Question: In class, we learned about PAC Learning, which stands for Probably Approximately Correct Learning. It helps us figure out the best number of hypotheses (
In class, we learned about PAC Learning, which stands for Probably Approximately
Correct Learning. It helps us figure out the best number of hypotheses or Machine
Learning algorithms the right sample sizes, and the threshold that indicates when
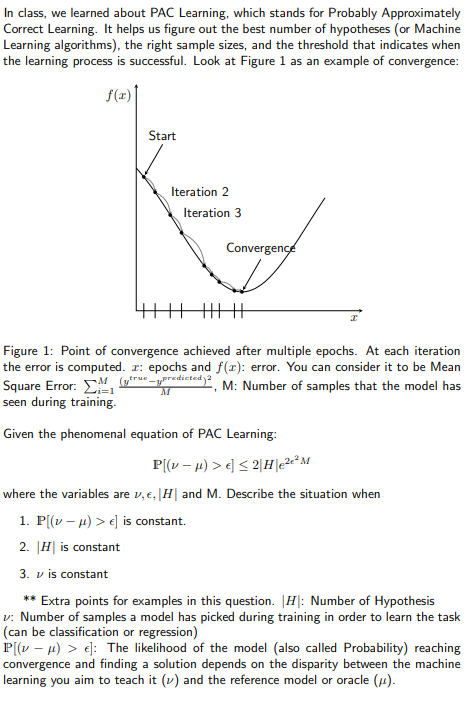
the learning process is successful. Look at Figure as an example of convergence:
Figure : Point of convergence achieved after multiple epochs. At each iteration
the error is computed. : epochs and : error. You can consider it to be Mean
Square Error: : Number of samples that the model has
seen during training.
Given the phenomenal equation of PAC Learning:
where the variables are
and Describe the situation when
is constant.
is constant
is constant
Extra points for examples in this question. : Number of Hypothesis
: Number of samples a model has picked during training in order to learn the task
can be classification or regression
: The likelihood of the model also called Probability reaching
convergence and finding a solution depends on the disparity between the machine
learning you aim to teach it
and the reference model or oracle
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


