Question: Need help with this C++ lab please!! Open with A262: Lab 1 Lab 1: Speed Sensors You may have seen a set of wires going
Need help with this C++ lab please!!



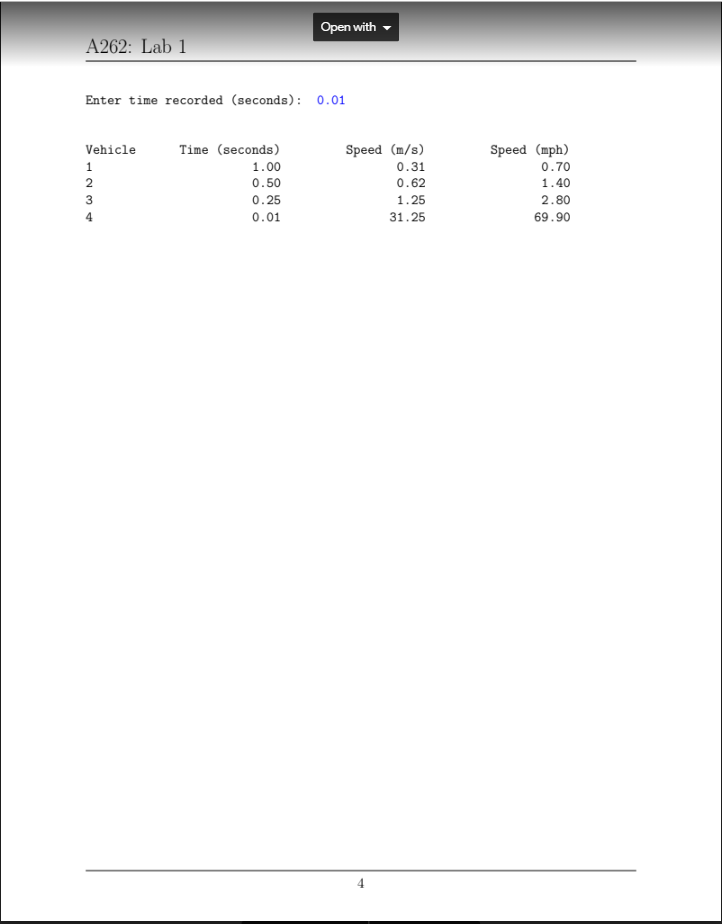
Open with A262: Lab 1 Lab 1: Speed Sensors You may have seen a set of wires going across the road while driving at some point. Usually, there are two in a row that cars will drive over. These can be used to count cars, but they can also be used to determine how fast a car is going. You will write a program that asks the user how far apart the wires are and the recorded times for four vehicles, then prints out a table showing each car's time in seconds, speed in meters per second (m/s), and speed in miles per hour (mph). Some Physics To compute the speed of the car, you can use the kinematic equation I=v*t where r is the distance covered, v is the velocity in meters per second, and t is the time in seconds. We will assume cars have a constant velocity. Since you know I, as that is the distance between the wires, and you know the time it takes for one wheel to cross both wires, as that is what is recorded, you just have to manipulate this equation a bit to get Beware of Units! Physics equations use the International System of Units (SI Units). What this means for us is distance is measured in meters; velocity is measures in meters per second; time is measured in seconds. You should ask for time in seconds. You should ask for the distance between the wires in inches. Thus, your program will have to do some unit conversions. To convert, remember 1 inch 2.5 centimeters 0.025 meters To convert from meters per second (m/s) to miles per hour (mph), use dimensional analysis. meter 3600 seconds 1 mile 1 second 1 hour 1609 meters For example, to convert 100 m/s, you would calculate 100 meter 3600 seconds 1 mile 100 * 3600 miles 1 second 223.7 mph 1 hour 1609 meters 1609 hour Recall that units cancel out like numbers can. You can also combine some of the calculations above and multiply 100 * 2.2374. 1 Page + A262: Lab 1 Functions To complete this program, you must implement (and use!) the following functions: getInput: Takes a string and returns a double. This function asks the user for a number, using the string argument as the prompt to the user. It continues to ask until the user enters a positive number, then returns the valid number. Note the number may or may not be an integer. Example: get Input("Enter a number: ") should ask the user for a number, us- ing the parameter string, until they enter a positive number; then return that number. So if the user entered 0, -2,5, the function would return 5. convertDistance: Takes a double and returns a double. The parameter is the number of inches. This function should convert the number of inches to meters, then return the number of meters. Do not round your answer. Example: convertDistance (10) => 0.25 getSpeed: Takes two doubles and returns a double. The parameters are the number of meters and the number of seconds (in that order). The function returns the speed of the object in meters per second. Example: getSpeed (30, 15) => 2.0; meaning an object that moved 30 meters in 15 seconds is moving 2 m/s convertSpeed: Takes a double and returns a double. The parameter is a measurement of meters per second. The function should convert the parameter to miles per hour and return that value. Do not round your answer. Example: getSpeed (100) => 223.7 The function declarations are given in functions.h. Do not modify the function signa- tures. Do not add other functions. I've also given you a main function that contains sample tests to test each of the functions. Be sure to test your functions thoroughly. Look at the example output below to see how your program should be formatted and what information needs to be printed out. Your program should look like the example program. Hints and Resources Use the iomanip functions to format your final table. You can find more information here: http://cplusplus.com/reference/iomanip/ Use an array to store the cars times Page 214 + Open with A262: Lab 1 The 'const' modifier in the function signatures just means that you cannot modify that argument - the strings' values can't be changed, and the array items cannot be changed. The strings are also passed as references (string&); this just means that rather than copying the value of the string into a new variable, the compiler tells the function the memory location of the argument. Neither of these things changes how you call the function! What to Turn In Upload your source files, main.cpp and functions.cpp. You don't need to turn in functions.h, as you should not have modified it. Example Output Here is an example of what your program should output. It is vitally important that your program takes input in the same order as shown here. User input is in blue. Example One Enter the distance between the wires (inches): 20 Enter time recorded (seconds): 10 Enter time recorded (seconds): 5 Enter time recorded (seconds): 2.5 Enter time recorded (seconds): 0.5 Vehicle 1 2 3 4 Time (seconds) 10.00 5.00 2.50 0.50 Speed (m/s) 0.05 0.10 0.20 1.00 Speed (mph) 0.11 0.22 0.45 2.2 Example Two Enter the distance between the wires (inches): 0 Enter the distance between the wires (inches): -4 Enter the distance between the wires (inches): 12.5 Enter time recorded (seconds): 0 Enter time recorded (seconds): -5 Enter time recorded (seconds): -2 Enter time recorded (seconds): Enter time recorded (seconds): 0.5 Enter time recorded (seconds): 0.25 1 3 Pane 2 Open with A262: Lab 1 Enter time recorded (seconds): 0.01 Vehicle 1 2 3 4 Time (seconds) 1.00 0.50 0.25 0.01 Speed (m/s) 0.31 0.62 1.25 31.25 Speed (mph) 0.70 1.40 2.80 69.90 4 File Edit View Git Project Build Debug Test Analyze Tools Extensions Window Help Search (Ctrl+Q) JT e CS262 Lab1 CE ? 11 - Debug - x86 Local Windows Debugger - Auto Live Share Solution Explorer - 4 x sample Tests.cpp main.cpp* + X o $ * * CS262Lab1 (Global Scope) 1 Search Solution Explorer (Ct 2 Solution 'CS262Labl' (1 of 1 3 #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


