Question: IN PYTHON: Please help me with this code and explain how you wrote it clearly in steps as I want to know how it works
IN PYTHON: Please help me with this code and explain how you wrote it clearly in steps as I want to know how it works as much as possible. The goal is to make a binary tree and search it.
The assignment asks: A Python program that implements functionality to generate a binary tree, produce a depth first search on its nodes, and plot the resulting tree. The Pythonscript you write must conform to all requirements listed in the next section. 1. Your program must define a binaryTree class with the following specifications: 2(a) Your binaryTree class must have as data attributes a dictionary called nodeChildren that maps a node to its (left_child,right_child) nodes, a dictionary called nodeParent that maps a node to its parent node, and a dictionary called treeXY that maps a node to its (x,y) location. (b) Your binaryTree class must have a method called addTrio(parent, left_child, right_child ) that adds a new pair of nodes (left_child, right_child) to the tree. If parent is the root then parent is added to the tree as well. (c) Your binaryTree class must have a method called leaves that returns a list of all leaf nodes in the tree and a method called nodes that returns a list of all nodes in the tree. (d) Your binaryTree class must have a method called addNodes(nNodes) adds at most nNodes to the tree, plus an additional root node if the tree is empty. For example, calling addNodes (4) on an empty tree would result in a tree with 5 nodes. Calling addNodes(3) on a tree that already has 3 nodes also results in a tree with 5 nodes since we dont need to add a new root node in this case. Why does the number of nodes have to be odd? Calling addNodes( nNodes) on a non-empty tree adds nNodes additional nodes to the tree. NOTE - the function addNodes in the template provided in Zybooks will implement this for you correctly. (e) Your binaryTree class must have a method called dfsTraverse that returns a depth first search ordered list of nodes in the tree. See Figure 1 and the code template in Zybooks for more detail. (f) Your binaryTree class must have a method called render that produces a plot of a binary tree with the number of nodes determined as described below. The leaf nodes are placed at integer locations in increasing order of their discovery by the depth first search. Parent nodes are set midway between each leaf node. Each node should have a vertical line extending from their node.y to node.y+1. Node labels should be printed at their (x,y) location, with left_child nodes right aligned, and right_child nodes left aligned. The root text label should be centered.
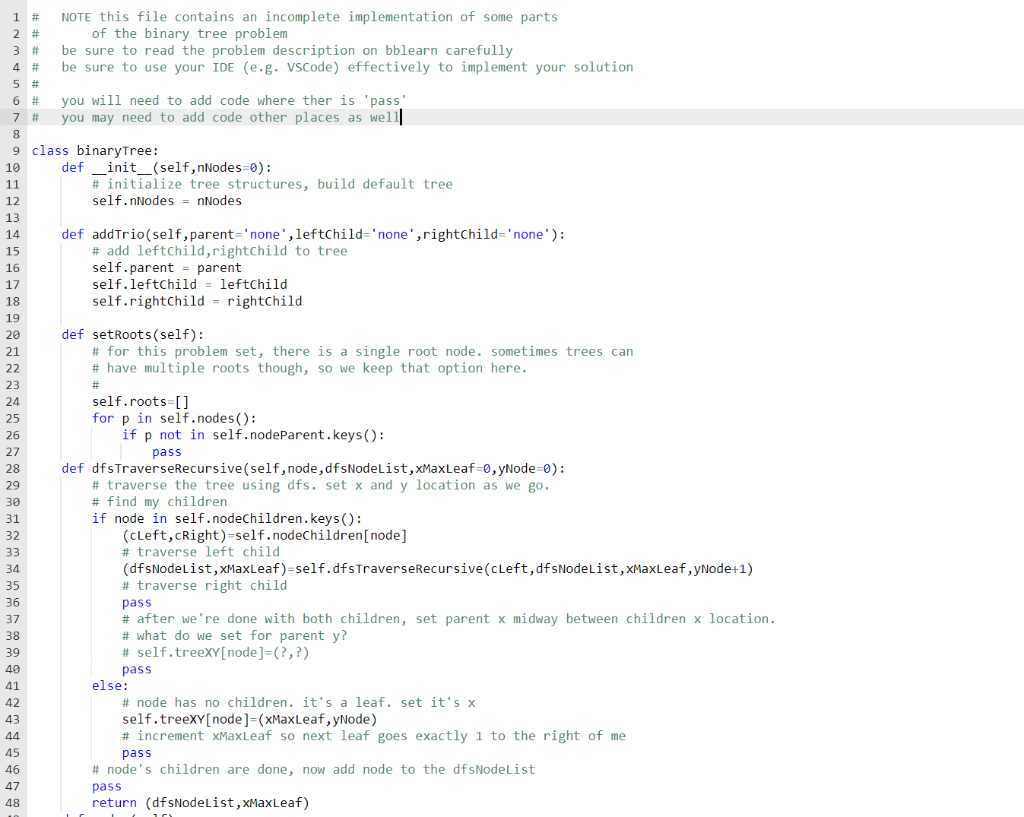
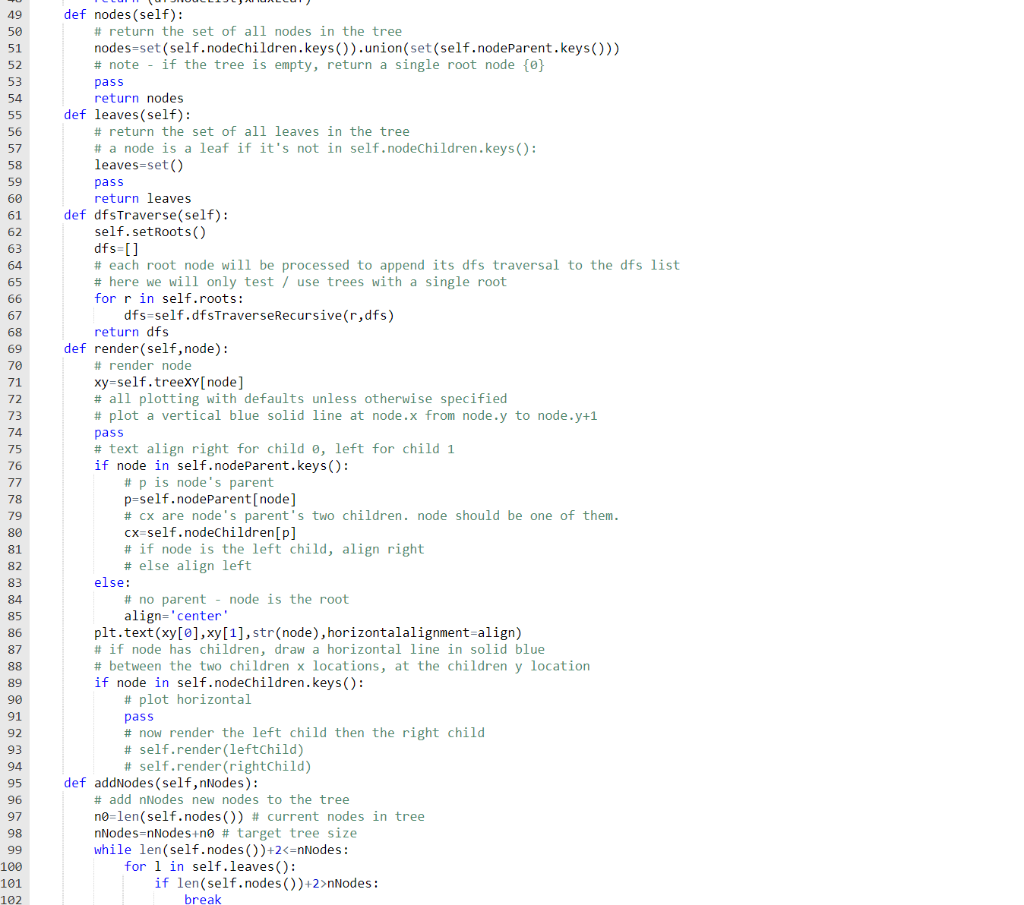
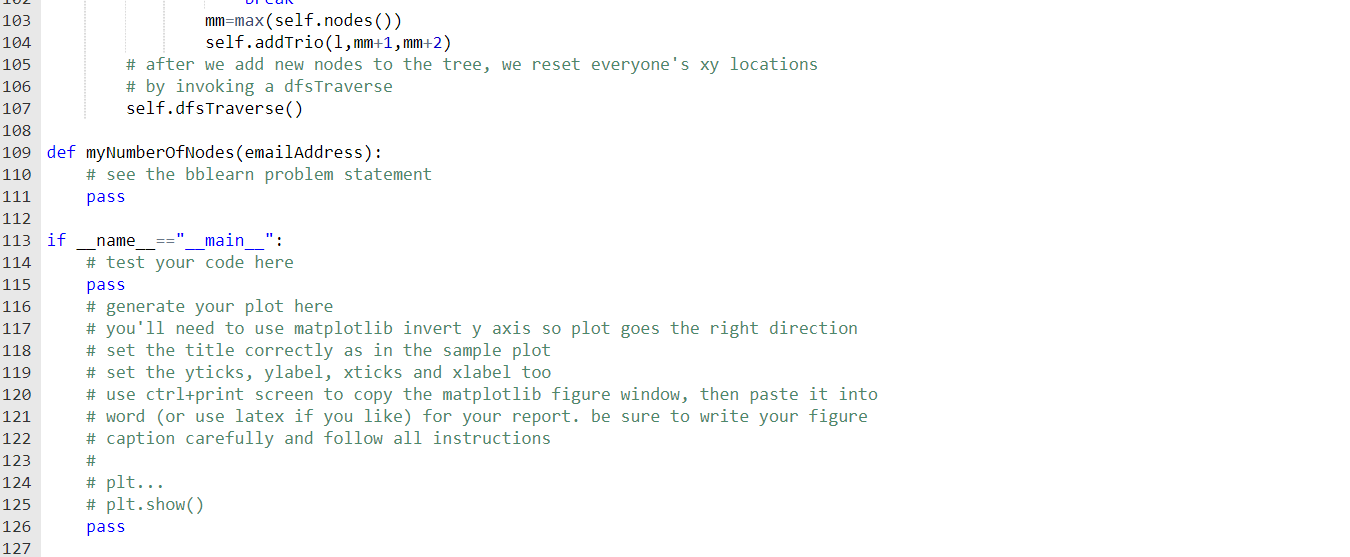
