
class DoublyLinkedList{ public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int stackSize; System.out.print("Enter the number of elements you want to insert: "); stackSize = input.nextInt(); int maxValue; System.out.print("Enter the maximum value for an element: "); maxValue = input.nextInt();
Random randGen = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); Stack stack = new Stack(); // Create an empty stack
System.out.print("Pushed: "); for (int i = 0; i
Q4 - 30 pts) Implement the Stack ADT as a Singly Linked List of integers. You will implement the push int), pop(), peek) and isEmpty) functions of the Stack. All the functions operate with the node at the beginning of the List. So, an element pushed to the Stack will be inserted as the first element in the List (i.e., as the next node of the head node). The peek operation will read the value of the first element in the List, whereas the pop operation will delete the first element from the List. The isEmpty function will check whether the next node of the head node is NULL or not. You will test your code with a main function that inputs 5 integers from the user (or generated randomly), pushes each of them to stack, reads/prints the top value of the Stack after pushing the 5 integers and finally pops all the elements of the Stack as well as prints the value of the integers popped. For reference, you are given the code for the implementation of Stack as a Doubly Linked List
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


