Question: In crystallography, a unit cell is a repeating unit in a crystal structure. A unit cell of a hypothetical crystal is the parallelepiped made from
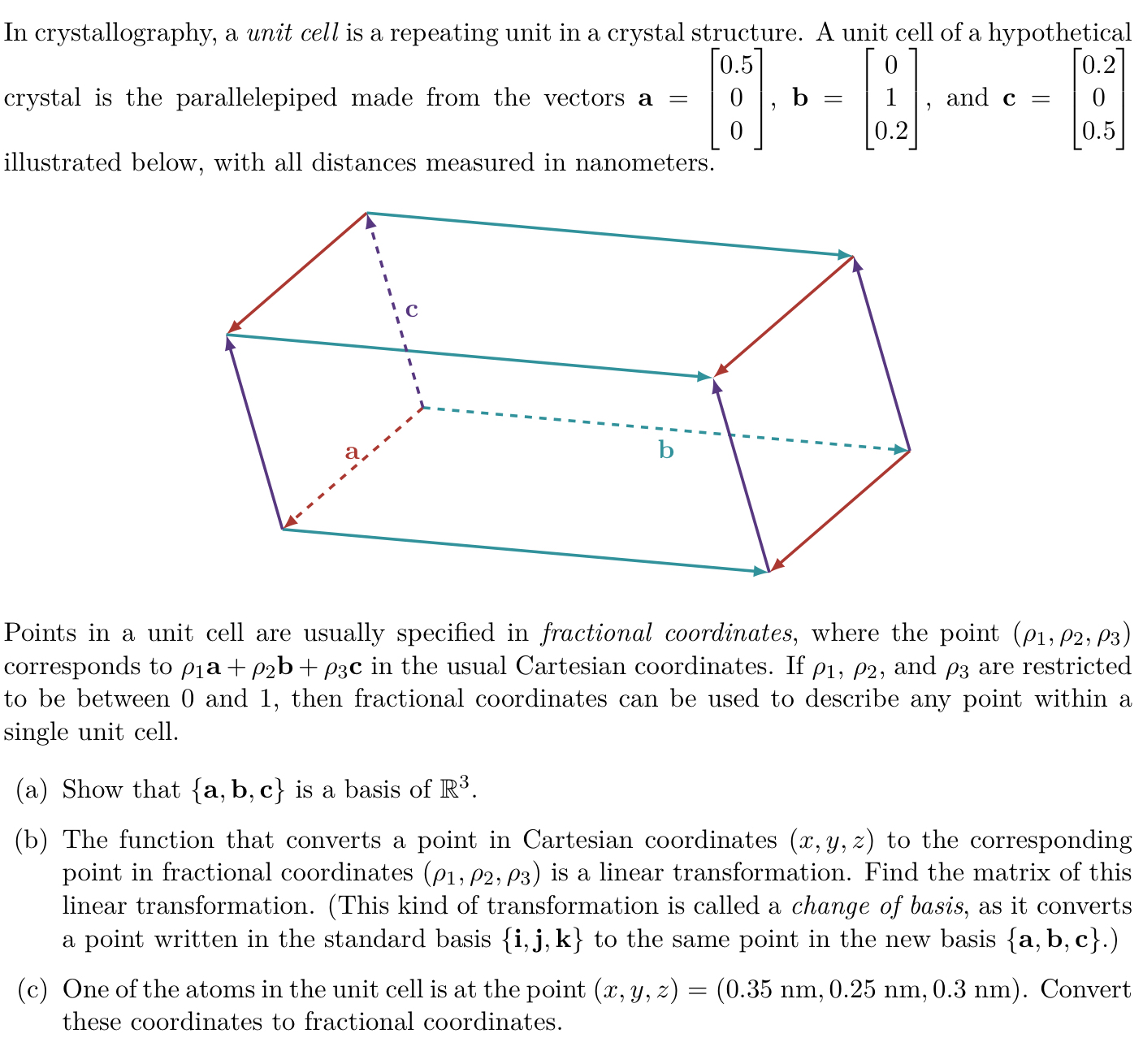
In crystallography, a unit cell is a repeating unit in a crystal structure. A unit cell of a hypothetical
crystal is the parallelepiped made from the vectors and
illustrated below, with all distances measured in nanometers.
Points in a unit cell are usually specified in fractional coordinates, where the point
corresponds to in the usual Cartesian coordinates. If and are restricted
to be between and then fractional coordinates can be used to describe any point within a
single unit cell.
a Show that is a basis of
b The function that converts a point in Cartesian coordinates to the corresponding
point in fractional coordinates is a linear transformation. Find the matrix of this
linear transformation. This kind of transformation is called a change of basis, as it converts
a point written in the standard basis to the same point in the new basis
c One of the atoms in the unit cell is at the point Convert
these coordinates to fractional coordinates.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