class binaryTree: def __init__(self,nNodes=0): # initialize tree structures, build default tree pass def addTrio(self,parent,leftChild,rightChild): # add leftChild,rightChild to tree pass def setRoots(self): # for this problem set, there is a single root node. sometimes trees can # have multiple roots though, so we keep that option here. # self.roots=[] for p in self.nodes(): if p not in self.nodeParent.keys(): pass def dfsTraverseRecursive(self,node,dfsNodeList,xMaxLeaf=0,yNode=0): # traverse the tree using dfs. set x and y location as we go. # find my children if node in self.nodeChildren.keys(): (cLeft,cRight)=self.nodeChildren[node] # traverse left child (dfsNodeList,xMaxLeaf)=self.dfsTraverseRecursive(cLeft,dfsNodeList,xMaxLeaf,yNode+1) # traverse right child pass # after we're done with both children, set parent x midway between children x location. # what do we set for parent y? # self.treeXY[node]=(?,?) pass else: # node has no children. it's a leaf. set it's x self.treeXY[node]=(xMaxLeaf,yNode) # increment xMaxLeaf so next leaf goes exactly 1 to the right of me pass # node's children are done, now add node to the dfsNodeList pass return (dfsNodeList,xMaxLeaf) def nodes(self): # return the set of all nodes in the tree nodes=set(self.nodeChildren.keys()).union(set(self.nodeParent.keys())) # note - if the tree is empty, return a single root node {0} pass return nodes def leaves(self): # return the set of all leaves in the tree # a node is a leaf if it's not in self.nodeChildren.keys(): leaves=set() pass return leaves def dfsTraverse(self): self.setRoots() dfs=[] # each root node will be processed to append its dfs traversal to the dfs list # here we will only test / use trees with a single root for r in self.roots: dfs=self.dfsTraverseRecursive(r,dfs) return dfs def render(self,node): # render node xy=self.treeXY[node] # all plotting with defaults unless otherwise specified # plot a vertical blue solid line at node.x from node.y to node.y+1 pass # text align right for child 0, left for child 1 if node in self.nodeParent.keys(): # p is node's parent p=self.nodeParent[node] # cx are node's parent's two children. node should be one of them. cx=self.nodeChildren[p] # if node is the left child, align right # else align left else: # no parent - node is the root align='center' plt.text(xy[0],xy[1],str(node),horizontalalignment=align) # if node has children, draw a horizontal line in solid blue # between the two children x locations, at the children y location if node in self.nodeChildren.keys(): # plot horizontal pass # now render the left child then the right child # self.render(leftChild) # self.render(rightChild) def addNodes(self,nNodes): # add nNodes new nodes to the tree n0=len(self.nodes()) # current nodes in tree nNodes=nNodes+n0 # target tree size while len(self.nodes())+2nNodes: break mm=max(self.nodes()) self.addTrio(l,mm+1,mm+2) # after we add new nodes to the tree, we reset everyone's xy locations # by invoking a dfsTraverse self.dfsTraverse()
def myNumberOfNodes(emailAddress): # see the bblearn problem statement pass
