Question: inclass3.py below # In this program we will experiment with the idea of multisorting # Multisorting is a process by which we sort a complex
 inclass3.py below
inclass3.py below
# In this program we will experiment with the idea of multisorting # Multisorting is a process by which we sort a complex dataset repeatedly by different attributes # When performing a multisort we care about the stability of the data (tied items preserve prior order) # For this practice you will need to modify the base sorting algorithm to work with complex data. # By default, the data is read in from file, broken into an array, and loaded into another array. # This gives us a two dimensional array. The interior arrays are composed of the following: # [first_name, last_name, major, age, GPA] # You will modify the stable sorting algorithm of your choice to work with this 2-D array # (all sorts from basic_sorts.py are included) # Reminder that we must use a stable sort, and that we must be able to select the attribute that # is to be sorted upon.
def main(): in_name = "large_student_list.txt"
try: my_data = [] in_file = open(in_name) for line in in_file: tmp = line.split('\t') my_data.append([tmp[0], tmp[1], tmp[2], int(tmp[3]), float(tmp[4])])
in_file.close()
except IOError: print("There was an error reading the file!")
# We complete the rest of the program after the try/except block for item in my_data: print(item) print("Below this print statement place multiple calls to the sorting method you modify") print("As an example, have bubblesort be called on first name, last name, major") print("Or insertion sort on age, last name, gpa")
# Bubblesort # Precondition: The input my_array is an array of Comparable elements. # Postcondition: The Comparable data inside my_array will be placed in sorted order. def bubbleSort(my_array): n = len(my_array) # operation # Traverse through all array elements for i in range(n): # instantiation of a loop is 2-4, every iteration is 2 swapped = False # Last i elements are already in place for j in range(0, n-i-1): # traverse the array from 0 to n-i-1 # Swap if the element found is greater # than the next element if my_array[j] > my_array[j+1]: # print("Swapping items %s and %s" % (my_array[j], my_array[j+1])) my_array[j], my_array[j+1] = my_array[j+1], my_array[j] swapped = True if (not swapped): break
# Selectionsort # Precondition: The input my_array is an array of Comparable elements. # Postcondition: The Comparable data inside my_array will be placed in sorted order. def selectionSort(my_array): # Traverse through all array elements for i in range(len(my_array)): # Find the minimum element in remaining # unsorted array min_idx = i for j in range(i+1, len(my_array)): if my_array[min_idx] > my_array[j]: min_idx = j # print("Min_index reassigned") # Swap the found minimum element with # the first element # print("Swapping %s into slot %d" % (my_array[min_idx], i)) my_array[i], my_array[min_idx] = my_array[min_idx], my_array[i]
# Insertionsort # Precondition: The input my_array is an array of Comparable elements. # Postcondition: The Comparable data inside my_array will be placed in sorted order. def insertionSort(my_array): # Traverse through 1 to len(my_array) for i in range(1, len(my_array)): key = my_array[i] # print("We are looking to correctly place %d into our array! It is currently the %d element" % (key, i)) # Move elements of my_array[0..i-1], that are # greater than key, to one position ahead # of their current position j = i-1 while j >= 0 and key
# Shellsort # Precondition: The input my_array is an array of Comparable elements. # Postcondition: The Comparable data inside my_array will be placed in sorted order. # Shellsort's efficiency depends on the gap sequence, and the method in which it changes. # Feel free to edit the gap sequence and its reduction def shellSort(my_array): # Start with a big gap, then reduce the gap n = len(my_array) gap = n//2 # Guarantees an integer result # print("Starting gap sequence is %d" % gap) # Do a gapped insertion sort for this gap size. # The first