Question: #include graph.h int main() { // OPTIONAL: Test your implementation here // This code will run if you click on the Run button. // //
#include "graph.h"
int main() { // OPTIONAL: Test your implementation here // This code will run if you click on the "Run" button. // // You can also click on the "Check" or "Submit" button // button to run the automated tests. // // Note that passing all the automated tests does not // necessarily mean that there are no issues in the code. // For example, the automated tests do not check for // memory leaks.
return 0; }
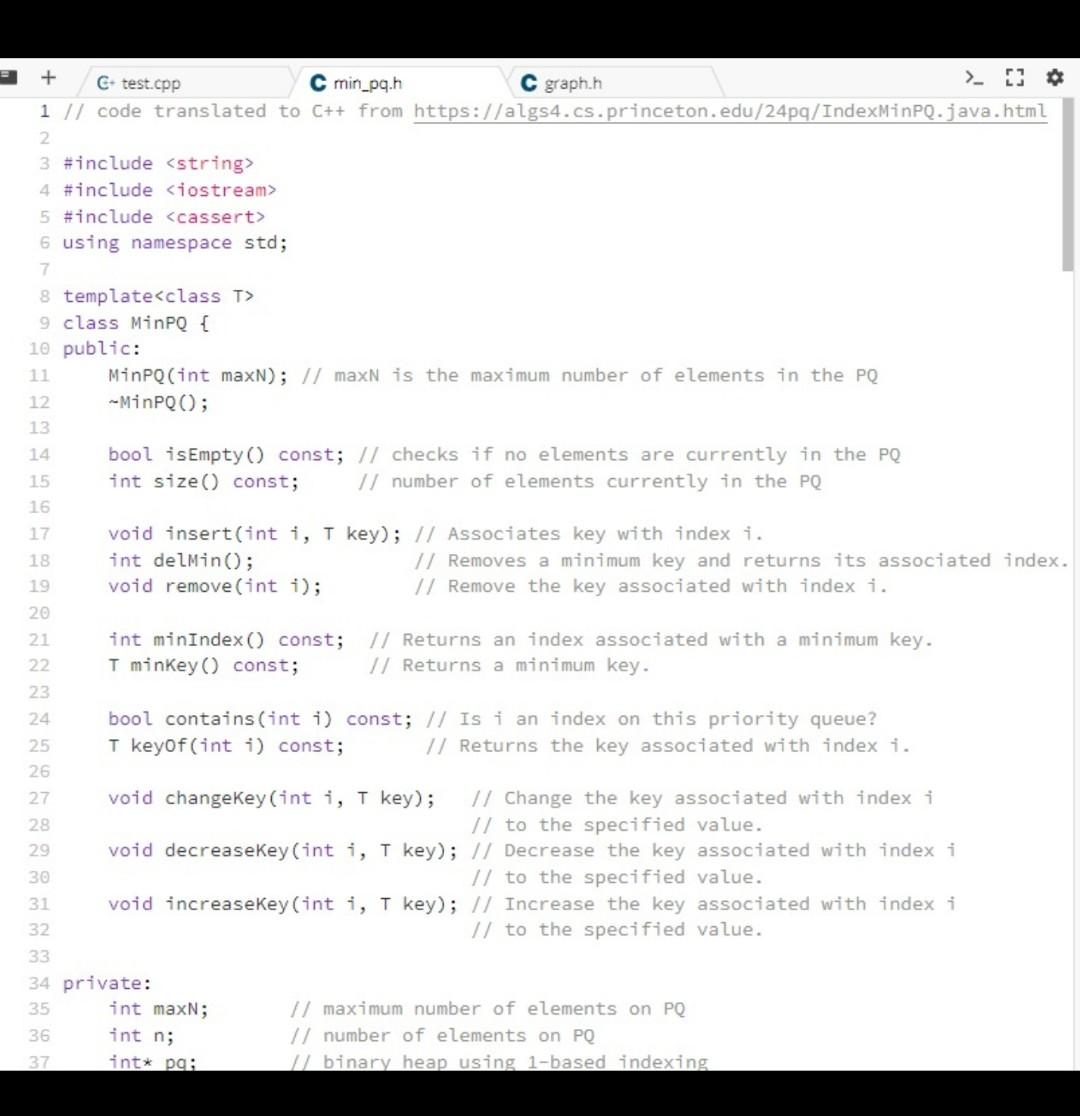
// code translated to C++ from https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/24pq/IndexMinPQ.java.html
#include #include #include using namespace std;
template class MinPQ { public: MinPQ(int maxN); // maxN is the maximum number of elements in the PQ ~MinPQ();
bool isEmpty() const; // checks if no elements are currently in the PQ int size() const; // number of elements currently in the PQ
void insert(int i, T key); // Associates key with index i. int delMin(); // Removes a minimum key and returns its associated index. void remove(int i); // Remove the key associated with index i.
