Question: #include stdio.h #include stdlib.h #include sys/stat.h /* A review on binary, octal, and decimal numbers. Converting from binary to base 10 ( decimal ): Binary
#include "stdio.h" #include "stdlib.h" #include "sys/stat.h"
/*
A review on binary, octal, and decimal numbers. Converting from binary to base 10 ( decimal ): Binary numbers are in this format ( for a 2 byte, 16-bit number ): PONM LKJI HGFE DCBA ---- ---- ---- ---- A: 1's place H: 128's place B: 2's place I: 256's place C: 4's place J: 512's place D: 8's place K: 1024's place E: 16's place L: 2048's place F: 32's place M: 4096's place G: 64's place N: 8192's place O: 16384's place P: 32768's place
Note: 0 is a bit turned off. 1 is a bit turned on. Let's convert the binary number 0000 1000 0101 0010 to base 10. Basically, you sum up each place, that has a 1. So for the above, we have 1 in 2048's place, 64's place, 16's place, and 2's place. So we sum up all those places: 2048+64+16+2 = 2130 So, 0000100001010010 = 2130 base10. Now, let's convert that to base8. If you group the bits into groups of 3, the number could look like this: 0 000 100 001 010 010 Each full 3 bit section can have a value from 0 through 7. In each section:
ABC --- A is the 4's place B is the 2's place C is the 1's place So the above number, comes down to 0 000 100 001 010 010 0 0 4 1 2 2 So in base 8, the number is 4122. So, the numbers, converted between bases looks like this: 0000100001010010 = 2130 = 4122 base2 base10 base8 binary decimal octal
0010 0000 32 base 10 in binary 00 100 000 40 base 8 in binary S_IRGRP = 00040 base 8 */
int main( int ac, char* av[] ) { int mode = S_IRGRP; // mode contains 32 base 10 == 00040 base 8 printf("%i ", mode ); // let's turn the 1's bit, using bitwise | and base 8 mode = mode | 01; printf("%i ", mode ); /* updated bit pattern: 0010 0001 33 base 10 in binary 00 100 001 41 base 8 in binary */ // let's turn on the 16's bit, using bitwise | and base 8 mode = mode | 010; printf("%i ", mode ); /* updated bit pattern 0011 0001 41 base 10 in binary 00 110 001 61 base 8 in binary */ /* let's determine if the 16's bit is turned on using bitwise & and masking. mode's current value: 41 base 10, 61 base 8 000 110 001 61 base 8 000 010 000 10 base 8 ___________ 000 010 000 16 base 8, =/= 0, therefore, true */ if ( mode & 010 ) printf("16's bit is on "); else printf("16's bit is off "); /* Ok, let's demonstrate turning off a bit. Here, we'll use assignment and bitwise and to turn bits off. 000 110 001 61 base8 111 101 111 757 base8 &= ___________ 000 101 001 51 base8, 41 base10 */ mode = mode & 0757; printf("%i ", mode ); return 0; }
