Question: in python Measure all 7 sorting algorithms by counting the number of compares and the number of swaps. Test on data ranging from size 8
in python
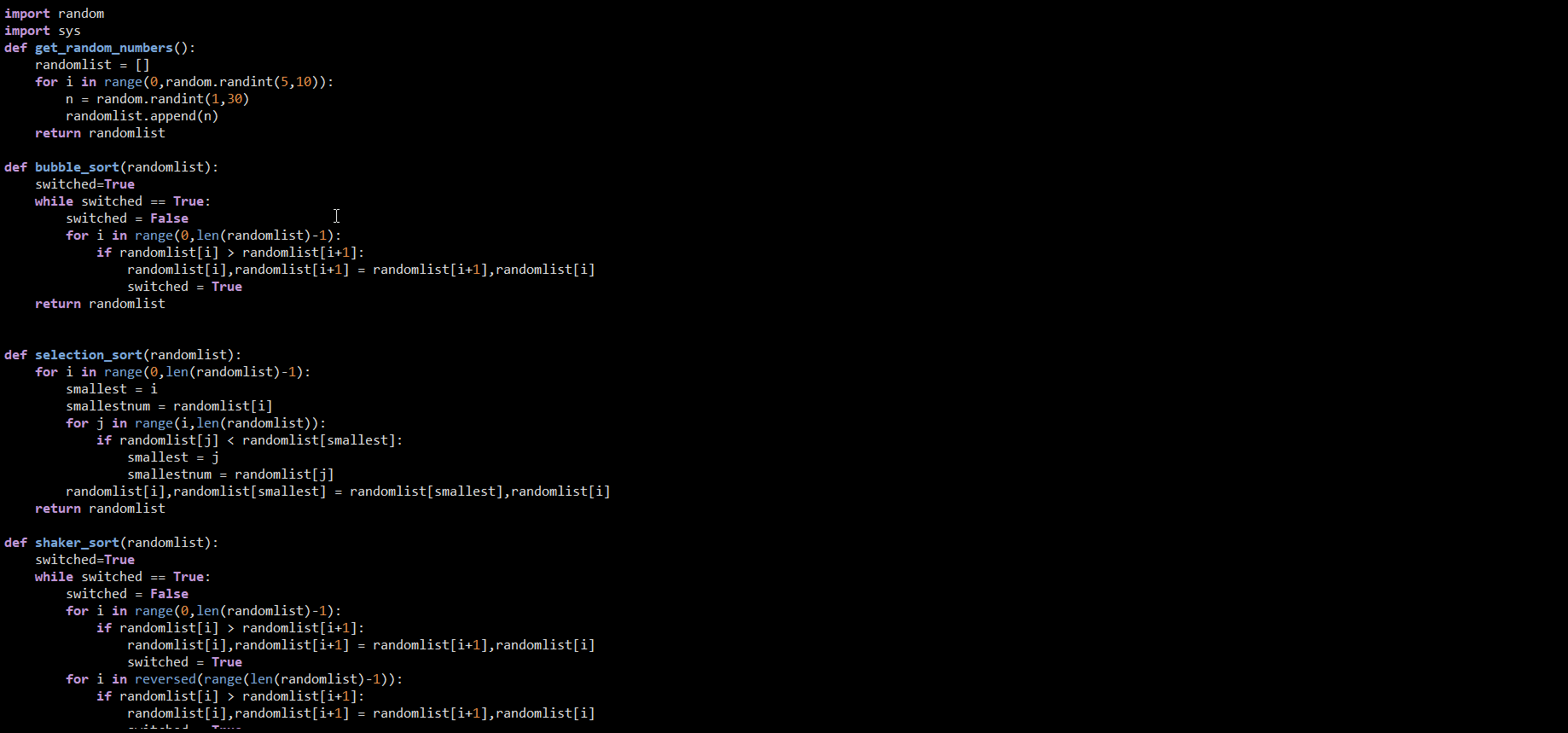
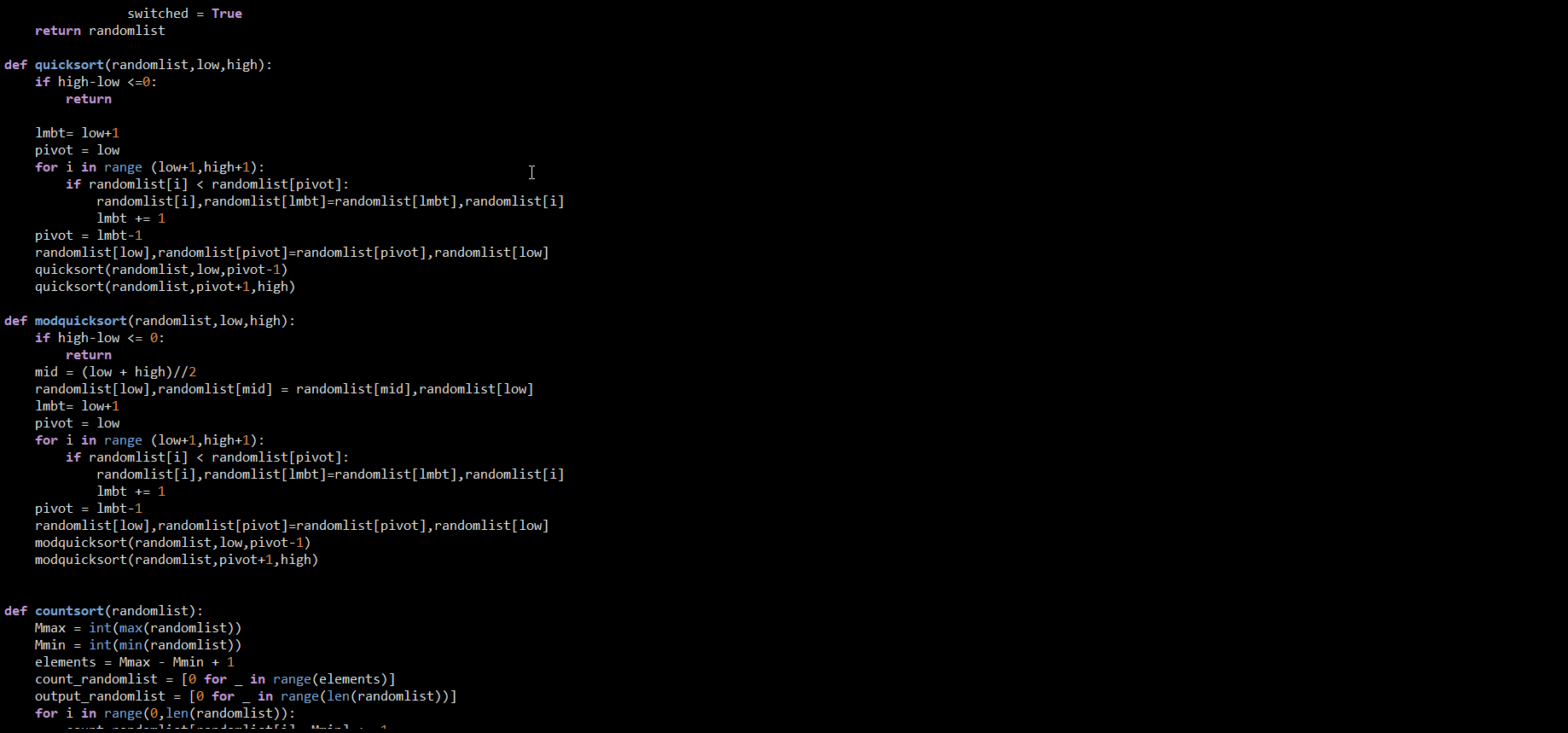
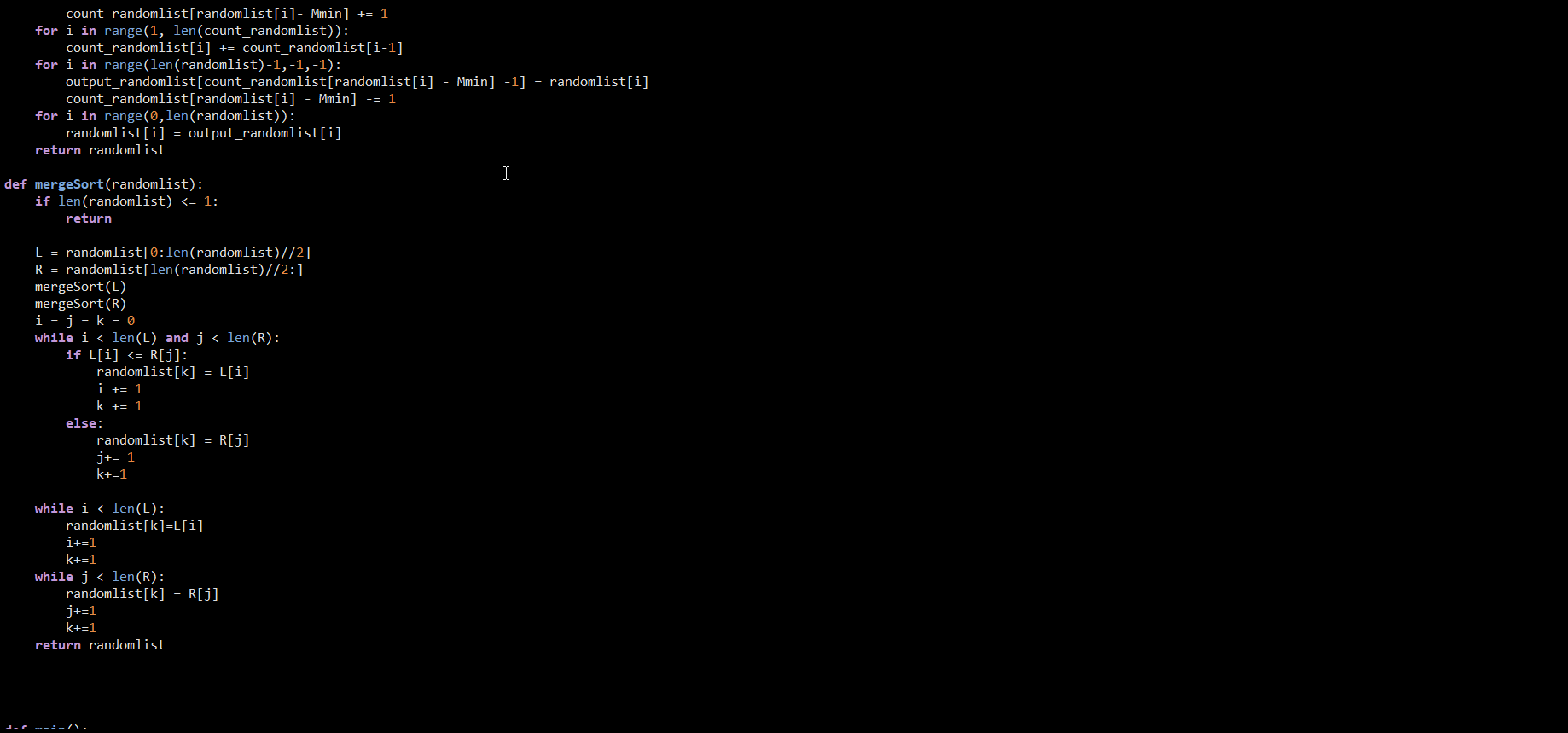
Measure all 7 sorting algorithms by counting the number of compares and the number of swaps. Test on data ranging from size 8 to size 4k, by powers of 2. Test on random data and on mostly sorted data. (Make a new function to create mostly sorted data. Have it first call the MakeRandomData function, have Python sort it, then swap the first and last elements.) Print all this data in organized tables, that you can then copy into Excel spreadsheets for making charts. You will need to create three data sets, with 1 Excel chart for each. The first data set and chart should plot Problem Size versus number of Compares when using Random data. The second data set and chart should plot Problem Size versus number of Swaps when using Random data. The third data set and chart should plot Problem Size versus