int minIndex() const; // Returns an index associated with a minimum key. T minKey() const; // Returns a minimum key.
bool contains(int i) const; // Is i an index on this priority queue? T keyOf(int i) const; // Returns the key associated with index i.
void changeKey(int i, T key); // Change the key associated with index i // to the specified value. void decreaseKey(int i, T key); // Decrease the key associated with index i // to the specified value. void increaseKey(int i, T key); // Increase the key associated with index i // to the specified value.
private: int maxN; // maximum number of elements on PQ int n; // number of elements on PQ int* pq; // binary heap using 1-based indexing int* qp; // inverse of pq - qp[pq[i]] = pq[qp[i]] = i T* keys; // keys[i] = priority of i
// Helper functions void validateIndex(int i) const; bool greater(int i, int j) const; void exch(int i, int j); void swim(int k); void sink(int k); };
template MinPQ::MinPQ(int maxN) { if (maxN maxN = maxN; n = 0;
keys = new T[maxN + 1]; pq = new int[maxN + 1]; qp = new int[maxN + 1]; for (int i = 0; i
template MinPQ::~MinPQ() { delete [] pq; delete [] qp; delete [] keys; }
template bool MinPQ::isEmpty() const { return n == 0; }
template int MinPQ::size() const { return n; }
// Is i an index on this priority queue? template bool MinPQ::contains(int i) const { validateIndex(i); return qp[i] != -1; }
// Associates key with index i. template void MinPQ::insert(int i, T key) { validateIndex(i); if (contains(i)) throw string("index is already in the priority queue"); n++; qp[i] = n; pq[n] = i; keys[i] = key; swim(n); }
// Returns an index associated with a minimum key. template int MinPQ::minIndex() const { if (n == 0) throw string("Priority queue underflow"); return pq[1]; }