if __name__=="__main__": # test your code here pass # generate your plot here # you'll need to use matplotlib invert y axis so plot goes the right direction # set the title correctly as in the sample plot # set the yticks, ylabel, xticks and xlabel too # use ctrl+print screen to copy the matplotlib figure window, then paste it into # word (or use latex if you like) for your report. be sure to write your figure # caption carefully and follow all instructions # # plt... # plt.show() pass
16 1 # NOTE this file contains an incomplete implementation of some parts 2# of the binary tree problem 3# be sure to read the problem description on bblearn carefully 4 # be sure to use your IDE (e.g. VsCode) effectively to implement your solution 5 # 6 # you will need to add code where ther is 'pass' 7 # you may need to add code other places as well 8 9 class binaryTree: 10 def _init__(self,nNodes=0): 11 # initialize tree structures, build default tree 12 self.nNodes = nNodes 13 14 def addTrio(self, parent='none',leftChild='none',rightChild='none'): 15 # add leftchild,rightchild to tree self.parent = parent 17 self.leftchild leftchild 18 self.rightChild = rightChild 19 20 def setRoots(self): 21 # for this problem set, there is a single root node. sometimes trees can 22 # have multiple roots though, so we keep that option here. 23 # 24 self.roots=[] 25 for p in self.nodes(): 26 if p not in self.nodeParent.keys(): 27 pass 28 def dfsTraverseRecursive(self, node,dfsNodeList,xMaxLeaf=0, yNode=0): 29 # traverse the tree using dfs. set x and y location as we go. # find my children 31 if node in self.nodechildren. keys(): 32 (cLeft, cRight)=self.nodeChildren(node] 33 # traverse left child 34 (dfsModelist, xMaxLeaf)=self.dfsTraverseRecursive (Cleft,dfsModelist, XMaxLeaf,yNode+1) 35 # traverse right child 36 pass 37 # after we're done with both children, set parent x midway between children x location. 38 # what do we set for parent y? 39 39 # self.treeXY [ node] =(?, ?) 40 pass 41 42 # node has no children. it's a leaf. set it's x 43 self.treeXY [node) = (xMaxLeaf, yNode) # increment xMaxLeaf so next leaf goes exactly 1 to the right of me pass # node's children are done, now add node to the dfsNodeList pass return (dfsNodeList, XMaxLeaf) 30 else: 44 45 46 47 48 def nodes (self): # return the set of all nodes in the tree nodesset (self.nodechildren.keys()).union(set (self.nodeParent.keys())) # note - if the tree is empty, return a single root node {0} pass return nodes def leaves(self): # return the set of all leaves in the tree # a node is a leaf if it's not in self.nodeChildren.keys(): leaves=set() pass return leaves def dfsTraverse(self): self.setRoots) 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 dfs=[] # each root node will be processed to append its dfs traversal to the dfs list # here we will only test / use trees with a single root for r in self.roots: dfs=self.dfsTraverseRecursive(r,dfs) return dfs def render(self, node): # render node xy=self. treeXY[ node] # all plotting with defaults unless otherwise specified # plot a vertical blue solid line at node.x from node.y to node.y+1 pass # text align right for child o, left for child 1 if node in self.nodeParent.keys(): # p is node's parent p=self.nodeParent[node] # cx are node's parent's two children. node should be one of