Question: #include #include #include #include struct element pop(struct node ** top); void push(struct node ** top, struct element new_data); bool isStackEmpty(struct node ** top); struct element
#include
struct element pop(struct node ** top); void push(struct node ** top, struct element new_data); bool isStackEmpty(struct node ** top);
struct element { int vertex_num; int cost_to_visit; }; struct node { struct element data;
struct node * next; };
struct element pop(struct node ** top) { struct element temp = (*top)->data; /// I copy the data at the top node into a temporary variable
struct node * ptr_temp = (*top)->next;
free(*top); *top = ptr_temp;
return(temp);
}
void push(struct node ** top, struct element new_data) { struct node * new_node = (struct node *) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
new_node->data = new_data; /// I can assign one struct to another if the type is the same
new_node->next = * top; * top = new_node; }
bool isStackEmpty(struct node ** top) { return(*top == NULL); }
#define NUM_VERTICES 10 /** This function takes a pointer to the the adjacency matrix of a Graph and the size of this matrix as arguments and prints the matrix */
void print_graph(int * graph, int size);
/** This function takes a pointer to the the adjacency matrix of a Graph, the size of this matrix, the source, and dest node numbers along with the weight or cost of the edge and fills the adjacency matrix accordingly. */ void add_edge(int * graph, int size, int src, int dst, int cost);
/** This function takes a pointer to the adjacency matrix of a graph, the size of this matrix, source, and destination vertex numbers as inputs and prints out the path from the source vertex to the destination vertex. It also prints the total cost of this path. */ void find_path_dfs(int * graph, int size, int src, int dst);
int main() { int my_graph[NUM_VERTICES][NUM_VERTICES]; /// An adjacency matrix representation of graph
memset(my_graph,-1,NUM_VERTICES * NUM_VERTICES * sizeof(int)); /// Initiallize with -1 representing infinte cost.
for(int i=0; i add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, i, i, 0); /// All the vertices have a cost of 0 for visiting themselves
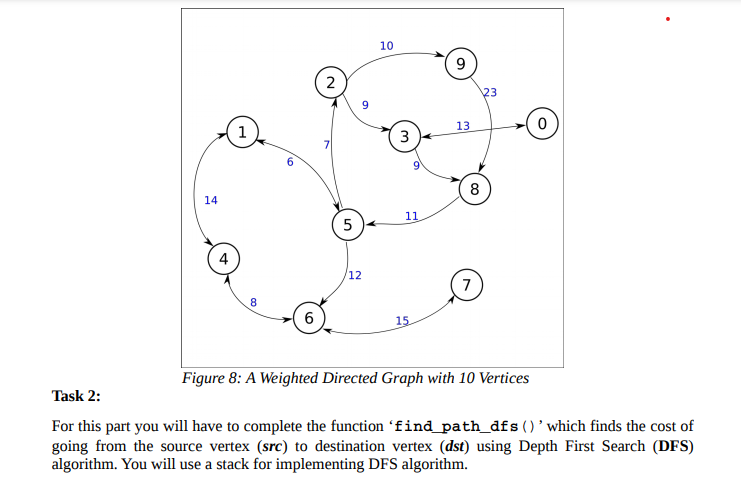
add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 0, 3, 13); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 1, 4, 14); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 1, 5, 6); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 2, 3, 9); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 2, 9, 10); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 3, 0, 13); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 3, 8, 9); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 4, 1, 14); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 4, 6, 8); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 5, 6, 12); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 5, 2, 7); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 6, 7, 15); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 6, 4, 8); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 7, 6, 15); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 8, 5, 11); add_edge(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 9, 8, 23);
/** Task 1: Complete the rest of the Adjacency Matrix according to Figure 8 **/
print_graph(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES); printf(" "); printf(" Find Path"); //find_path_dfs(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 4, 8); find_path_dfs(&my_graph[0][0], NUM_VERTICES, 7, 9); getchar(); return 0; }
void add_edge(int * graph, int size, int src, int dst, int cost) { *(graph+(src*size+dst)) = cost; /// Look carefully how the indices are calculated. You will need it for 2nd task. }
void print_graph(int * graph, int size) { //char vertices[size]; for(int i=0; i { printf("\t%d", i); } printf(" "); for(int x=0; x { printf("%d\t", x); for(int y=0; y printf("%d\t", *(graph+(x*size+y))); printf(" "); } }
void find_path_dfs(int * graph, int size, int src, int dst) {
int array_visited[NUM_VERTICES] = {0}; /// This array contains all the vertices that have been visited
struct node * top = NULL;
int current_visiting = src; //Setting the source vertex as the current vertex at the beginning int current_traversing = src; int path_cost = 0; bool PATH_FOUND = false;
while(!PATH_FOUND) { array_visited[current_visiting] = 1; ///Setting value of visited vertex to 1 struct element temp;
if(current_visiting == dst) //Checks if we have reached the destination { printf(" Path found: "); printf(" Cost: %d ", path_cost);
while(!isStackEmpty(&top)) { printf("Pop "); pop(&top); }
PATH_FOUND = true; continue; } else //If a current vertex is not the destination, traverse the other vertices { //complete this function } }
}
you only have to complete the else function in the end to find the cost
10 9 2 23 1 13 . 3 8 14 11 5 12 7 8 6 15 Figure 8: A Weighted Directed Graph with 10 Vertices Task 2: For this part you will have to complete the function 'find_path_dfs ()'which finds the cost of going from the source vertex (src) to destination vertex (dst) using Depth First Search (DFS) algorithm. You will use a stack for implementing DFS algorithm
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