// Returns a minimum key. template T MinPQ::minKey() const { if (n == 0) throw string("Priority queue underflow"); return keys[pq[1]]; }
// Removes a minimum key and returns its associated index. template int MinPQ::delMin() { if (n == 0) throw string("Priority queue underflow"); int min = pq[1]; exch(1, n--); sink(1); assert(min == pq[n+1]); qp[min] = -1; // delete pq[n+1] = -1; // not needed return min; }
// Returns the key associated with index i. template T MinPQ::keyOf(int i) const { validateIndex(i); if (!contains(i)) throw string("index is not in the priority queue"); else return keys[i]; }
// Change the key associated with index i to the specified value. template void MinPQ::changeKey(int i, T key) { validateIndex(i); if (!contains(i)) throw string("index is not in the priority queue"); keys[i] = key; swim(qp[i]); sink(qp[i]); }
// Decrease the key associated with index i to the specified value. template void MinPQ::decreaseKey(int i, T key) { validateIndex(i); if (!contains(i)) throw string("index is not in the priority queue"); if (keys[i] == key) throw string("Calling decreaseKey() with a key equal to the key in the priority queue"); if (keys[i] the key in the priority queue"); keys[i] = key; swim(qp[i]); }
// Increase the key associated with index i to the specified value. template void MinPQ::increaseKey(int i, T key) { validateIndex(i); if (!contains(i)) throw string("index is not in the priority queue"); if (keys[i] == key) throw string("Calling increaseKey() with a key equal to the key in the priority queue"); if (keys[i] > key) throw string("Calling increaseKey() with a key // Remove the key associated with index i. template void MinPQ::remove(int i) { validateIndex(i); if (!contains(i)) throw string("index is not in the priority queue"); int index = qp[i]; exch(index, n--); swim(index); sink(index); qp[i] = -1; }