number of Compares when using Mostly Sorted data instead of Random data. To pass off, show me the 3 spreadsheet plots that illustrate swaps and compares for random and mostly sorted data, in the 3 combinations specified. Be prepared to explain what they mean. It is important to make the charts Log/Log. That is, modify your python code to print the Log of the Problem Size and the Log of the number of Comparisons or Swaps. Otherwise it will be really hard to see and interpret the results. Also, make an effort to organize your python code to reduce repeating code as much as possible. import random import sys def get_random_numbers(): randomlist = [] for i in range(0, random.randint(5,10)): n = random.randint(1,30) randomlist.append(n) return randomlist def bubble_sort(randomlist): switched=True while switched == True: switched = False I for i in range(0, len(randomlist)-1): if randomlist[i] > randomlist[i+1]: randomlist[i],randomlist[i+1] = randomlist[i+1], randomlist[i] switched = True return randomlist def selection_sort (randomlist): for i in range(0, len (randomlist)-1): smallest = i smallestnum = randomlist[i] for j in range(i, len(randomlist)): if randomlist[j] randomlist[i+1]: randomlist[i], randomlist[i+1] = randomlist[i+1], randomlist[i] switched = True for i in reversed(range(len (randomlist)-1)): if randomlist[i] > randomlist[i+1]: randomlist[i], randomlist[i+1] = randomlist[i+1], randomlist[i] switched = True return randomlist def quicksort(randomlist, low, high): if high-low randomlist[i+1]: randomlist[i],randomlist[i+1] = randomlist[i+1], randomlist[i] switched = True return randomlist def selection_sort (randomlist): for i in range(0, len (randomlist)-1): smallest = i smallestnum = randomlist[i] for j in range(i, len(randomlist)): if randomlist[j] randomlist[i+1]: randomlist[i], randomlist[i+1] = randomlist[i+1], randomlist[i] switched = True for i in reversed(range(len (randomlist)-1)): if randomlist[i] > randomlist[i+1]: randomlist[i], randomlist[i+1] = randomlist[i+1], randomlist[i] switched = True return randomlist def quicksort(randomlist, low, high): if high-low
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


