Question: In Python please! Simplified model of magnetic braking Consider a circular coil with / turns of wire. and radius a. The coil has an intrinsic
In Python please!
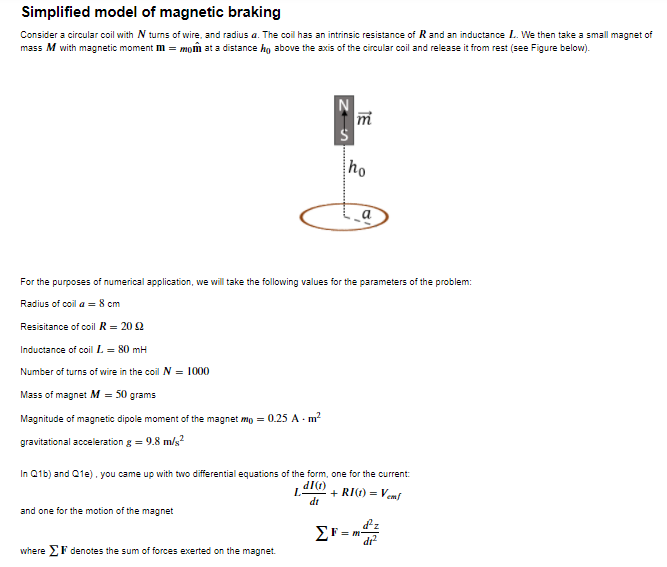

Simplified model of magnetic braking Consider a circular coil with / turns of wire. and radius a. The coil has an intrinsic resistance of R and an inductance I.. We then take a small magnet of mass M with magnetic moment I = mom at a distance hy above the axis of the circular coil and release it from rest (see Figure below). m ho a For the purposes of numerical application, we will take the following values for the parameters of the problem: Radius of coil a = 8 cm Resistance of coil R = 20 0 Inductance of coil L = 80 mH Number of turns of wire in the coil N = 1000 Mass of magnet M = 30 grams Magnitude of magnetic dipole moment of the magnet mo = 0.25 A . m- gravitational acceleration g = 9.8 m/s In Q1b) and Q1e) , you came up with two differential equations of the form, one for the current: + RI(1) = Vemf and one for the motion of the magnet EF=moz where _' I denotes the sum of forces exerted on the magnet.Taking for initial conditions z(0) = 20, v = z = () (the magnet starts from rest at a distance Za from the centre of the coil), and /(0) = 0 (initially there is no current running through the coil), solve the two differential equations numerically. Note that bemy will depend on z (the position of the magnet) so you'll need to solve the differential equation for the motion of the magnet first, and then use that to solve the differential equation for the current. Take a total time of 3 seconds. If you need a review of Euler's method, see Appendix below. In [ ]: H Xmatplotlib inline import matplotlib. pyplot as pit import numpy as rip "Numerical constants (in SI units) a = 0. 08, R = 20, L = 80e-3, N = 1000, M = 50e-3, me = 0.25, g = 9.8; mu_0 = 4=mp. pi$10**(-7) #permeability of free space _max = 3; #max time Athis function is for you to insert your expression for the induced emf. Make sure to replace None as input with whatever Avariables you need. def V_ent ( None) : Complete this return None #change this to return desired output Athis function is for you to insert your expression for the force exerted on the magnet by the coil's magnetic field. Make sure to replace None as input with whatever variables you need. def F_m(None) : "Complete this return None #change this to return desired output "Implementation of Euler's method to solve differential equations. Don't forget to choose an appropriate time step. # Don't forget to allocate memory for numpy arrays (one for the position of the magnet 2, and one for the current Winitial conditions on magnet's position and velocity Winitial conditions on current in coil # Complete implementation belowQuestions 1 - Plot the current ](1) as a function of time (again, take a total max of 3s, for the given numerical values). 2- On the same graph, plot the current as a function of time, but this time assuming the coil has no inductance ( = 0). Comment on the difference between these two curves in light of the physical meaning of inductance 3 - For an inductance . = 80 mH, on a different graph, plot the force exerted on the magnet by the coil's magnetic field (do not include the force of gravity). Interpret the results of the graph in terms of magnetic braking. Will the magnet be slowed down significantly? 3b) You'll notice that there is a brief period of time where the coil is actually trying to expel the magnet. Plot this force again assuming the coil has no inductance L. = 0 - what do you notice? Can you explain why this happens? In [ ]: MAPLots for Q1 In [ ]: MAPLots for Q2 In [ ]: MAPLots for Q3 Feel free to play around with the parameters, and see what kind of behaviour you can get. In particlar, can you ever get the magnet to levitate? (This is extra - you do NOT need to do this for the assignment). You can also evaluate numerically how much heat is dissipated in the coil as heat and how much charge is displaced. (This is also extra, but you can use it to check your answer to Q1c) Appendix Euler's method Euler's method is the simplest numerical method that exists. We'll consider the first-order differential equation dz(1) = /(z()) (1) with the initial condition z(ro) = zo. If we know the value of z(f) at f = / and want to know the value of z at some short time interval later z(1 + A), we approximate the value of z(f + /) by its Taylor series expansion. The more terms we keep the more accurate the approximation but this comes at the cost of computing more terms. Recall that a function z(r + A) has a general Taylor series:2! di2 + 3! dil - +... (2) where the ellipsis indicates higher order terms. Euler's method takes only the linear term such that z(1 + A) = z(1) + h- dz(1) = z(0) + h/(t, z(0) (3) Euler's method finds the slope of the solution dz/or at point t, and finds the value of z(f + 4) by extrapolationg the slope from z(). For example, from the initial condition z(ro) = yo, we can find the value of z(ro + A) = z(mo) + Adz(mo)/dd. The idea then is to successively apply this to build the solution in steps of h. The algorithm then is as follows: To find the solution in an interval [ fo. r]. split up the interval into NV partitions of length h. Given an initial condition zo at fo: z[0 ] = ze h = (t-te)/N for O En EN{ 2 [n+1] = z[n] + h f(t[m],z[n]) t[n+1] = t[m] + h Higher order differential equations Recall that when you have higher-order differential equations (second-order or higher), these can be decomposed into a system of first-order differential equations, which can then be solved sequentially. For example, a second-order differential equation of the form d'z = f(z,1) where /(z, () is some function of z and r, can be decomposed into the following system of first-order differential equations dz - = D given some initial conditions. These two differential equations can then be solved sequentially
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