// throw an IllegalArgumentException if i is an invalid index template void MinPQ::validateIndex(int i) const { if (i = maxN) throw string("index >= capacity: " + i); }
template bool MinPQ::greater(int i, int j) const { return keys[pq[i]] > keys[pq[j]]; }
template void MinPQ::exch(int i, int j) { int swap = pq[i]; pq[i] = pq[j]; pq[j] = swap; qp[pq[i]] = i; qp[pq[j]] = j; }
template void MinPQ::swim(int k) { while (k > 1 && greater(k/2, k)) { exch(k, k/2); k = k/2; } }
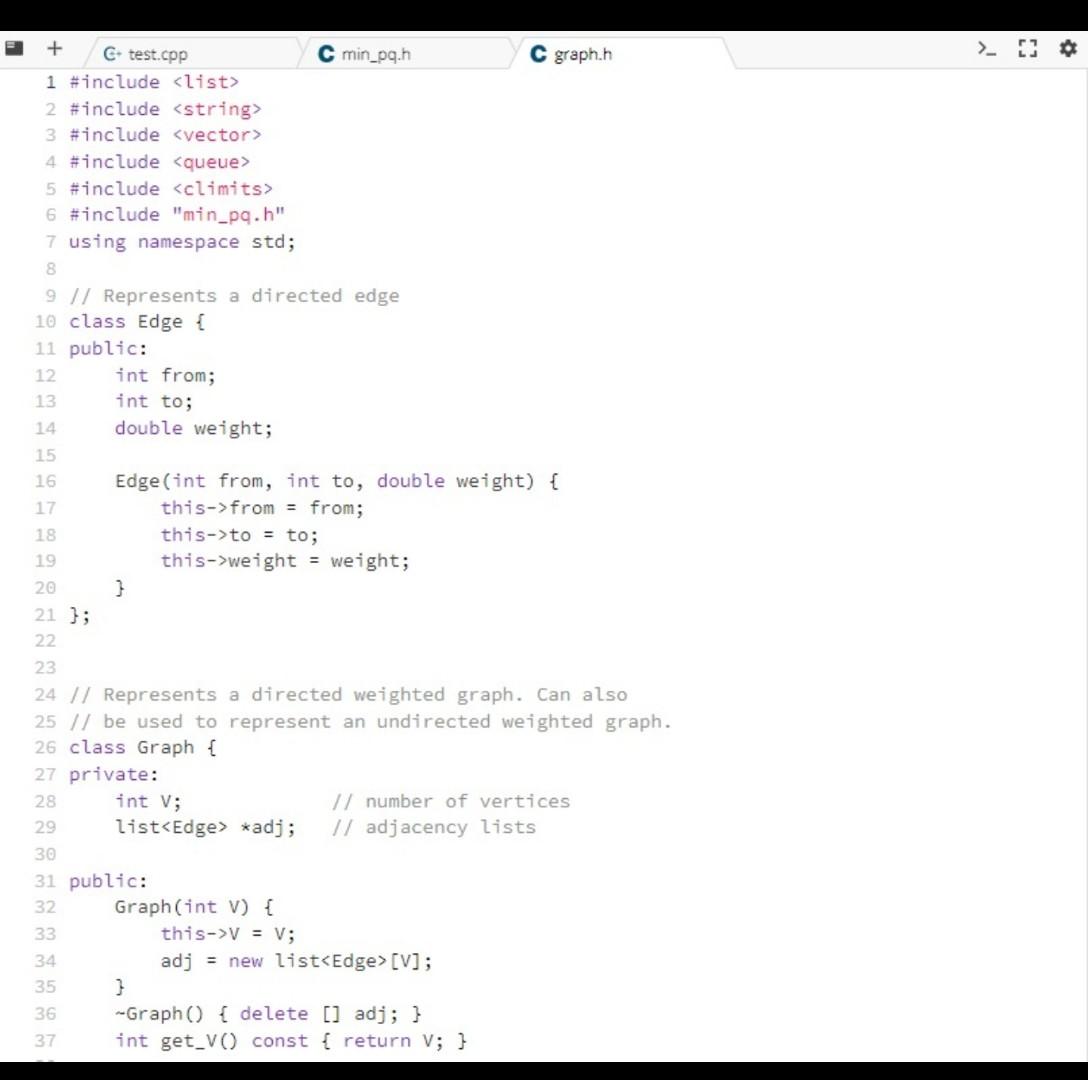
template void MinPQ::sink(int k) { while (2*k #include #include #include #include #include #include "min_pq.h" using namespace std;
// Represents a directed edge class Edge { public: int from; int to; double weight;
Edge(int from, int to, double weight) { this->from = from; this->to = to; this->weight = weight; } };
// Represents a directed weighted graph. Can also // be used to represent an undirected weighted graph. class Graph { private: int V; // number of vertices list *adj; // adjacency lists
public: Graph(int V) { this->V = V; adj = new list[V]; } ~Graph() { delete [] adj; } int get_V() const { return V; }
// adds an edge from v to w with the given weight void add_edge(int v, int w, double weight) { if (weight
// checks if there is an edge from v to w bool has_edge(int v, int w) const { for (Edge edge : adj[v]) if (edge.to == w) return true; return false; }
// prints the graph void print() const { for (int v = 0; v
// Q1 bool is_undirected() const;
// Q2.A vector get_reachable_from(int s) const;
// Q2.B vector> connected_components() const;
// Q3 void shortest_paths(const vector& sources, vector& dist, vector& parent) const; };
// Returns true if the graph can be considered an undirected // graph. I.e. if for every edge v -> w there is also an edge w -> v // with the same weight. bool Graph::is_undirected() const { // ADD YOUR CODE HERE