them. cx=self.nodeChildren[p] # if node is the left child, align right # else align left else: # no parent node is the root align='center' plt.text(xy[@],xy[1],str(node), horizontalalignment=align) # if node has children, draw a horizontal line in solid blue # between the two children x locations, at the children y location if node in self.nodechildren.keys(): # plot horizontal 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 pass now render the left child then the right child # self.render(leftchild) # self.render(rightChild) def addNodes (self,nNodes): # add nNodes new nodes to the tree no-len(self.nodes() # current nodes in tree nNodes=nNodes+no # target tree size while len(self.nodes())+2nNodes: break 103 mm=max(self.nodes()) 104 self.addTrio(1,mm+1, mm+2) 105 # after we add new nodes to the tree, we reset everyone's xy locations 106 # by invoking a dfsTraverse 107 self.dfsTraverse() 108 109 def myNumberOfNodes (emailAddress): 110 # see the bblearn problem statement 111 pass 112 113 if name main": 114 # test your code here 115 pass 116 # generate your plot here 117 # you'll need to use matplotlib invert y axis so plot goes the right direction 118 # set the title correctly as in the sample plot 119 # set the yticks, ylabel, xticks and xlabel too 120 # use ctrl+print screen to copy the matplotlib figure window, then paste it into # word (or use latex if you like) for your report. be sure to write your figure 122 # caption carefully and follow all instructions 123 # 124 # plt... 125 # plt.show() 126 pass 127 121 16 1 # NOTE this file contains an incomplete implementation of some parts 2# of the binary tree problem 3# be sure to read the problem description on bblearn carefully 4 # be sure to use your IDE (e.g. VsCode) effectively to implement your solution 5 # 6 # you will need to add code where ther is 'pass' 7 # you may need to add code other places as well 8 9 class binaryTree: 10 def _init__(self,nNodes=0): 11 # initialize tree structures, build default tree 12 self.nNodes = nNodes 13 14 def addTrio(self, parent='none',leftChild='none',rightChild='none'): 15 # add leftchild,rightchild to tree self.parent = parent 17 self.leftchild leftchild 18 self.rightChild = rightChild 19 20 def setRoots(self): 21 # for this problem set, there is a single root node. sometimes trees can 22 # have multiple roots though, so we keep that option here. 23 # 24 self.roots=[] 25 for p in self.nodes(): 26 if p not in self.nodeParent.keys(): 27 pass 28 def dfsTraverseRecursive(self, node,dfsNodeList,xMaxLeaf=0, yNode=0): 29 # traverse the tree using dfs. set x and y location as we go. # find my children 31 if node in self.nodechildren. keys(): 32 (cLeft, cRight)=self.nodeChildren(node] 33 # traverse left child 34 (dfsModelist, xMaxLeaf)=self.dfsTraverseRecursive (Cleft,dfsModelist, XMaxLeaf,yNode+1) 35 # traverse right child 36 pass 37 # after we're done with both children, set parent x midway between children x location. 38 # what do we set for parent y? 39 39 # self.treeXY [ node] =(?, ?) 