gap elements a[0..gap-1] are already in gapped # order keep adding one more element until the entire array # is gap sorted while gap > 0: for i in range(gap,n): # add a[i] to the elements that have been gap sorted # save a[i] in temp and make a hole at position i temp = my_array[i] # shift earlier gap-sorted elements up until the correct # location for a[i] is found j = i while j >= gap and my_array[j-gap] >temp: my_array[j] = my_array[j-gap] # print("Swapping %s and %s" % (my_array[j], temp)) j -= gap # put temp (the original a[i]) in its correct location my_array[j] = temp gap //= 2 # print("Our new gap sequence is %d" % gap) # print(my_array)
# Mergesort # Precondition: The input my_array is an array of Comparable elements. # Postcondition: The Comparable data inside my_array will be placed in sorted order. def mergeSort(my_array): if len(my_array) > 1: mid = len(my_array)//2 #Finding the mid of the array L = my_array[:mid] # Dividing the array elements (grabs allelements until mid) R = my_array[mid:] # into 2 halves # print(L) # print(R)
mergeSort(L) # Sorting the first half mergeSort(R) # Sorting the second half # Continues until array of size 1 i = j = k = 0 # Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[] while i
# Partition # Helper method for quicksort def partition(my_array,low,high): i = ( low-1 ) # index of smaller element pivot = my_array[high] # pivot # print("We are using %s as the pivot" % pivot) for j in range(low , high): # If current element is smaller than the pivot if my_array[j]
main()
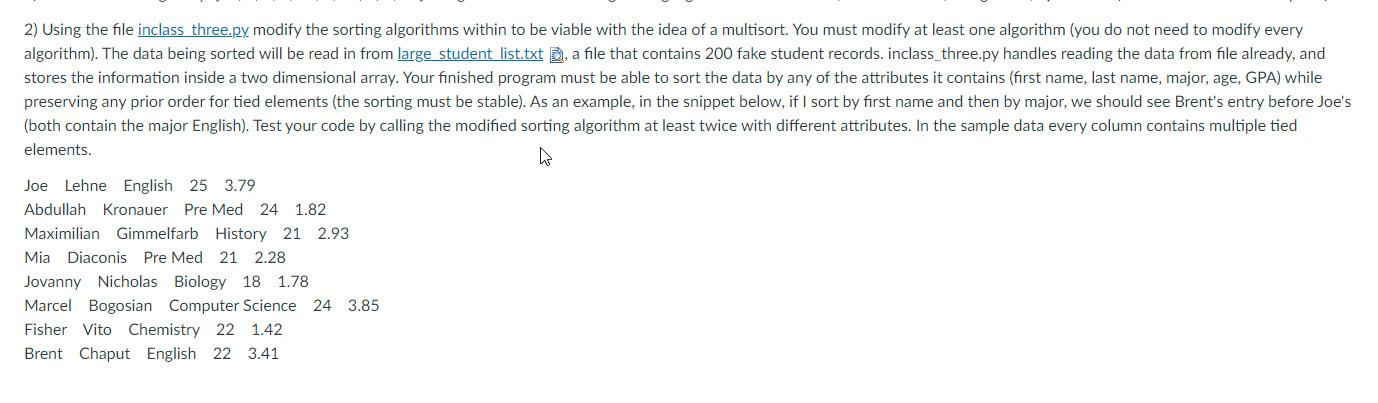
2) Using the file inclass three.py modify the sorting algorithms within to be viable with the idea of a multisort. You must modify at least one algorithm (you do not need to modify every algorithm). The data being sorted will be read in from large student list.txt , a file that contains 200 fake student records, inclass_three.py handles reading the data from file already, and stores the information inside a two dimensional array. Your finished program must be able to sort the data by any of the attributes it contains (first name, last name, major, age, GPA) while preserving any prior order for tied elements (the sorting must be stable). As an example, in the snippet below, if I sort by first name and then by major, we should see Brent's entry before Joe's (both contain the major English). Test your code by calling the modified sorting algorithm at least twice with different attributes. In the sample data every column contains multiple tied elements. Joe Lehne English 25 3.79 Abdullah Kronauer Pre Med 24 1.82 Maximilian Gimmelfarb History 21 2.93 Mia Diaconis Pre Med 21 2.28 Jovanny Nicholas Biology 18 1.78 Marcel Bogosian Computer Science 24 3.85 Fisher Vito Chemistry 22 1.42 Brent Chaput English 22 3.41 2) Using the file inclass three.py modify the sorting algorithms within to be viable with the idea of a multisort. You must modify at least one algorithm (you do not need to modify every algorithm). The data being sorted will be read in from large student list.txt , a file that contains 200 fake student records, inclass_three.py handles reading the data from file already, and stores the information inside a two dimensional array. Your finished program must be able to sort the data by any of the attributes it contains (first name, last name, major, age, GPA) while preserving any prior order for tied elements (the sorting must be stable). As an example, in the snippet below, if I sort by first name and then by major, we should see Brent's entry before Joe's (both contain the major English). Test your code by calling the modified sorting algorithm at least twice with different attributes. In the sample data every column contains multiple tied elements. Joe Lehne English 25 3.79 Abdullah Kronauer Pre Med 24 1.82 Maximilian Gimmelfarb History 21 2.93 Mia Diaconis Pre Med 21 2.28 Jovanny Nicholas Biology 18 1.78 Marcel Bogosian Computer Science 24 3.85 Fisher Vito Chemistry 22 1.42 Brent Chaput English 22 3.41
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