return false; }
// Returns all the vertices in the graph that are // reachable from the given {source} vertex. vector Graph::get_reachable_from(int s) const { vector result;
// ADD YOUR CODE HERE
return result; }
// Returns all the connected components in the graph assuming // that the graph is undirected. The vertices of each component // are stored in a separate vector. vector> Graph::connected_components() const { vector> result;
// ADD YOUR CODE HERE
return result; }
// Computes the shortest paths from the given source vertices // to every vertex in the graph. // Store the result in the given {dist} and {parent} vectors, // where the {dist} vector stores the shortest distances and // the {parent} vector stores the shortest paths. void Graph::shortest_paths(const vector& sources, vector& dist, vector& parent) const { dist.clear(); parent.clear();
// ADD YOUR CODE HERE }
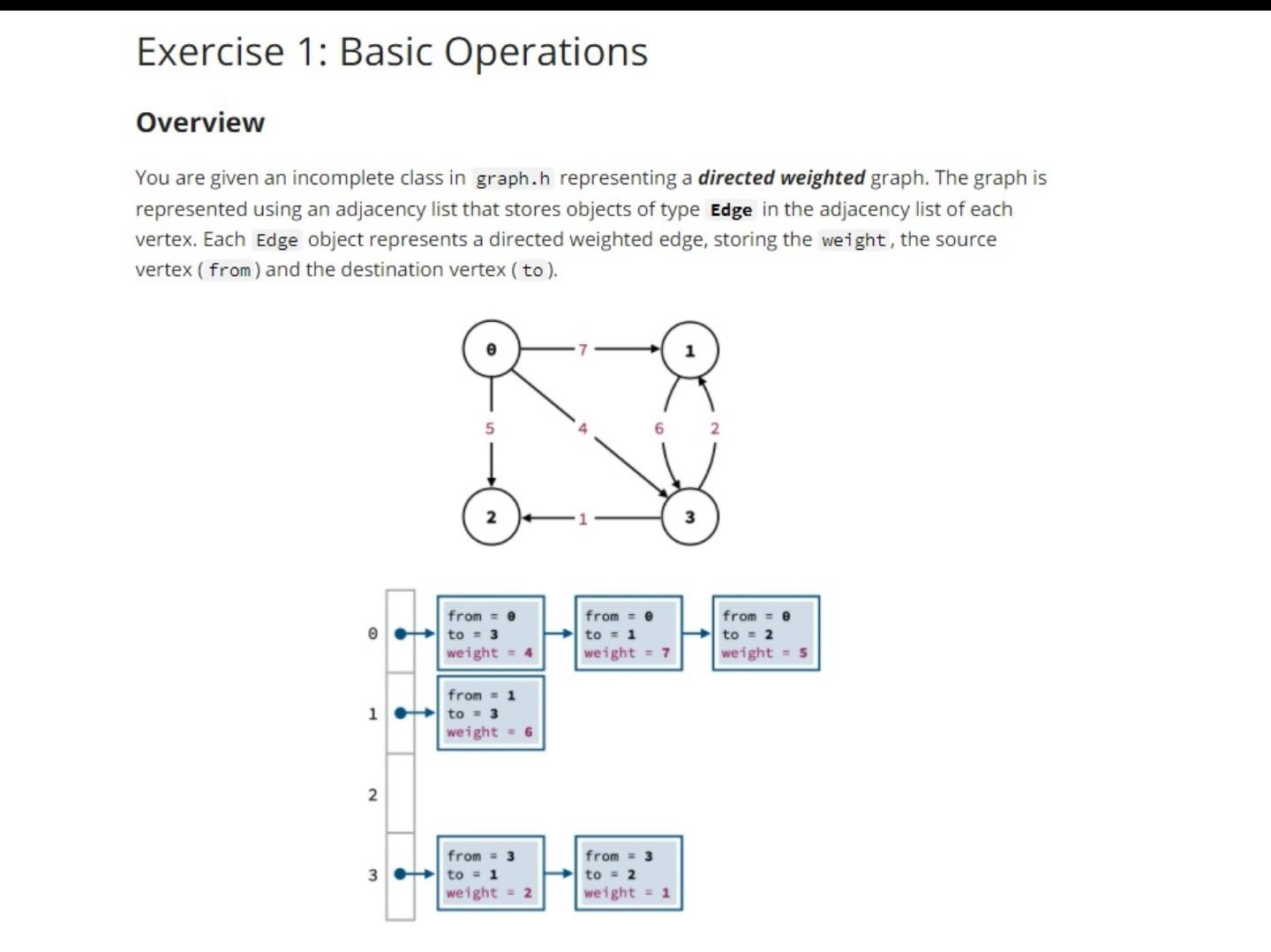
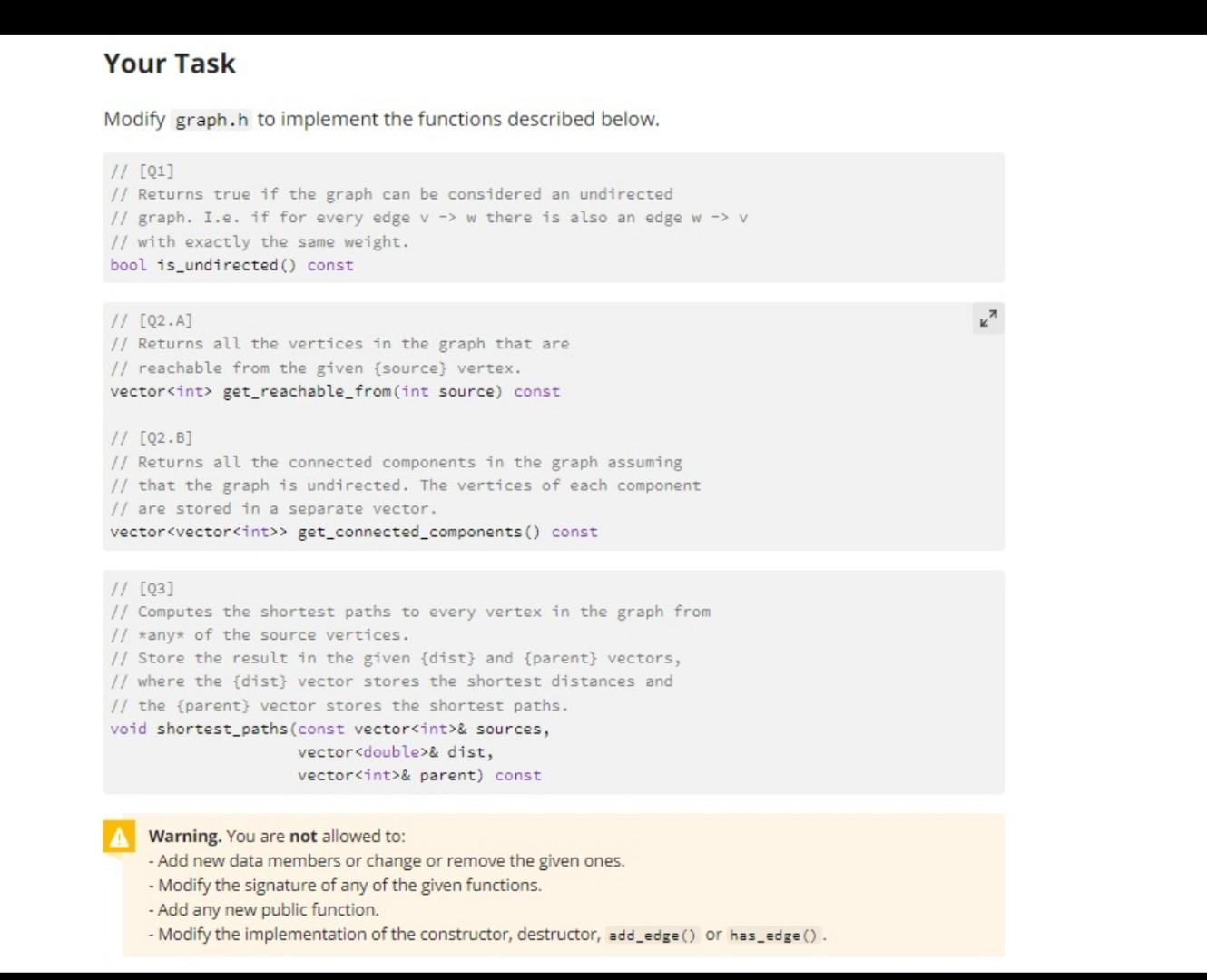
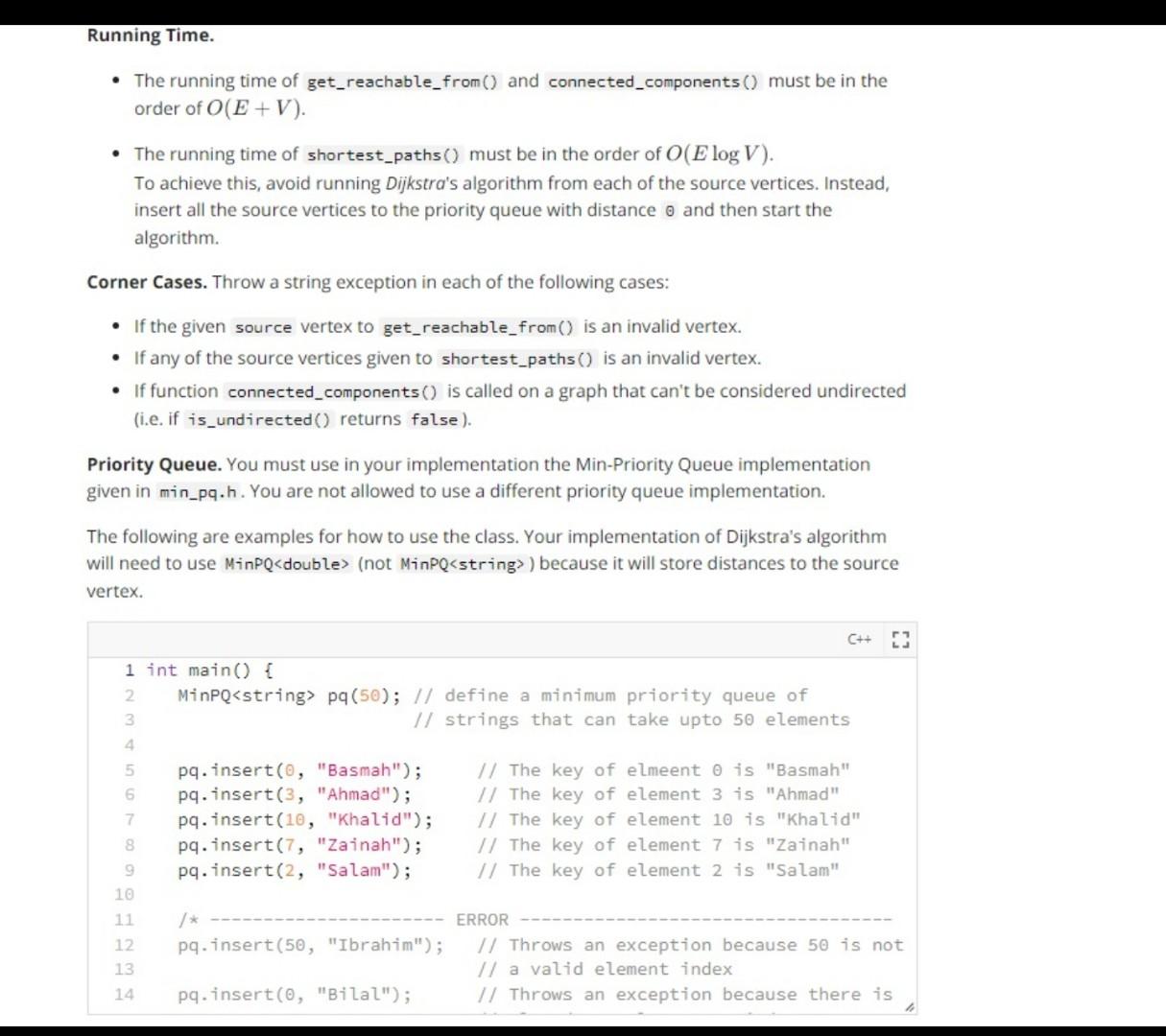
Exercise 1: Basic Operations Overview You are given an incomplete class in graph.h representing a directed weighted graph. The graph is represented using an adjacency list that stores objects of type Edge in the adjacency list of each vertex. Each Edge object represents a directed weighted edge, storing the weight, the source vertex (from) and the destination vertex (to). from to = 3 weight from = 0 to = weight = 7 from = to = 2 weight = 5 1 from = 1 to = 3 weight = 6 2 3 from = 3 to = 1 weight = 2 from = 3 to = 2 weight = 1 Your Task Modify graph.h to implement the functions described below. // [21] // Returns true if the graph can be considered an undirected // graph. I.e. if for every edge v -> W