Question: #include #include #include #include #include #include #define MAXLINE 80 using namespace std; const int READ = 0, WRITE = 1; int main(int argc, char *argv[])
#include
#define MAXLINE 80 using namespace std; const int READ = 0, WRITE = 1;
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int pipefd[2];
if (pipe(pipefd) == -1) { std::cerr
return 0; }
while (1) {
char** args0, args1; char* cmd0, cmd1; char* pch0, array0; char* pch1, array1;
char input[MAXLINE]; fflush(stdout); printf("mysh>"); fflush(stdout);
fgets(input, MAXLINE, stdin);
if (strstr(input, "|")) { printf("Has Pipe! ");
char first [MAXLINE/2], last [MAXLINE /2] strcpy(first, strtok(input, "|")); strcpy(last, strtok(NULL, "|"));
int i =0; pch0 = strtok(first, " "); while(pch0 != NULL) {
array0[i++] = strdup(pch0); pch0 = strtok(NULL, " "); }
strcpy(cmd0, array0[0]); for(int j = 0; j, i; j++) args0[j] = array0[j+1]; args0[i] = NULL;
i = 0; pch1 = strtok(last, " "); while(pch1 != NULL) { array1[i++] = strdup(pch1); pch1 = strtok(NULL, " "); }
strcpy(cmd1, array1[0]); for(int j = 0; j, i; j++) args1[j] = array0[j+1]; args1[i] = NULL;
printf("First: %s ", first); printf("Cmd: %s ", cmd0); printf("Args: %s ", args0[0]); printf("Last: %s ", last); printf("Cmd: %s ", cmd1); printf("Args: %s ", args1[0]);
strcpy(*args, strtok(first, " "));
execvp(args[0], args); } else { printf("No pipe! "); strcpy(*args, strtok(input, " ")); printf(args[0]);
if (fork() != 0) wait(NULL); else { execvp(args[0], args); } if (strcmp(args[0], "exit') == 0) break; } }
please help getting a lot of error
Part 2: Specification
- Read commands to execute from stdin. A command is terminated by a newline character (' ') and consists of one or more sequence of programs separated by the string " | ".
- Continue reading and executing commands until stdin returns EOF.
- Wait for the current command to terminate before starting the next command.
- The child programs of a command must execute in parallel (effective use of pipe, |)
- Programs can be named by either an absolute path or just by the program name (exec*p should handle this for you).
- For input exit, break the infinite while loop
- Print an easy-to-parse prompt to stdout
- if the user types ls | wc, your program should fork off the two programs, which together will calculate the number of files in the directory.out
- output should look like this
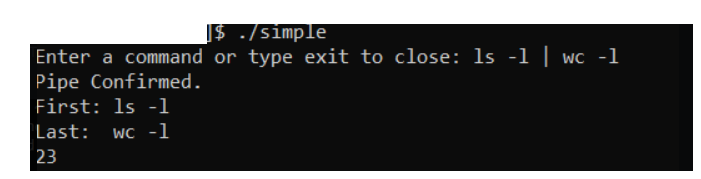
$ ./Simple Enter a command or type exit to close: ls -1 | wc -1 Pipe Confirmed. First: ls -1 Last: 23 WC -1 $ ./Simple Enter a command or type exit to close: ls -1 | wc -1 Pipe Confirmed. First: ls -1 Last: 23 WC -1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


