Question: In Exercises 9-14, calculate v x w. 9. v = (1, 2, 1), w = (3, 1, 1) 10. v = (2, 0,0), w =

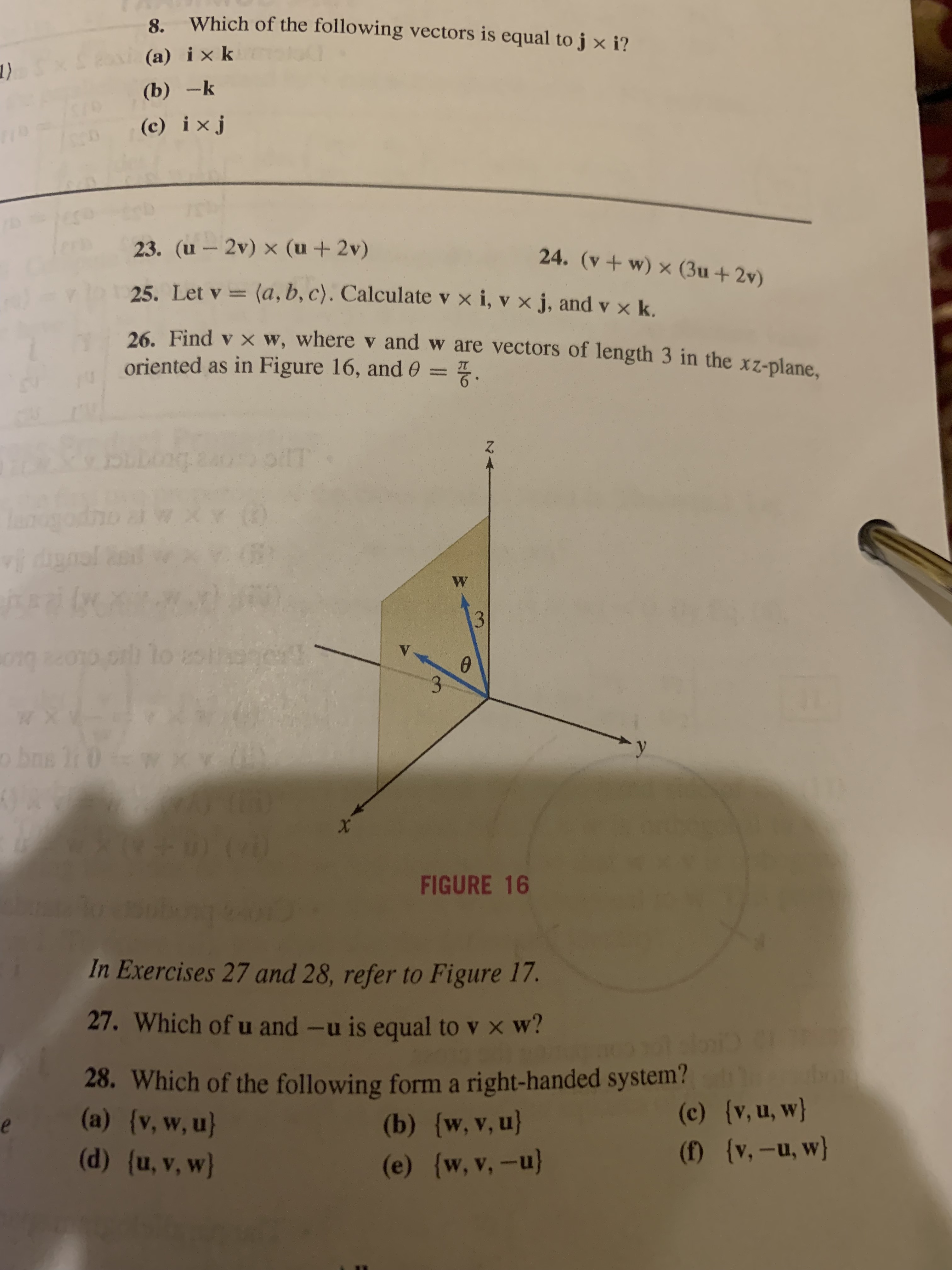

In Exercises 9-14, calculate v x w. 9. v = (1, 2, 1), w = (3, 1, 1) 10. v = (2, 0,0), w = (-1,0,1) ) xv bun 11. v = (3, 1, 3), w = (4, -6, 3) 12. v = (1, 1, 0), w = (0, 1,1) 13. v = (1, 2, 3), w = (1, 2, 3.01) 14. v = (2.4, -1.25, 3), w = (-7.68,4, -9.6) [x al In Exercises 15-18, use the relations in Eqs. (5) and (6) to calculate the cross product. 15. (i+ j) x k 16. (j - k) x (j + k) 17. (i - 3j + 2k) x (j - k) 18. (2i - 3j + 4k) x (i+ j-7k)(x) assuming that8. Which of the following vectors is equal to j x i? (a) ixk (b) -k (c) ixj 23. (u - 2v) x (u+2v) 24. (v + w) x (3u+ 2v) 25. Let v = (a, b, c). Calculate v x i, v x j, and v x k. 26. Find v x w, where v and w are vectors of length 3 in the xz-plane, oriented as in Figure 16, and 0 = 7. lugogodno a w X x () of dignol and we x v. or W ong zeoto pill to es theticatt V 3 W X bre 10 W x x / X FIGURE 16 In Exercises 27 and 28, refer to Figure 17. 27. Which of u and -u is equal to v x w? 28. Which of the following form a right-handed system? (a) {v, w, u} (b) {w, v, u) (c) {v, u, w} (d) {u, v, w} (e) {w, v, -u} (f) {v, -u, w}geomelin 30. What are the possible angles 0 between two unit vectors e and f if lle x fll = 3 31. Show that if v and w lie in the yz-plane, then v x w is a multiple of i. orthogonal to both a = (3. 1, 1) and b
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