there is also an edge w -> V // with exactly the same weight. bool is_undirected() const // [Q2.A] // Returns all the vertices in the graph that are // reachable from the given {source} vertex. vector int> get_reachable_from(int source) const II (02.B] // Returns all the connected components in the graph assuming // that the graph is undirected. The vertices of each component // are stored in a separate vector. vector> get_connected_components() const // [23] // Computes the shortest paths to every vertex in the graph from // *any of the source vertices. // Store the result in the given {dist) and {parent} vectors, // where the dist} vector stores the shortest distances and // the {parent} vector stores the shortest paths. void shortest_paths (const vector int>& sources, vector& dist, vector int>& parent) const A Warning. You are not allowed to: - Add new data members or change or remove the given ones. Modify the signature of any of the given functions. - Add any new public function. - Modify the implementation of the constructor, destructor, add_edge() or has_edge(). Running Time. The running time of get_reachable_from() and connected_components() must be in the order of O(E+V). The running time of shortest_path() must be in the order of O(E log V). To achieve this, avoid running Dijkstra's algorithm from each of the source vertices. Instead, insert all the source vertices to the priority queue with distance and then start the algorithm Corner Cases. Throw a string exception in each of the following cases: If the given source vertex to get_reachable_from() is an invalid vertex. If any of the source vertices given to shortest_path() is an invalid vertex. If function connected_components() is called on a graph that can't be considered undirected (i.e. if is_undirected() returns