40 pass 41 42 # node has no children. it's a leaf. set it's x 43 self.treeXY [node) = (xMaxLeaf, yNode) # increment xMaxLeaf so next leaf goes exactly 1 to the right of me pass # node's children are done, now add node to the dfsNodeList pass return (dfsNodeList, XMaxLeaf) 30 else: 44 45 46 47 48 def nodes (self): # return the set of all nodes in the tree nodesset (self.nodechildren.keys()).union(set (self.nodeParent.keys())) # note - if the tree is empty, return a single root node {0} pass return nodes def leaves(self): # return the set of all leaves in the tree # a node is a leaf if it's not in self.nodeChildren.keys(): leaves=set() pass return leaves def dfsTraverse(self): self.setRoots) 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 dfs=[] # each root node will be processed to append its dfs traversal to the dfs list # here we will only test / use trees with a single root for r in self.roots: dfs=self.dfsTraverseRecursive(r,dfs) return dfs def render(self, node): # render node xy=self. treeXY[ node] # all plotting with defaults unless otherwise specified # plot a vertical blue solid line at node.x from node.y to node.y+1 pass # text align right for child o, left for child 1 if node in self.nodeParent.keys(): # p is node's parent p=self.nodeParent[node] # cx are node's parent's two children. node should be one of them. cx=self.nodeChildren[p] # if node is the left child, align right # else align left else: # no parent node is the root align='center' plt.text(xy[@],xy[1],str(node), horizontalalignment=align) # if node has children, draw a horizontal line in solid blue # between the two children x locations, at the children y location if node in self.nodechildren.keys(): # plot horizontal 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 pass now render the left child then the right child # self.render(leftchild) # self.render(rightChild) def addNodes (self,nNodes): # add nNodes new nodes to the tree no-len(self.nodes() # current nodes in tree nNodes=nNodes+no # target tree size while len(self.nodes())+2nNodes: break 103 mm=max(self.nodes()) 104 self.addTrio(1,mm+1, mm+2) 105 # after we add new nodes to the tree, we reset everyone's xy locations 106 # by invoking a dfsTraverse 107 self.dfsTraverse() 108 109 def myNumberOfNodes (emailAddress): 110 # see the bblearn problem statement 111 pass 112 113 if name main": 114 # test your code here 115 pass 116 # generate your plot here 117 # you'll need to use matplotlib invert y axis so plot goes the right direction 118 # set the title correctly as in the sample plot 119 # set the yticks, ylabel, xticks and xlabel too 120 # use ctrl+print screen to copy the matplotlib figure window, then paste it into # word (or use latex if you like) for your report. be sure to write your figure 122 # caption carefully and follow all instructions 123 # 124 # plt... 125 # plt.show() 126 pass 127 121
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To complete this binary tree implementation in Python lets follow each required functionality step by step Ill provide explanations along the way Step ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