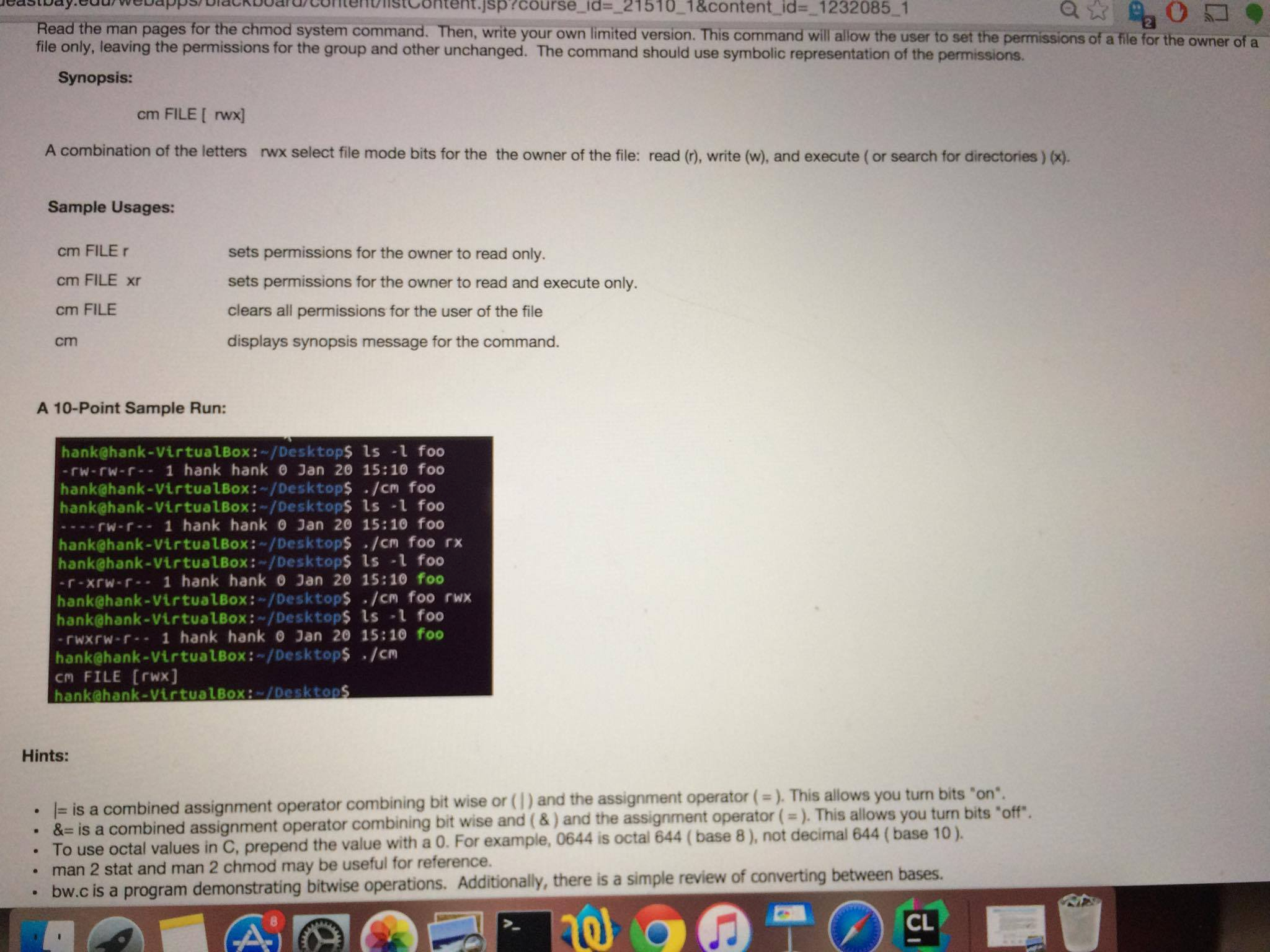
sibay:edur webappsackboardrcontenuistoontentjsprcourse id21510 1&content id 12320851 Read the man pages for the chmod system command. Then, write your own limited version. This command will allow the user to set the permissions of a file for the owner of a file only, leaving the permissions for the group and other unchanged. The command should use symbolic representation of the permissions 2 Synopsis: cm FILE [ rwx] A combination of the letters rwx select file mode bits for the the owner of the file: read (), write (w), and execute (or search for directories) o) Sample Usages: cm FILE cm FILE xr cm FILE cm sets permissions for the owner to read only. sets permissions for the owner to read and execute only clears all permissions for the user of the file displays synopsis message for the command A 10-Point Sample Run hank@hank-VirtualBox: /Desktop$ ls 1 foo rw-rw-r- 1 hank hank 0 Jan 20 15:10 foo hank@hank-VirtualBox: /Desktop$ /cm foo hank@hank-VirtualBox:-/Desktops 1s l foo rwr1 hank hank 0 Jan 20 15:10 foo hank@hank-VirtualBox:-/Deskt hank@hank-VirtualBox:-/Desktop$ ls l foo op$ /cm foo rx r-xrw-r 1 hank hank 0 Jan 20 15:10 foo hank@hank-VirtualBox:-/Desktop./cm foo rwx hank@hank-VirtualBox:-/Desktop$ ls l foo rwxrw-r1 hank hank 0 Jan 20 15:10 foo hank@hank-VirtualBox: /Desktop ./cr cm FILE [rwx] hankahank-VirtualBox:-/Desktops Hints: . - is a combined assignment operator combining bit wise or (1) &s is a combined assignment operator combining bit wise l- is a combined assignment &- is a combined assignment operator combining bit wise and (&) and the assignment operator ( To use octal values in C, prepend man 2 stat and man 2 chmod may be useful for reference. operator combining bit wise or () and the assignment operator (). This allows you turn bits "on the value with a 0. For example, 0644 is octal 644 (base 8), not decimal 644 (base 10). Additionally, there is a simple review of converting between bases bw.c is a program demonstrating bitwise operations. CL
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