false ). Priority Queue. You must use in your implementation the Min-Priority Queue implementation given in min_pq.h. You are not allowed to use a different priority queue implementation. The following are examples for how to use the class. Your implementation of Dijkstra's algorithm will need to use MinPQ (not MinPQ ) because it will store distances to the source vertex. C++ 3 1 int main() { 2 MinPQ pq (50); // define a minimum priority queue of 3 Il strings that can take upto 50 elements 4 5 pq.insert(0, "Basmah"); // The key of elmeent 0 is "Basmah" 6 pq.insert(3, "Ahmad"); // The key of element 3 is "Ahmad" 7 pq.insert(10, "Khalid"); // The key of element 10 is "Khalid" 8 pq.insert(7, "Zainah"); // The key of element 7 is "Zainah" 9 pq.insert(2, "Salam"); // The key of element 2 is "Salam" 10 11 ERROR 12 pq.insert(50, "Ibrahim"); I! Throws an exception because 50 is not 13 Il a valid element index 14 pq.insert(0, "Bilal"); // Throws an exception because there is . * + G+ test.cpp min_pq.h C graph.h 1 #include "graph.h" 2 3 int main() { 4 // OPTIONAL: Test your implementation here Il This code will run if you click on the "Run" button. I Il You can also click on the "Check" or "Submit" button 8 // button to run the automated tests. 9 10 // Note that passing all the automated tests does not 11 necessarily mean that there are no issues in the code. 12 For example, the automated tests do not check for 13 // memory leaks. 14 15 return; 16 ] 000 + C+ test.cpp C min_pq.h C graph.h 1 // code translated to C++ from https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/24pq/IndexMinPQ.java.html 2 3 #include 4 #include 5 #include 6 using namespace std; 7 8 template 9 class MinPQ { 10 public: 11 MinPo(int maxN); // max is the maximum number of elements in the PQ 12 -MinPQ(); 13 14 bool isEmpty() const; // checks if no elements are currently in the PQ 15 int size() const; Il number of elements currently in the PQ 16 17 void insert(int i, T key); // Associates key with index 1. 18 int delMin(); // Removes a minimum key and returns its associated index. 19 void remove(int i); // Remove the key associated with index i. 20 21 int minIndex() const; // Returns an index associated with a minimum key. 22 T minkey() const; // Returns a minimum key. 23 24 bool contains (int i) const; // Is an index on this priority queue? 25 T keyof(int i) const; // Returns the key associated with index i. 26 27 void changeKey (int i, T key); 1/ Change the key associated with index i 28 // to the specified value. 29 void decreaseKey(int i, T key); // Decrease the key associated with index i 30 Il to the specified value. 31 void increaseKey(int i, T key); // Increase the key associated with index i 32 // to the specified value. 33 34 private: 35 int maxN; // maximum number of elements on PQ 36 // number of elements on PQ 37 int* poi // binary heap using 1-based indexing int n; > I + G test.cpp C min_pq.h C graph.h 1 #include 2 #include 3 #include 4 #include 5 #include 6 #include "min_pq.h" 7 using namespace std; 8 9 // Represents a directed edge 10 class Edge { 11 public: 12 int from; 13 int to; 14 double weight; 15 16 Edge (int from, int to, double weight) { 17 this->from = from; 18 this->to = to; 19 this->weight = weight; 20 } 21 }; 22 23 24 // Represents a directed weighted graph. Can also 25 // be used to represent an undirected weighted graph. 26 class Graph { 27 private: 28 int V; // number of vertices 29 list *adj; // adjacency lists 30 31 public: 32 Graph(int V) { 33 this->V = V; 34 adj = new list [V]; 35 } 36 --Graph() { delete [] adj; } 37 int get_V) const { return V; }